When an earth fault occurs outside the protected zone (Figure 2-60), a starpoint current Ι
Ctrl
will flow equally;
but an equal current 3Ι
0
must flow through the phase current transformers. Since the current direction is
normally defined as positive in the direction of the protected object, this current is in phase opposition with
Ι
Ctrl
.
[erddiff-erdkurzschluss-ausserhalb-020926-rei, 1, en_GB]
Figure 2-60 Example of an earth fault outside a transformer with current distribution
When a fault without earth connection occurs outside the protected zone, a residual current may occur in the
residual current path of the phase current transformers which is caused by different saturation of the phase
current transformers under strong through-current conditions. This current could simulate a fault in the
protected zone. Measures must be taken to prevent this current from causing a trip. For this, the restricted
earth fault protection provides stabilisation methods which differ strongly from the usual stabilisation
methods of differential protection schemes since it uses, besides the magnitude of the measured currents, the
phase relationship, too.
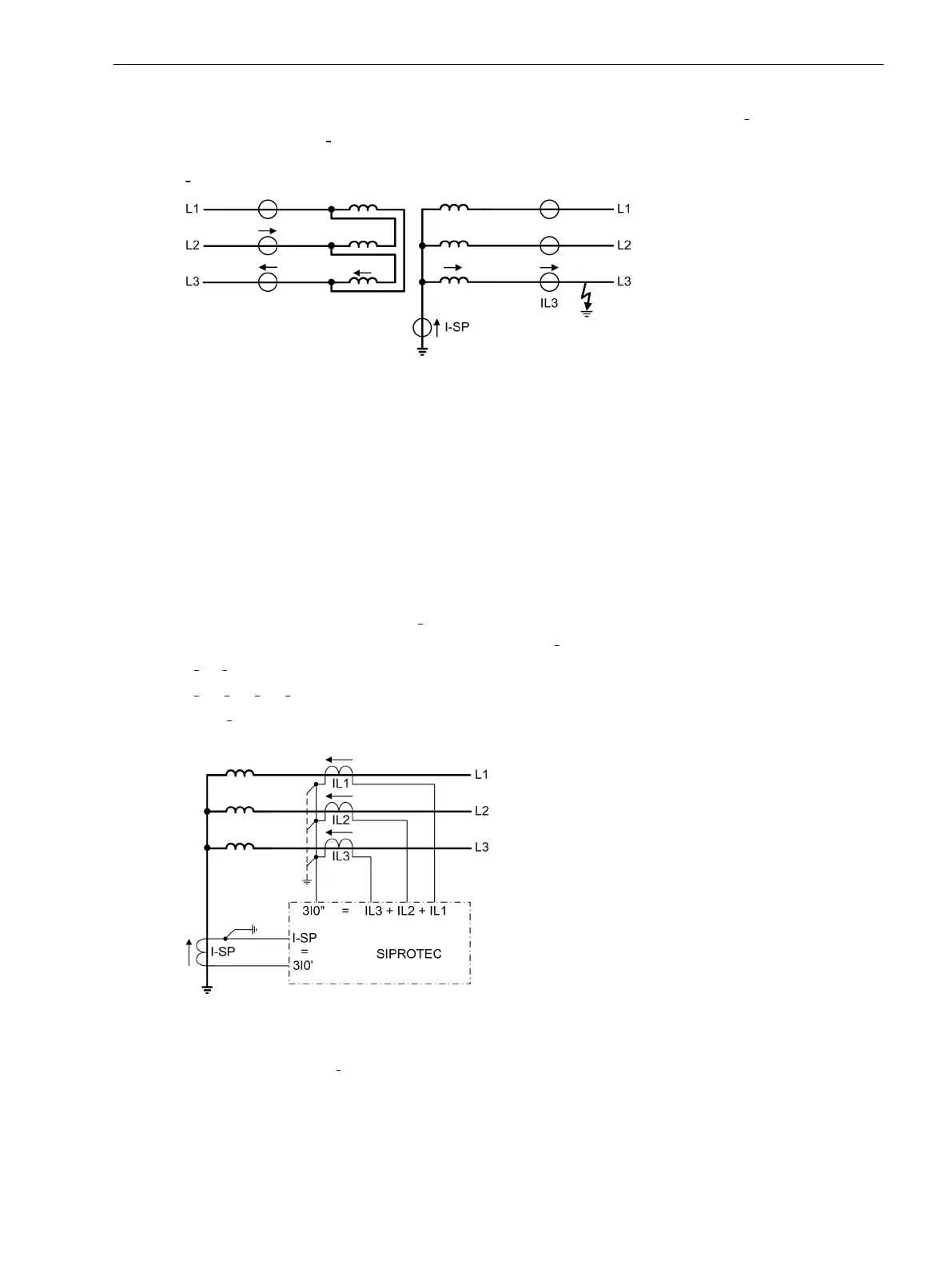
Evaluation of Measurement Quantities
The earth fault differential protection compares the fundamental wave of the current flowing in the starpoint
connection, which is designated as 3
Ι
0
' in the following, with the fundamental wave of the sum of the phase
currents, which should be designated in the following as 3Ι
0
". Thus, the following applies (Figure 2-61):
3Ι
0
' = Ι
Ctrl
3Ι
0
" = Ι
L1
+ Ι
L2
+ Ι
L3
Only 3Ι
0
' acts as the tripping effect quantity. During a fault within the protected zone this current is always
present.
[erddiff-prinzip-020926-rei, 1, en_GB]
Figure 2-61 Principle of restricted earth fault protection
For auto-transformers 3Ι
0
" is valid as the sum of all phase currents flowing to auto-connected winding (full
winding and tap(s)).
When an earth fault occurs outside the protected zone, another earth currents flows through the phase
current transformers. This is, on the primary side, in counter-phase with the starpoint current and has equal
magnitude. The maximum information of the currents is evaluated for restraint: the magnitude of the currents
and their phase position. The following is defined:
Functions
2.3 Restricted Earth Fault Protection
SIPROTEC 4, 7UT6x, Manual 129
C53000-G1176-C230-5, Edition 09.2016
 Loading...
Loading...











