System Control
ARM DDI 0388I Copyright © 2008-2012 ARM. All rights reserved. 4-40
ID073015 Non-Confidential
MCR p15, 0, <Rt>, c11, c1, 1; Read PLEPCR
MRC p15, 0, <Rt>, c11, c1, 1; Write PLEPCR
4.3.21 Virtualization Interrupt Register
The VIR characteristics are:
Purpose Indicates that there is a virtual interrupt pending.
Usage constraints The VIR is:
• only accessible in privileged modes
• only accessible in Secure state.
Configurations Available in all configurations.
Attributes See the register summary in Table 4-13 on page 4-10.
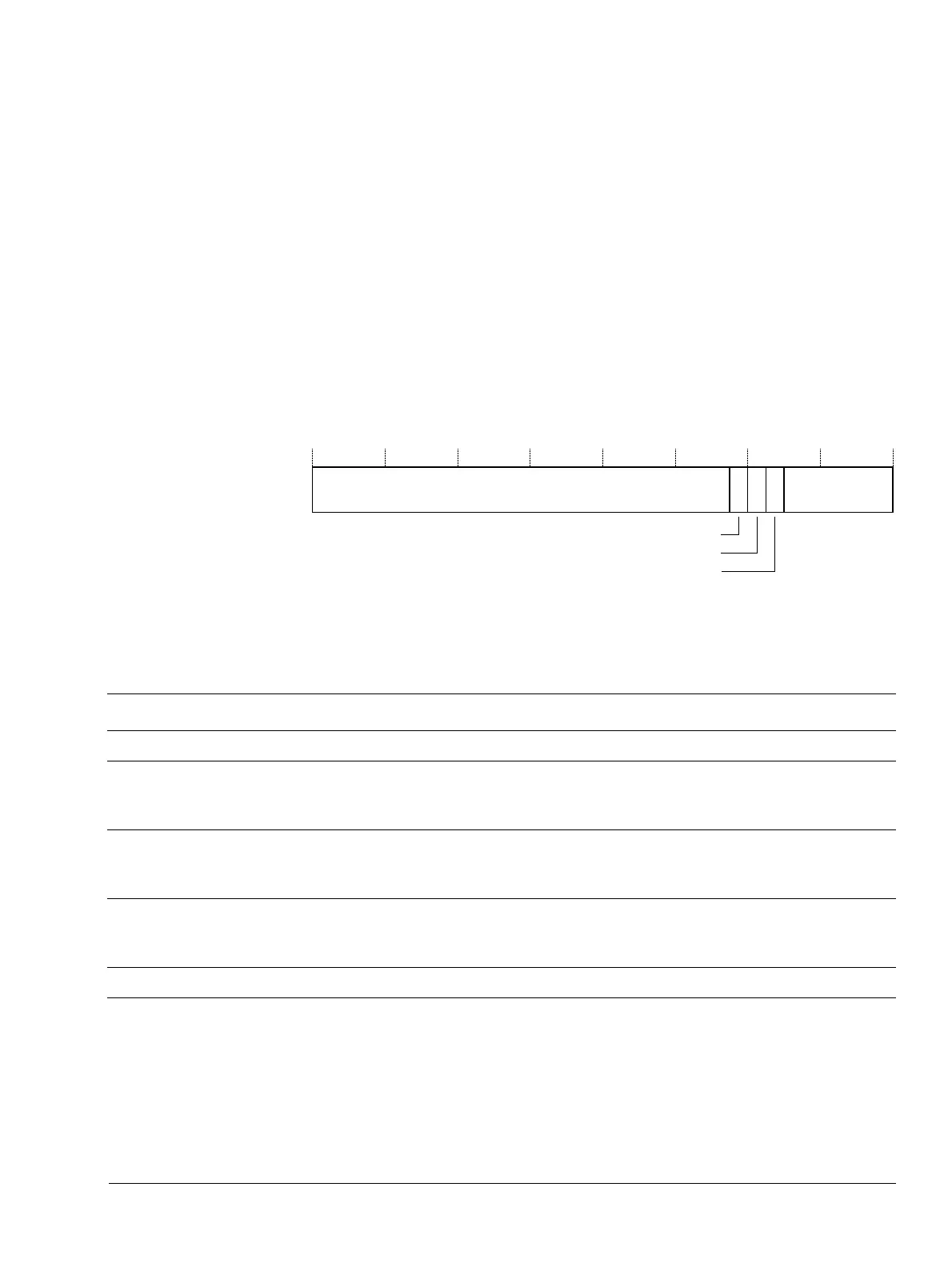
The virtual interrupt is delivered as soon as the processor is in NS state. Figure 4-20 shows the
VIR bit assignments.
Figure 4-20 VIR bit assignments
Table 4-47 shows the Virtualization Interrupt Register bit assignments.
To access the VIR, read or write the CP15 register with:
MRC p15, 0, <Rd>, c12, c1, 1 ; Read Virtualization Interrupt Register
MCR p15, 0, <Rd>, c12, c1, 1 ; Write Virtualization Interrupt Register
31 0
UNK/SBZP
56789
UNK/SBZP
VA
VI
VF
Table 4-47 Virtualization Interrupt Register bit assignments
Bits Name Function
[31:9] - UNK/SBZP.
[8] VA Virtual Abort bit.
When set the corresponding Abort is sent to software in the same way as a normal Abort. The virtual abort happens
only when the processor is in Non-secure state.
[7] VI Virtual IRQ bit.
When set the corresponding IRQ is sent to software in the same way as a normal IRQ. The virtual IRQ happens
only when the processor is in Non-secure state.
[6] VF Virtual FIQ bit.
When set the corresponding FIQ is sent to software in the same way as a normal FIQ. The FIQ happens only when
the processor is in Non-secure state.
[5:0] - UNK/SBZP.
 Loading...
Loading...