– To 1.2 m for devices with a 2 m operating range
– To 3 m for devices with a 5 m operating range
– To 5 m for devices with an 8.5 m operating range
•
This operating mode can only be configured on an MLG-2 with fewer than
240 beams.
3.9 Interfaces
The MLG-2 can be used to evaluate the measurements in different ways. The MLG-2
provides various interfaces for data output.
•
Switching outputs (Push-Pull)
•
Analog outputs
•
RS-485 interface
•
IO-Link interface
The MLG-2 can output the raw data via the interfaces in the form of the beam status or
run-length code, so the user can evaluate the data him/herself.
The MLG-2 can also preprocess the raw data (beam function, e.g., NBB – number of
beams blocked) and output the data via bus or analog interfaces.
The preprocessed data can be assigned directly to the switching outputs via a program‐
mable function logic or via predefined applications.
3.9.1 Output of measurement data (raw data)
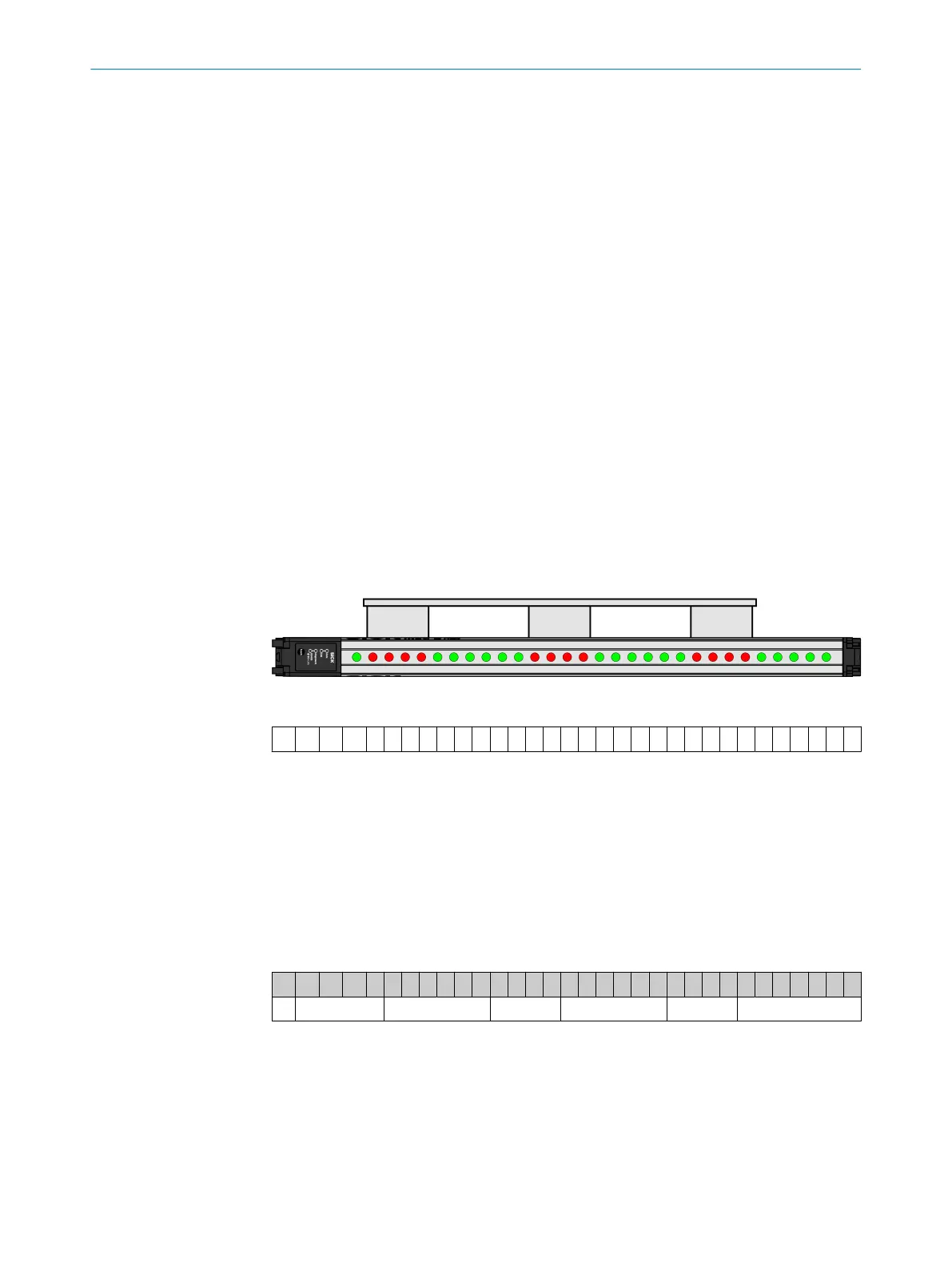
The MLG-2 provides the status of all beams at its data interface using a data message.
Figure 16: Status of the beams
0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 17: Example status for an MLG-2 with 32 beams
0
Beam clear
1
Beam blocked
The data message can be output continuously or in response to particular events.
Run-length code
In order to reduce the volume of data, the run-length code can be output instead of the
complete status of all beams. This code only contains the status change of the beams.
The run-length code indicates how many beams currently have the same status.
0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 4 6 4 6 4 7
Table 18: Example status for the run-length code of an MLG-2 with 32 beams
RLC = 1464645
The example shows: 1 beam made, 4 beams blocked, 6 beams made, 4 beams
blocked, 6 beams made, 4 beams blocked, 5 beams made.
The first value always indicates the number of unblocked beams. If the first beam is
blocked, the first value will therefore be zero. The second value indicates how many
beams are blocked; in the example in table 19, this value = 1.
3 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
28
O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | MLG-2 Pro 8017460.ZIK1/2017-02-13 | SICK
Subject to change without notice
 Loading...
Loading...