Functions
6-128 7SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C133-1
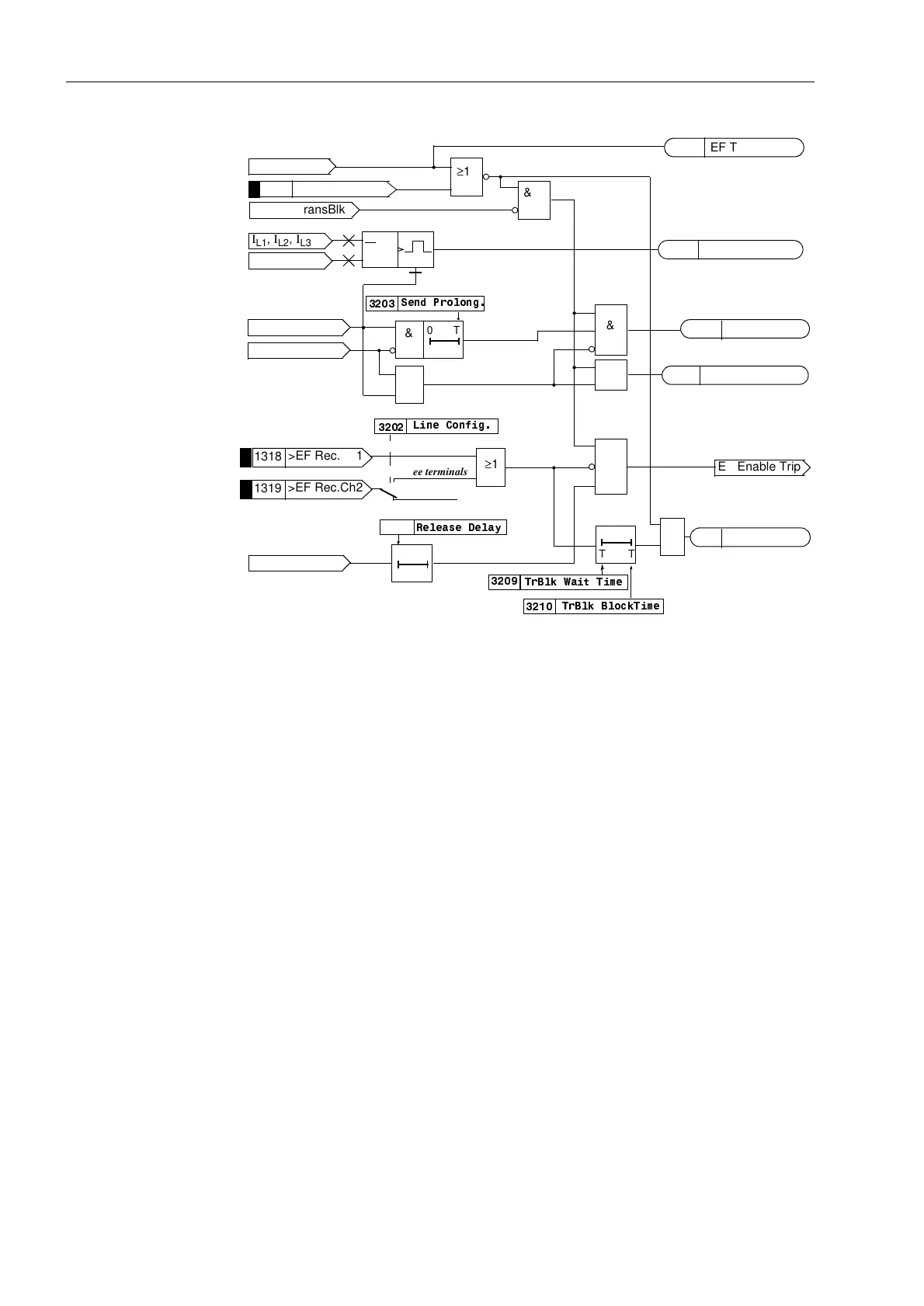
Figure 6-76 Logic diagram of the blocking scheme (one line end)
6.6.1.4 Transient Blocking
Transient blocking provides additional security against erroneous signals due to
transients caused by clearance of an external fault or by fault direction reversal during
clearance of a fault on a parallel line.
The principle of transient blocking scheme is that following the incidence of an external
fault, the formation of a release signal is prevented for a certain (settable) time. In the
case of permissive schemes, this is achieved by blocking of the transmit and receive
circuit.
Figure 6-77 shows the principle of the transient blocking for a directional comparison
and directional unblocking scheme.
If a fault in the reverse direction is detected within the waiting time 7U%ON:DLW7LPH
(address ) following fault detection, the transmit circuit and the trip release are
inhibited. This blocking is maintained for the duration of the transient blocking time
7U%ON%ORFN7LPH (address ) also after the reset of the blocking criterion.
In the case of the blocking scheme, the transient blocking prolongs the received
blocking signal as shown in the logic diagram Figure 6-76.
3IoMin Teleprot
6HQG3URORQJ
&
T0
≥1
I
L1
, I
L2
, I
L3
d
dt
40 ms
(u,i)
(A)
U
L1
, U
L2
, U
L3
EF forward
&
&
EF Pickup
3208
5HOHDVH'HOD\
0T
/LQH&RQILJ
Two terminals
Three terminals
EF Enable Trip
7U%ON:DLW7LPH
TT
7U%ON%ORFN7LPH
&
≥1
&
&
&
EF Telep. off
1313
>EF TeleprotBLK
EF TeleTransBlk
1318
>EF Rec.Ch1
1319
>EF Rec.Ch2
EF Telep. OFF
1381
EF Tele SEND
1384
EF Tele BL STOP
1384
EF TeleTransBlk
1386
EF Tele BL Jump
1390

 Loading...
Loading...











