MODULE 6: CALIBRATION
6-8 AEROSET
®
Customer Training Guide
94858-103 — July 2003
Multi-Point Linear
On the AEROSET System, the multi-point linear calibration uses a
reagent blank (water) and two levels of calibrators. The following table
describes the steps used to calculate the calibration curve.
The following formula is used to calculate QC and patient sample
concentrations:
Concentration = (Sample Abs - Rgt Blank Abs) x Factor*
* The factor from the appropriate section of the curve is used according
to the measured absorbance value of the sample.
Step Action Example
1
Absorbance values are measured
for the reagent blank (water) and
the two calibrator levels.
Rgt Blk = 0.0023
(Conc = 0.0)
Level 1 = 0.1105
(Conc = 2.0)
Level 2 = 0.3010
(Conc = 5.1)
2
For each of the two calibrators, the
reagent blank absorbance is
subtracted from the measured
absorbance.
Level 1
0.1105 - 0.0023 = 0.1082
Level 2
0.3010 - 0.0023 = 0.2987
3
The reagent blank absorbance and
the corrected calibrator
absorbances are plotted vs. the
concentration.
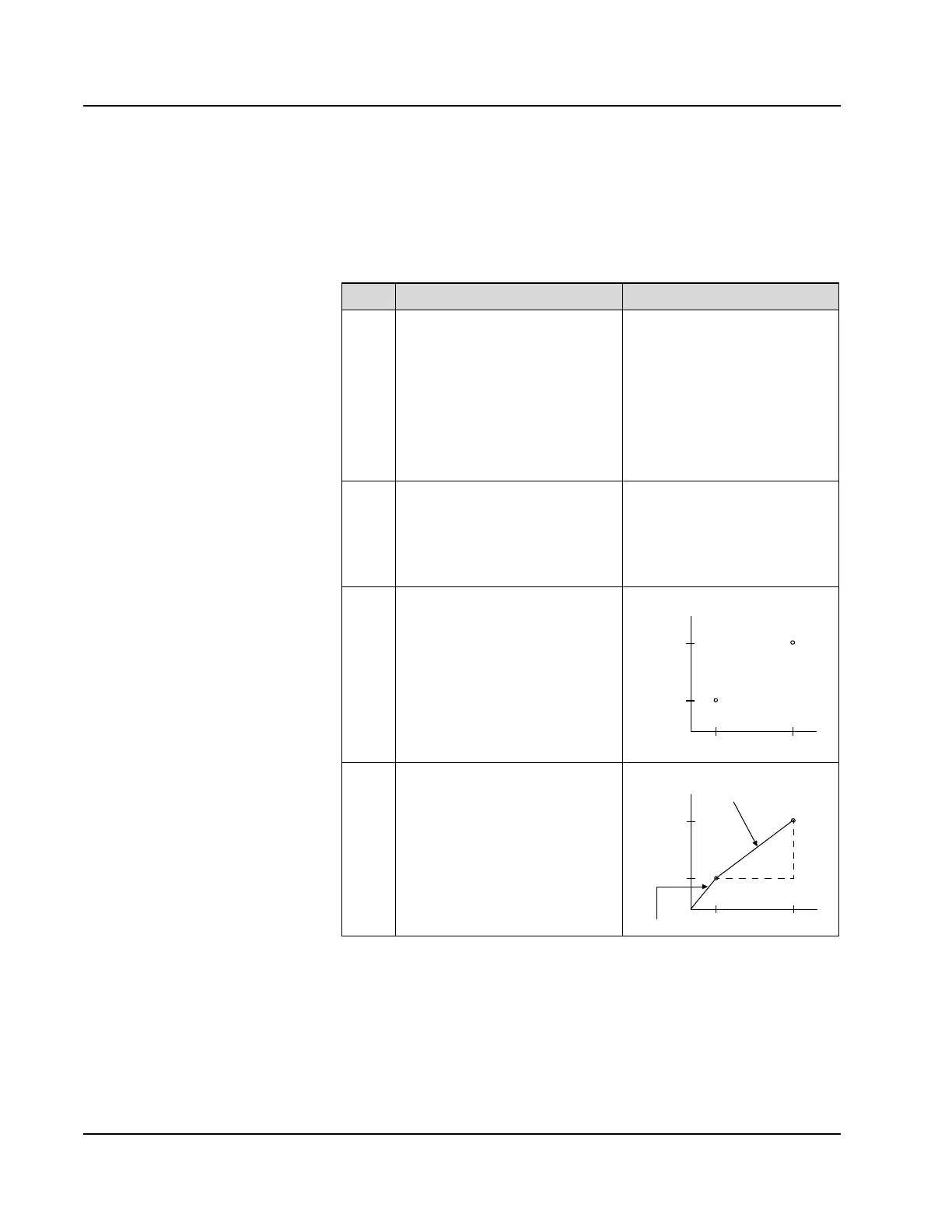
4
Each point is connected for a
point-to-point line. The calibration
factor is calculated for each
segment of the line.
Factor = 1 / Slope
(Slope = ∆Y / ∆X)
• Even though you are doing point-to-
point, linearity is a best fit line, so it
should still show a linear curve for
studies.
• Linear Rates-show Crea and/or Urea.
- These assays are multi-point
linear but are rates.
- Show curve and how it takes a
measurement over time instead
of at an endpoint.
0.2987
0.1082
2.0
5.1
Abs
Conc
Abs
Conc
Factor 2 = 16.3
Factor 1 = 18.5
∆Y
∆X
0.2987
0.1082
2.0
5.1
 Loading...
Loading...