BGP Features
ExtremeWare XOS 11.3 Concepts Guide
569
BGP Features
This section describes the following BGP features supported by ExtremeWare XOS:
● Route Reflectors on page 569
● Route Confederations on page 571
● Route Aggregation on page 574
● Using the Loopback Interface on page 574
● BGP Peer Groups on page 574
● BGP Route Flap Dampening on page 575
● BGP Route Selection on page 577
● Route Redistribution on page 577
● BGP Static Network on page 578
Route Reflectors
Another way to overcome the difficulties of creating a fully meshed AS is to use route reflectors. Route
reflectors allow a single router to serve as a central routing point for the AS.
A cluster is formed by the route reflector and its client routers. Peer routers that are not part of the
cluster must be fully meshed according to the rules of BGP.
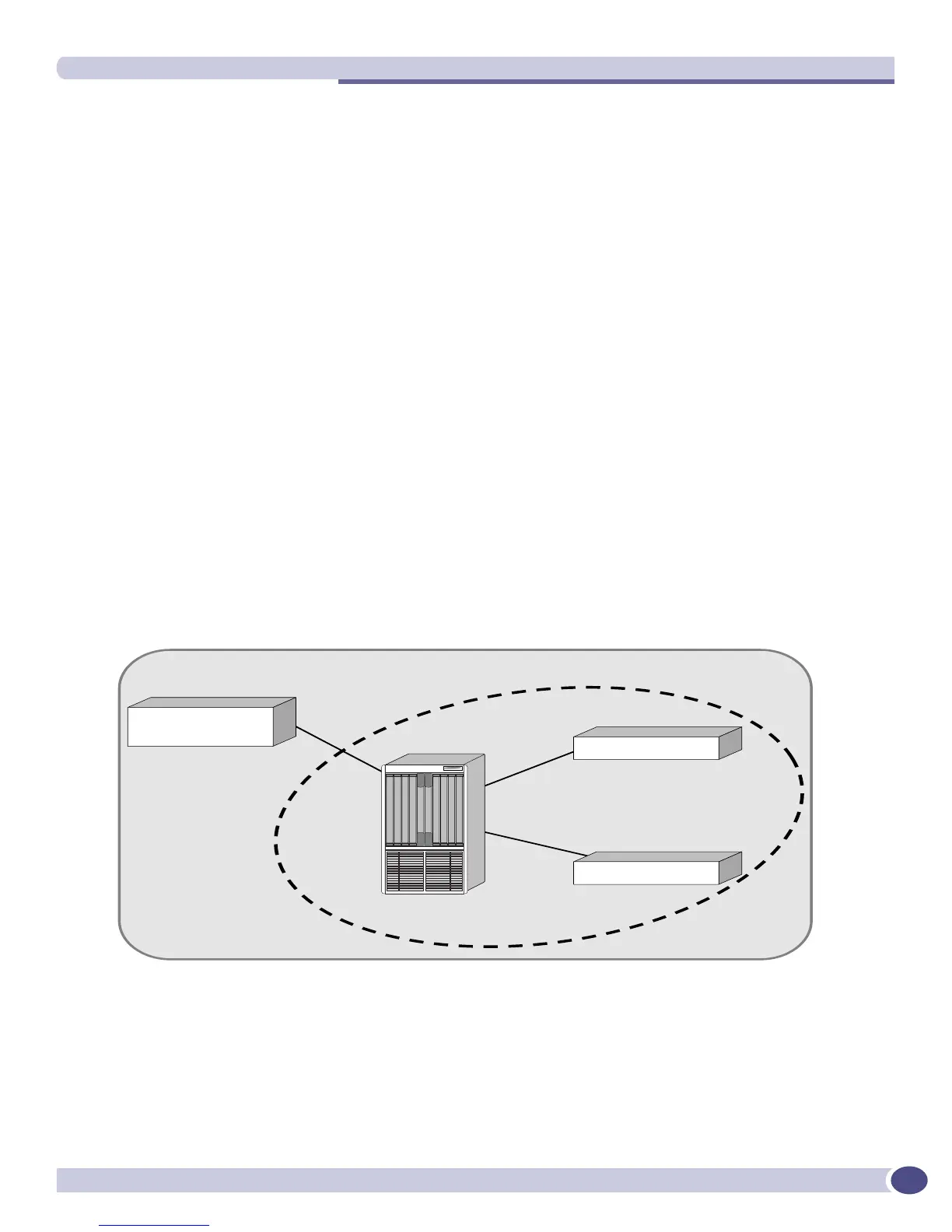
A BGP cluster, including the route reflector and its clients, is shown in Figure 76.
Figure 76: Route reflectors
The topology shown in Figure 76 minimizes the number of BGP peering sessions required in an AS by
using route reflectors.
In this example, although the BGP speakers 3.3.3.3 and 4.4.4.4 do not have a direct BGP peering session
between them, these speakers still receive routes from each other indirectly through 2.2.2.2. The router
2.2.2.2 is called a route reflector and is responsible for reflecting routes between its clients. Routes
EX_042
Client
Client
Route Reflector
Non-client
10.0.0.1
10.0.0.2
30.0.0.1
30.0.0.2
20.0.0.2
20.0.0.1
1.1.1.1
2.2.2.2
4.4.4.4
3.3.3.3
Cluster
AS 100

 Loading...
Loading...