Software Control: Software Interface Elements
C O N F I D E N T I A L – FEI Limited Rights Data3-4
2D Controls
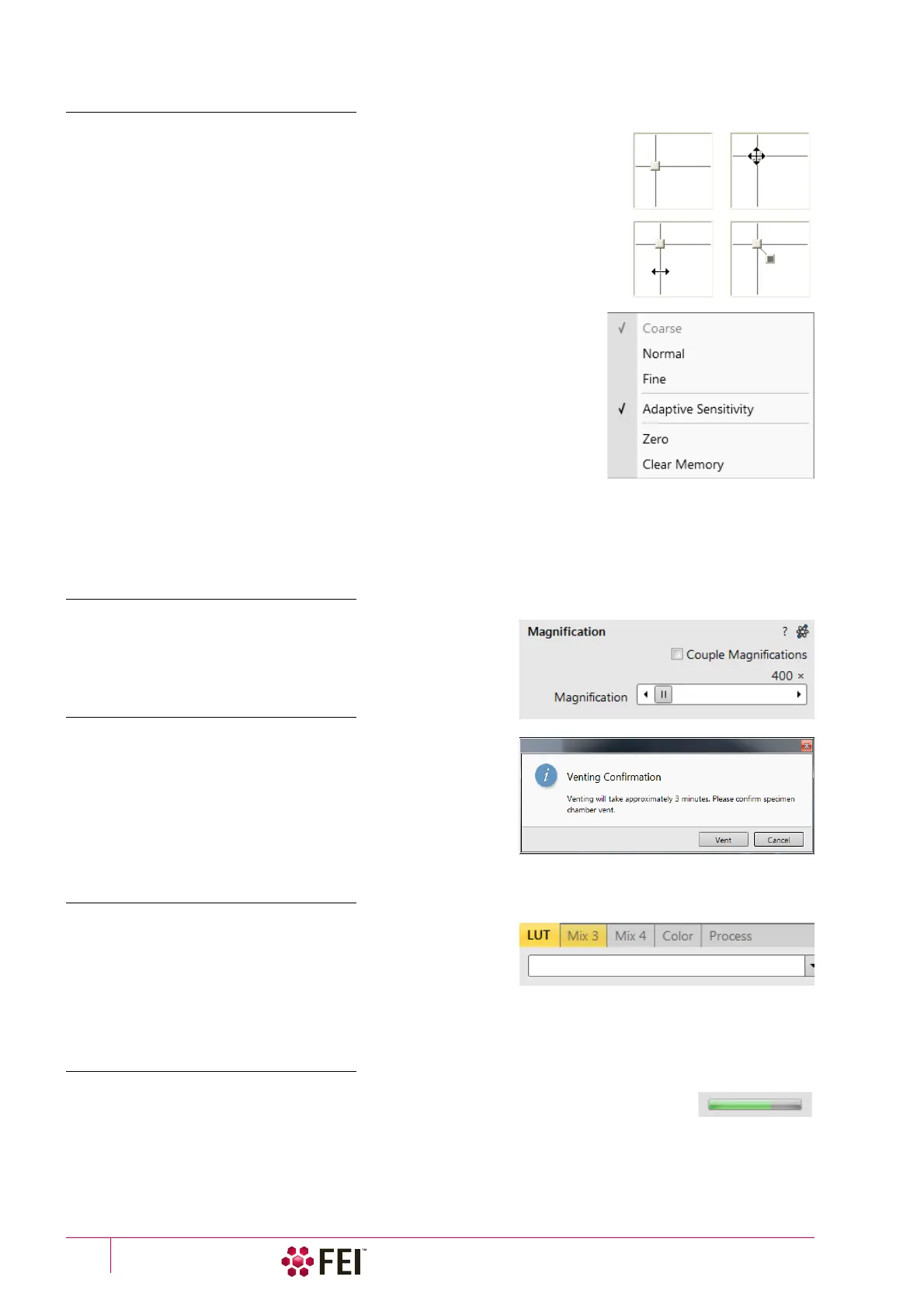
This way of control is represented by an X–Y box. The position of the crosshair
corresponds to the actual parameter value with respect to its full range being
represented by the perimeter of the box.
Clicking on & dragging anywhere inside the box changes the active display cursor
to the 4-ended arrow and positions it to the screen point corresponding to the
actual control value (minimum in the middle of the screen and maximum at the
edges). It can be dragged in four directions. Clicking on & dragging directly on the X
/ Y axis changes the active display cursor to the 2-ended arrow, which can be
dragged in the corresponding direction only. To apply the values, release the mouse
button.
The right-clicking on the 2D box opens a context menu with choices:
• Coarse / Normal / Fine item – sets the mouse sensitivity from long to short
mouse path necessary for the full range cursor move.
• Adaptive Sensitivity item – adjusts the mouse control response to be the
same at any magnification.
• Zero item –brings the control value to zero and the cursor to the center of the
box.
• Clear Memory item – clears condition values, which have been remembered
automatically during the considered 2D control use. These remembered
values are used to estimate new values, which have not been remembered
yet.
The menu may contain less or some other functions that are actually available for the particular parameter.
Selecting the corresponding menu item activates the function.
Modules
Visually combine various software elements, which are related
into a labelled group. Complex software elements like Control
pages or dialogs are typically composed of modules.
Dialogs
An dialog appears when the system needs more information from
you before it can carry out a command, or wants to give you some
important information. Some dialogs do not let you access other
functions until you close them, other ones let you perform other
tasks while they remain onscreen and active (for example, the
Preferences dialog can remain opened while performing other
tasks).
Tabs
In modules or dialogs containing more interface elements than
would fit into the limited area the Tab s are used. These related
elements are split into the groups (sections) and each one is
supplemented with the labelled Tab. Clicking on the Tab brings it
to the foreground showing the corresponding group of interface
elements. Tabs where some parameters were changed are highlighted (orange background).
Progress Bars
An progress of long ongoing procedures over time is indicated in a dedicated dialogs or
modules.
 Loading...
Loading...