OSPF
ExtremeWare XOS 11.3 Concepts Guide
544
OSPF Edge Mode
OSPF Edge Mode is a subset of OSPF available on platforms with an Advanced Edge license. There are
two restrictions on OSPF Edge Mode:
● At most, two Active OSPF VLAN interfaces are permitted. There is no restriction on the number of
Passive interfaces.
● The OSPF Priority on VLANs is zero, and is not configurable. This prevents the system from acting
as a DR or BDR
Link State Database
Upon initialization, each router transmits a link state advertisement (LSA) on each of its interfaces.
LSAs are collected by each router and entered into the LSDB of each router. Once all LSAs are received,
the router uses the LSDB to calculate the best routes for use in the IP routing table. OSPF uses flooding
to distribute LSAs between routers. Any change in routing information is sent to all of the routers in the
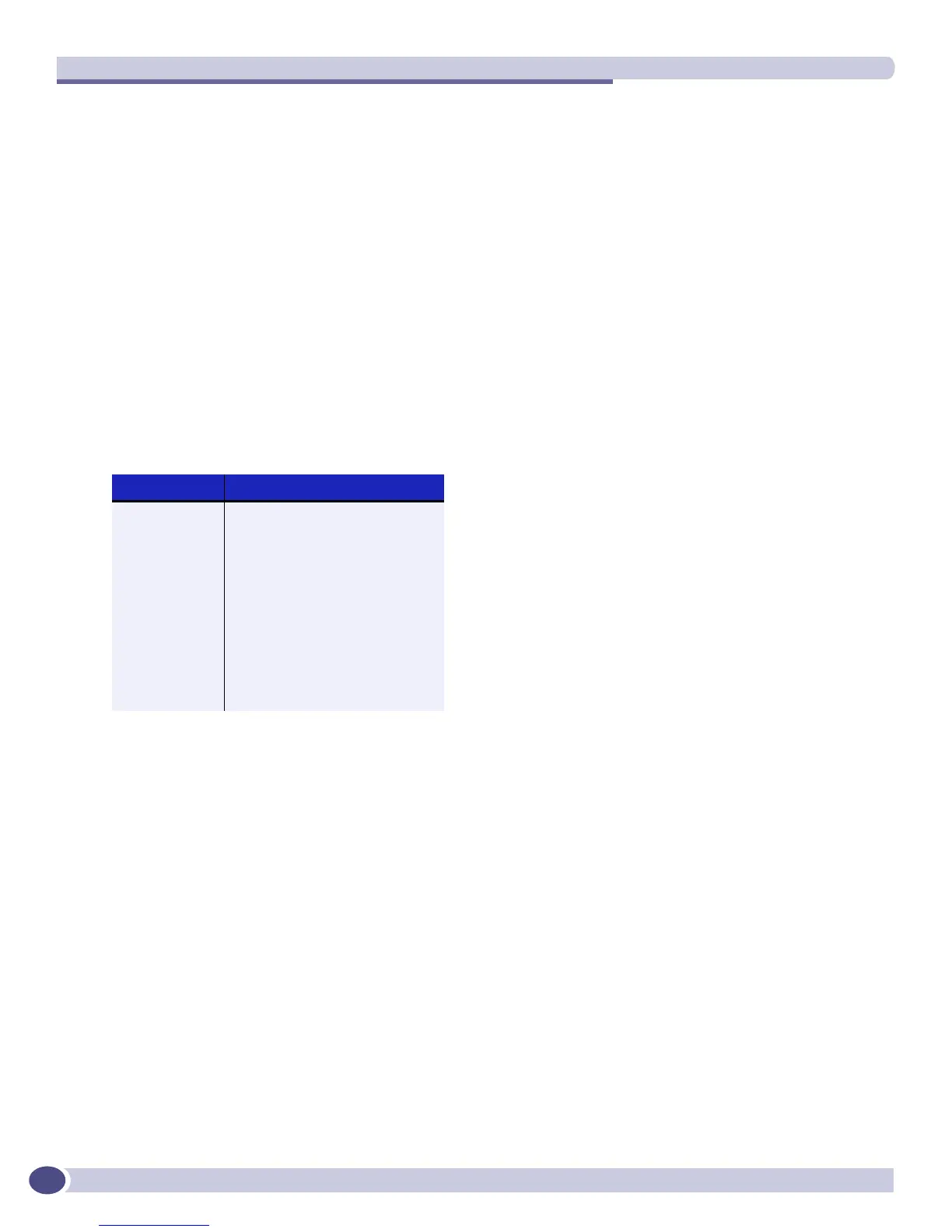
network. All routers within an area have the exact same LSDB. Table 67 describes LSA type numbers.
Database Overflow
The OSPF database overflow feature allows you to limit the size of the LSDB and to maintain a
consistent LSDB across all the routers in the domain, which ensures that all routers have a consistent
view of the network.
Consistency is achieved by:
● Limiting the number of external LSAs in the database of each router.
● Ensuring that all routers have identical LSAs.
To configure OSPF database overflow, use the following command:
configure ospf ase-limit <number> {timeout <seconds>}
where:
● <number>—Specifies the number of external LSAs that the system supports before it goes into
overflow state. A limit value of zero disables the functionality.
When the LSDB size limit is reached, OSPF database overflow flushes LSAs from the LSDB. OSPF
database overflow flushes the same LSAs from all the routers, which maintains consistency.
Table 67: LSA type numbers
Type Number Description
1 Router LSA
2 Network LSA
3 Summary LSA
4 AS summary LSA
5 AS external LSA
7 NSSA external LSA
9 Link local—Opaque
10 Area scoping—Opaque
11 AS scoping—Opaque

 Loading...
Loading...