16 - 58
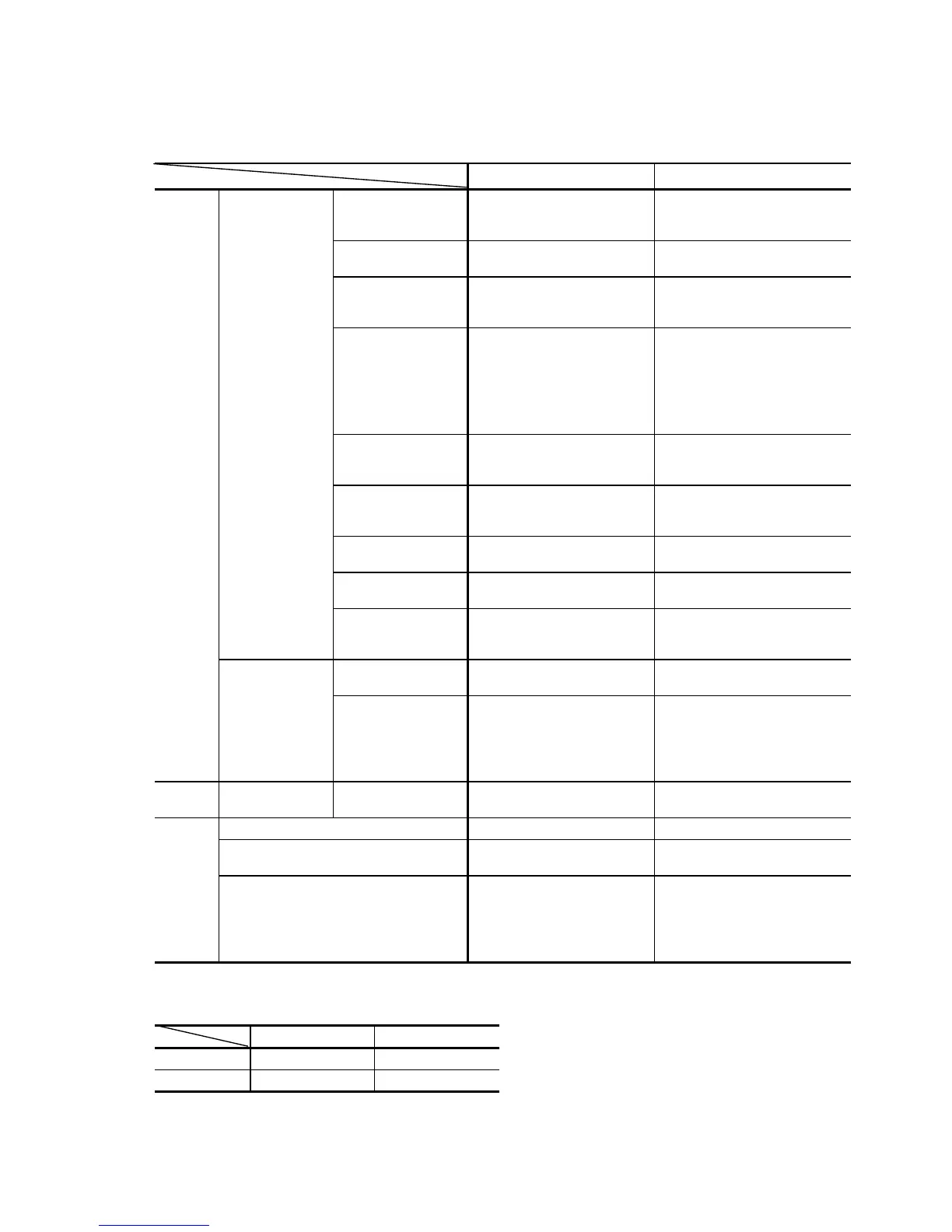
Comparison between Conventional Analyzer and Model 902 in Host Communication
Model 7170 (7070) Model 902
Test
inquiry
S. No. Host inquiry
information
Sample No., disk position,
ID (can be input through
screen)
Sample No., disk position,
ID (can be input through
screen)
T/S batch transfer Possible Possible (in routine mode
only)
Sample
registration to
analyzer
Unnecessary Routine mode unnecessary
Simple analysis necessary
Handling when
analyzer has T/S
Same as right Mode selectable by system
parameter
1) Full-time inquiry (priority
given to host)
2) Inquiry when without
T/S (same as before)
Analysis
prohibitive
specification
T/S all zero ←
S. Stop
specification from
host
Possible (POS = 0) Impossible
Host-priority
function
Possible None, time-out in 2 cycles
(36 sec)
Request for serum
indexes
Possible Impossible
Sample volume
increase/decrease,
kind and age
Possible Impossible
ID (basically
same as S. No.
Host inquiry
information
ID, disk position ID, sample No. (space)
mode) ID read error
support
• No inquiry to host
• Inquiry allowed
through manual ID
input
Routine analysis:
No inquiry to host
Simple analysis:
Inquiry made via ID
space and position No.
Data
transfer
S. No. ID Reaction process
data
Batch transfer Real-time transfer
Data
Retrieval via ID Available Unavailable
review
Addition/change of ID, comment
and data
Possible Impossible
Handling of identical sample Routine sample:
Handled in units of
test (overlay)
Stat sample:
Overwrite (NOTE)
Routine sample:
Handled in units of
test (overlay)
Stat sample:
Same as above
NOTE: Condition: Previous data, TP 8.0, GOT 30
Current Data Stored Data
Over lay TP 5.0 TP 5.0 GOT 30
Over write TP 5.0 TP 5.0
 Loading...
Loading...