266
B.3. About Optimization of the TCP Throughput using iperf
To obtain the best effort result in bidirectional communication like TCP, the window size from RTT(Round Trip Time)
must be optimized.
To determine the TCP/IP window size, clarlfy RTT using PING (although the result is not accurate).
The RTT depends on the your test environment, so the RTT must be checked for each test environments.
The TCP/IP window size optimization method is described below.
B.3.1. Setting of TCP Window Size
1. Put the UE into the Connected state. Refer to Chapter 5.
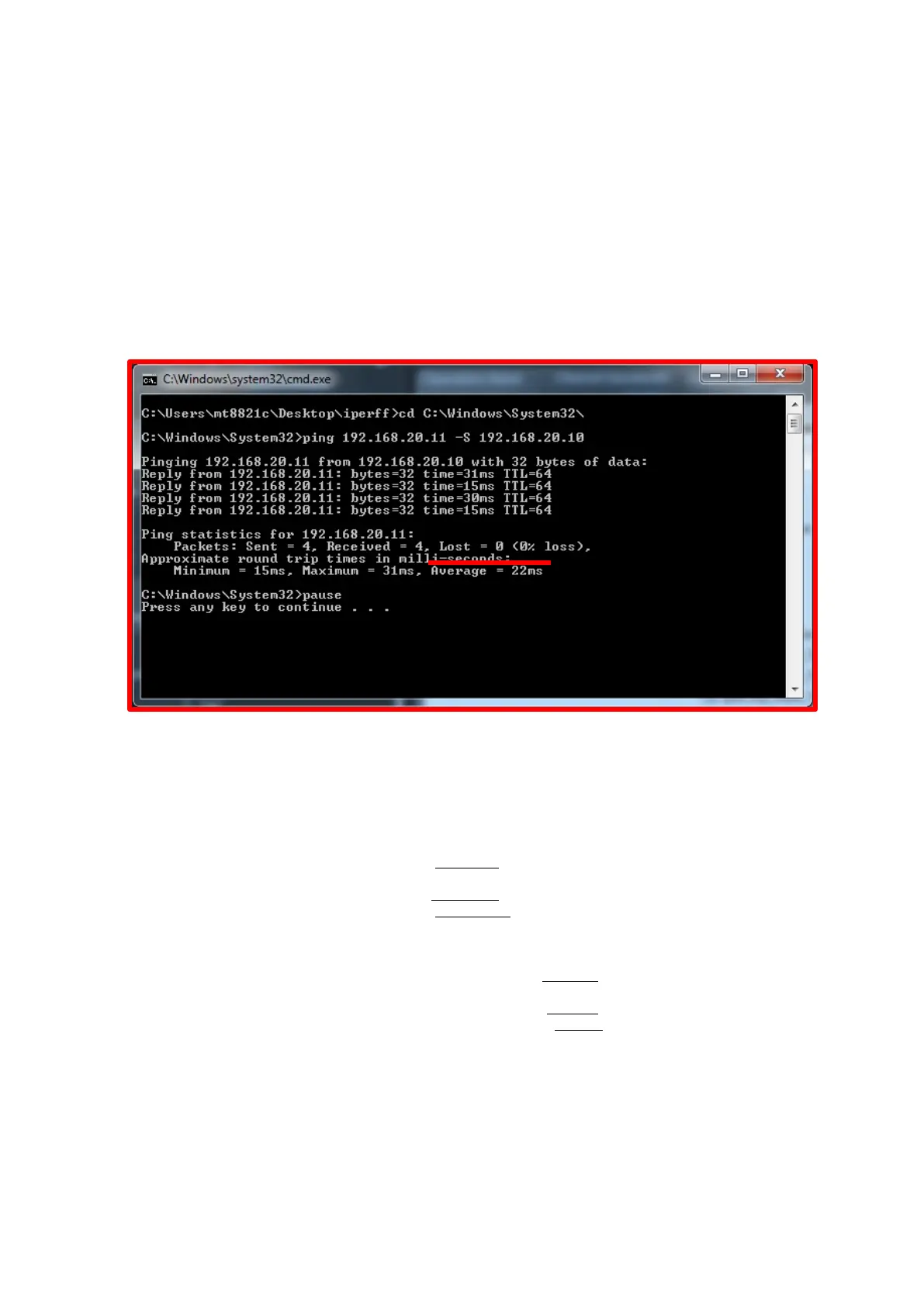
2. Execute the PING command using the default setting (ex. ping 192.168.20.11 -S 192.168.20.10) multiple
times
Then check the RTT(Average)
Figure B.3.1-1 Average of RTT(from Ping)
3. Choose the slowest average time from the results in No.2
4. Calculate the TCP window size to be used for the TCP/IP test of iperf using the following equaltion
(Desired throughput for 1 IP stream(bps) / 8) x average time(s) = TCP window size(bytes)
Example:
2CA 300Mbps / 8 x 0.022s = 825kbyte
3CA(Default Bearer) 300Mbps / 8 x 0.022s = 825kbyte
(Dedicated Bearer) 150Mbps / 8 x 0.022s = 412.5kbyte
5. Set the -w argument at the result in No.4 when running iperf(Client side)
Example:
2CA iperf -c -192.168.20.11 -B 192.168.20.10 -w 825k -i 1
3CA(Default Bearer) iperf -c -192.168.20.11 -B 192.168.20.10 -w 825k -i 1
(Dedicated Bearer) iperf -c -192.168.20.11 -B 192.168.20.100 -w412k -i 1
6. Adjust the TCP window size(if neccesary)
・Throughput is lower than desired throughput
Expand TCP window size in steps of 10k
Example:
iperf -c -192.168.20.11 -B 192.168.20.10 -w 975k -i -> iperf -c -192.168.20.11 -B 192.168.20.10 -w 985k -i 1
・Throughput is unstable(This situation, TCP window size too large)
Reduce TCP window size in steps of 10k
Example:
iperf -c -192.168.20.11 -B 192.168.20.10 -w 975k -i -> iperf -c -192.168.20.11 -B 192.168.20.10 -w 965k -i 1

 Loading...
Loading...