System Control
ARM DDI 0388I Copyright © 2008-2012 ARM. All rights reserved. 4-18
ID073015 Non-Confidential
4.3 Register descriptions
This section describes the implementation-defined CP15 system control registers by
coprocessor register number order that are not already described in the ARM Architecture
Reference Manual.
4.3.1 Main ID Register
The MIDR characteristics are:
Purpose Provides identification information for the processor, including an
implementer code for the device and a device ID number.
Usage constraints The MIDR is:
• a read-only register
• common to the Secure and Non-secure states
• only accessible in privileged modes.
Configurations Available in all configurations.
Attributes See the register summary in Table 4-2 on page 4-5.
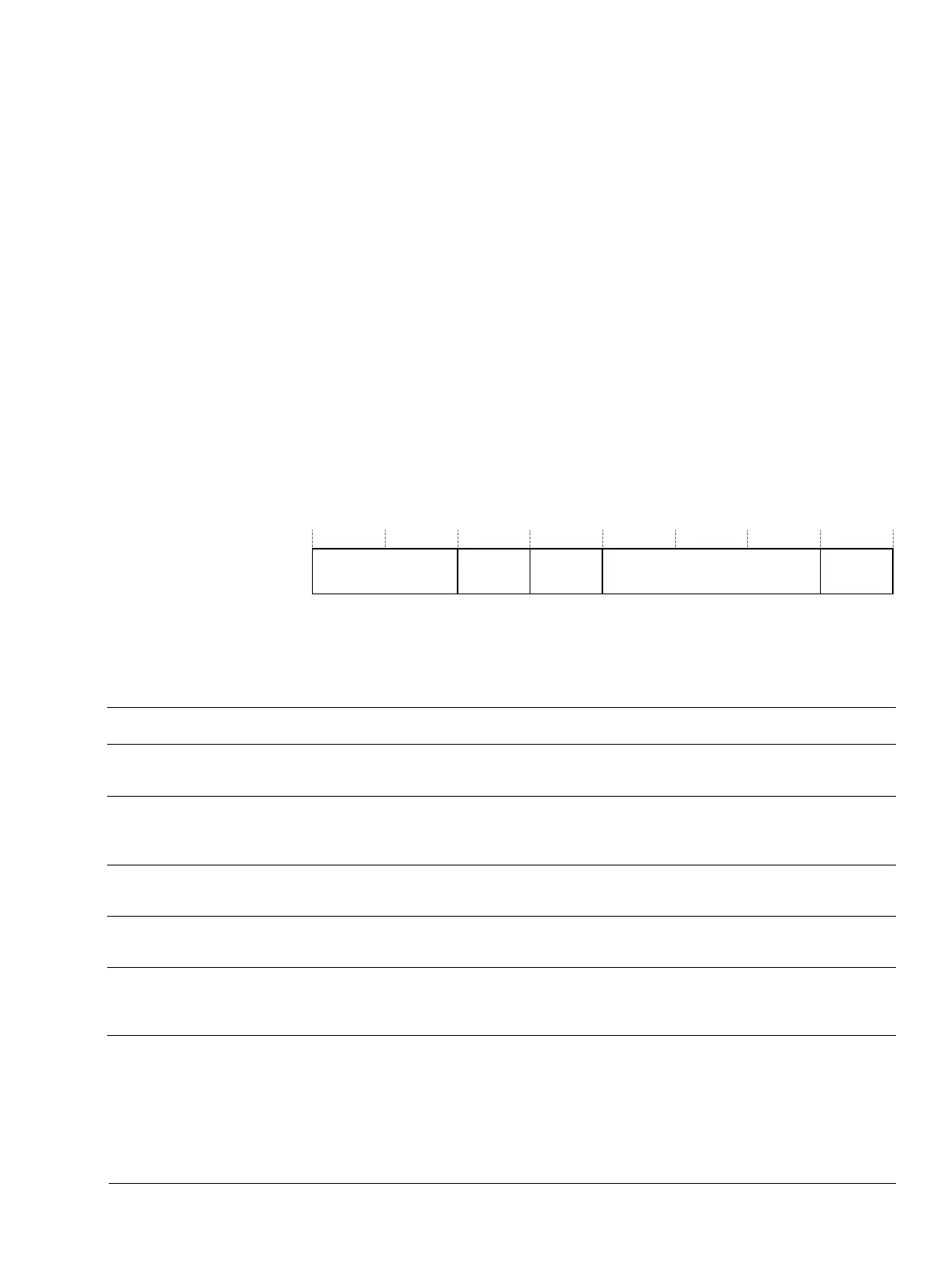
Figure 4-1 shows the MIDR bit assignments.
Figure 4-1 MIDR bit assignments
Table 4-28 shows the MIDR bit assignments.
To access the MIDR, read the CP15 register with:
MRC p15, 0, <Rt>, c0, c0, 0; Read Main ID Register
VariantImplementer
31 23 20 19 16 15 4 3 0
Architecture Primary part number Revision
24
Table 4-28 MIDR bit assignments
Bits Name Function
[31:24] Implementer Indicates the implementer code:
0x41
ARM Limited.
[23:20] Variant Indicates the variant number of the processor. This is the major revision number n in the rn part of
the rnpn description of the product revision status, for example:
0x4
Major revision number.
[19:16] Architecture Indicates the architecture code:
0xF
Defined by CPUID scheme.
[15:4] Primary part number Indicates the primary part number:
0xC09
Cortex-A9.
[3:0] Revision Indicates the minor revision number of the processor. This is the minor revision number n in the pn
part of the rnpn description of the product revision status, for example:
0x1
Minor revision number.
 Loading...
Loading...