Operation
42 900-0117-01-00 Rev B
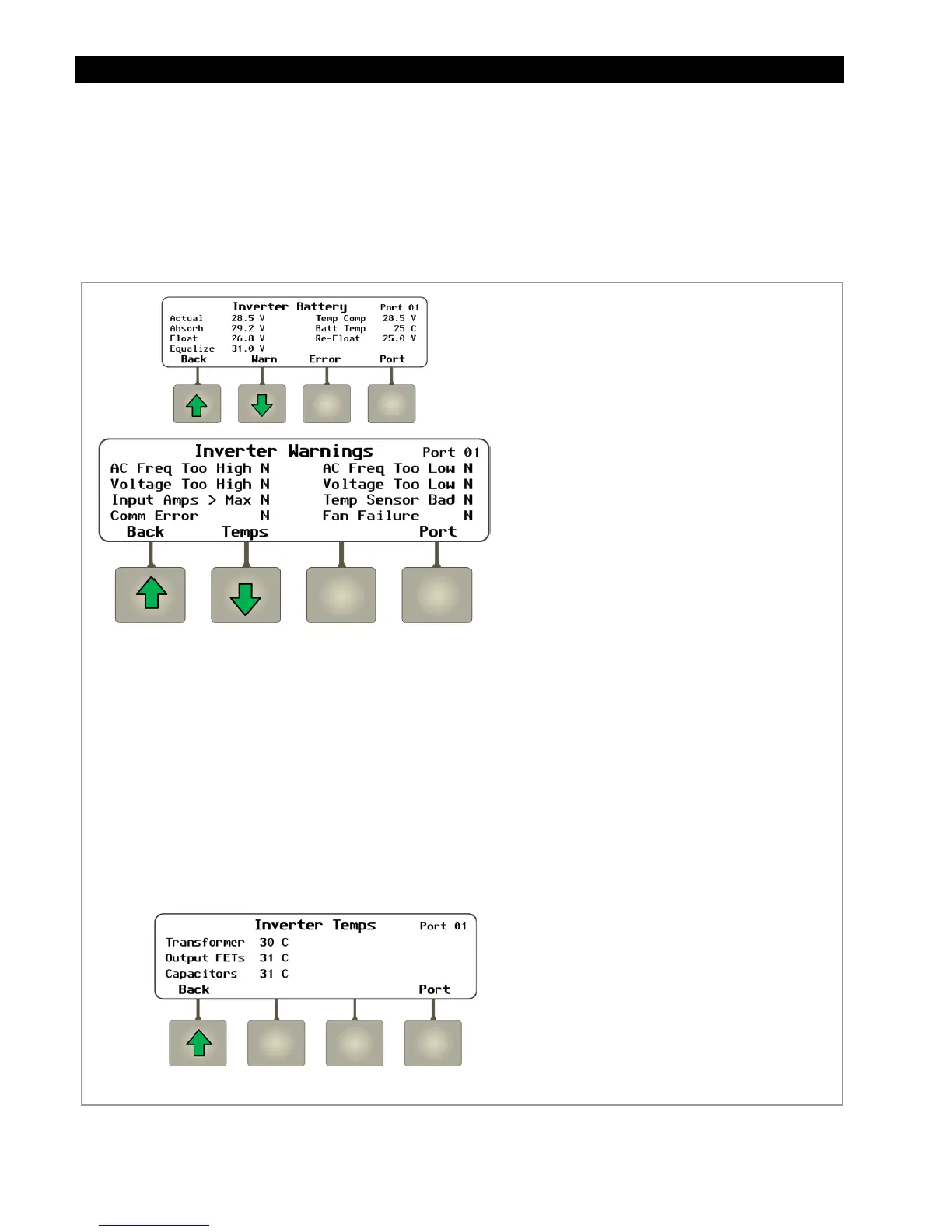
Warning Messages
A Warning message is caused by a non-critical inverter fault. When this occurs, the inverter will not
shut down, but will display a fault LED. One or more messages in this menu will change from
N
to
Y
.
A warning is also accompanied by an event message (see page
2461).
Some warnings can become errors if left unattended. Frequency and voltage warnings are meant to warn
of a problematic AC source. See the inverter Operator’s Manual for more information on troubleshooting a
specific warning.
Figure 30 Inverter Warnings and Temperatures
Screen Items:
AC Freq Too High:
he AC source is above the
acceptable frequency limit and prevents
connection.
AC Freq Too Low:
The AC source is below the
acceptable frequency limit and prevents
connection.
Voltage Too High:
The AC source is above the
upper acceptable voltage limit and prevents
connection.
Voltage Too Low:
The AC source is below the
lower acceptable voltage limit and prevents
connection.
Input Amps > Max:
AC loads are drawing
more current from the AC source than allowed
by the input setting.
Temp Sensor Bad:
An internal inverter
temperature sensor may be malfunctioning.
This is indicated by an unusual
Transformer
,
Output FETs
, or
Capacitors
reading.
Comm Fault:
Probable failure on inverter’s
control board which has interrupted internal
communications.
Fan Failure:
The inverter’s internal cooling fan
is not operating properly. Lack of cooling may
result in derated inverter output wattage.
Soft Keys:
<Temps> brings up a screen which displays the readings
for the inverter’s internal temperature sensors. One sensor
is attached to the main transformer, another is on the heat
sink for the Field Effect Transistors (FETs), and one is on the
filter capacitors. Normally all three sensors read
approximately the same. An unusually high or unusually
low reading on one sensor indicates a defective sensor.
Contact OutBack Technical Support if necessary (see inside
front cover of this manual).
<Back> returns to the previous screen.
<Port> cycles through each device connected to
the network.
 Loading...
Loading...