Appendix for Lorrca® MaxSis
Lorrca Maxsis User Manual Page 213
Version 5.04 MRN-231-EN
11.6.2.3.1. Diaphragm adjustment and sample thermostation
The measurement procedure can be cancelled by clicking “Cancel”. If the procedure is continued,
by clicking the “Ok” button, a new window appears in which the operator is asked to adjust the
camera diaphragm to scale the diffraction pattern for maximum size within the screen. The applied
shear stress (<S
ETTINGS> <SHEAR> stress for camera adjustment>) is taken high enough to fully
elongate the cells in order to get a maximum elliptical diffraction pattern.
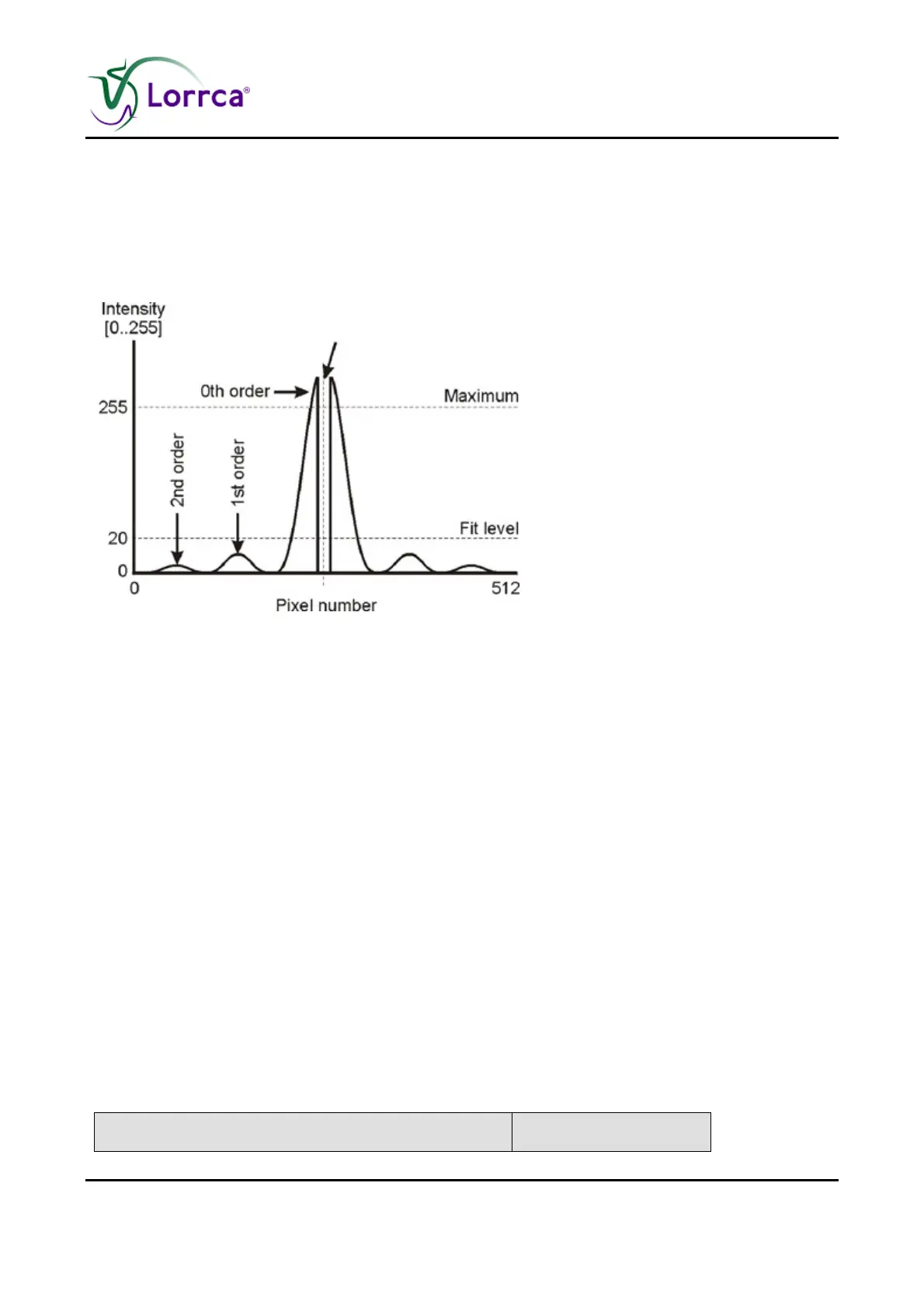
Figure 9. Optimum contrast is obtained if the fit level excludes
higher order diffraction patterns but is low enough to get a large
image.
The original image is a gray scale image containing an intense zero order diffraction pattern and
some weak higher order patterns. Figure. 9 shows the intensity distribution of a single image line.
The intensity drop in the middle of the zero-order peak is caused by the laser absorber dot, which
prevents camera overexposure. The smaller peaks at both sides of the zero-order peak represent
the higher orders. When opening the diaphragm, light intensity increases, hereby increasing also
the higher order patterns. As soon as the intensity of the higher order patterns exceed the "Fit gray
level" (see <Settings><Fit gray level>), they participate in the iso-intensity curve and the pattern
ellipse is detected incorrectly. When the diaphragm is closed too far, the diffraction pattern can
hardly be distinguished from the laser spot, which also results in a wrong detection of the iso-
intensity curve. Thus, the diaphragm should be opened to scale the diffraction pattern for maximum
size within the screen, yet without including higher order diffraction patterns and without
introducing secondary reflections.
Since it is difficult to distinguish the zero-order diffraction pattern from higher order patterns within
the gray-scale image, each gray level (range 0..255) is assigned a colour. The on-screen
diffraction pattern is created using this colour look up table (see table Colour look-up table).
The “User colours” checkbox can be used to switch between gray images and colour images. Click
the “Ok” button if the camera diaphragm is well adjusted and the sample has reached the desired
temperature.
Gray level Colour
 Loading...
Loading...