138
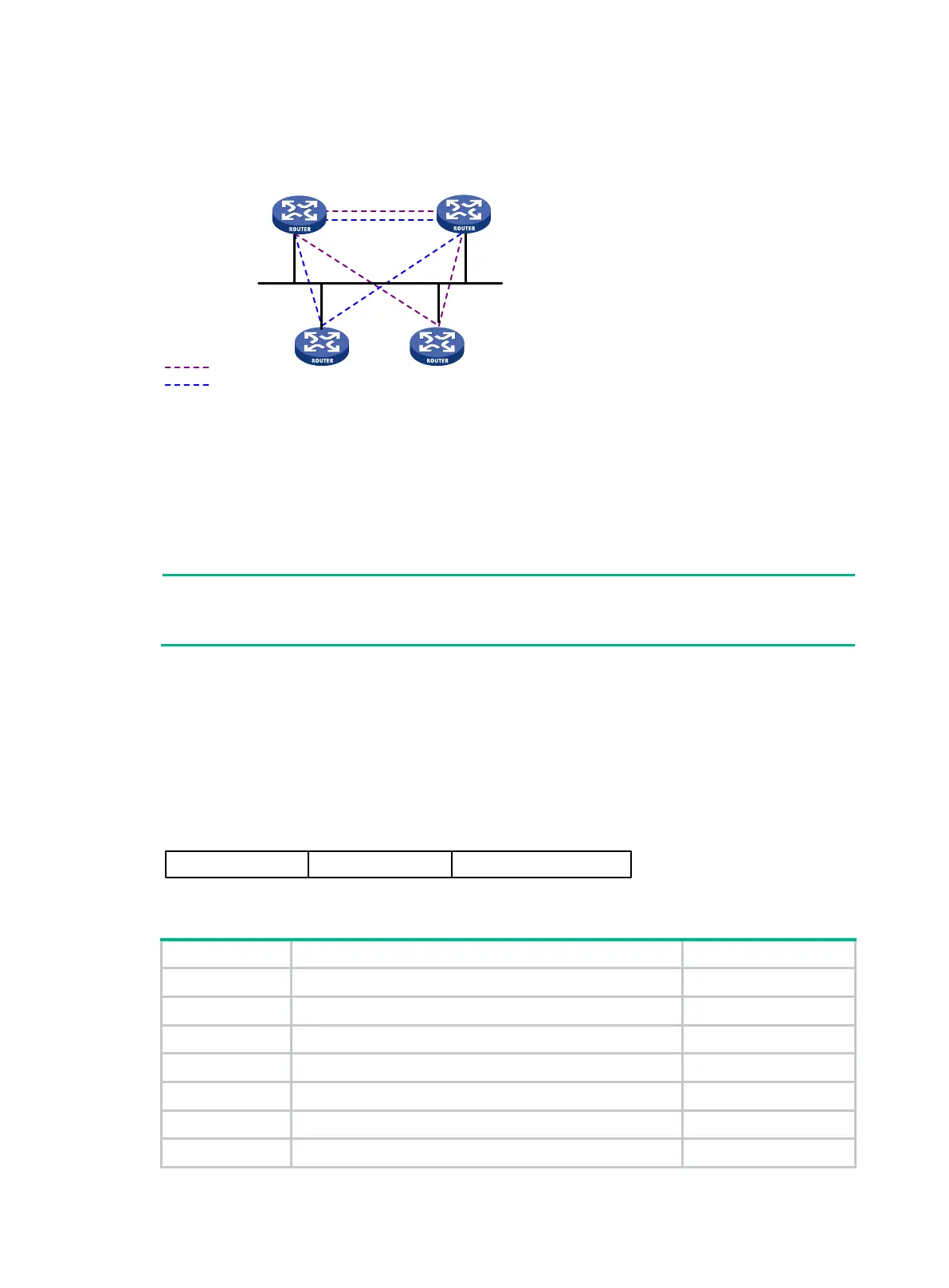
As shown in Figure 38, the same level routers on a network, including non-DIS routers, establish
adjacency with each other.
Figure 38 DIS in the IS-IS broadcast network
The DIS creates and updates pseudonodes, and generates LSPs for the pseudonodes, to describe
all routers on the network.
A pseudonode represents a virtual node on the broadcast network. It is not a real router. In IS-IS, it is
identified by the system ID of the DIS and a 1-byte Circuit ID (a non-zero value).
Using pseudonodes simplifies network topology and can reduce the amount of resources consumed
by SPF.
an IS-IS broadcast network, all routers es
tablish adjacency relationships, but they synchronize
their LSDBs through the DIS.
IS-IS PDUs
PDU
IS-IS PDUs are encapsulated into link layer frames. An IS-IS PDU has two parts, the headers and
the variable length fields. The headers comprise the PDU common header and the PDU specific
header. All PDUs have the same PDU common header. The specific headers vary by PDU type.
Figure 39 PDU format
Table 11 PDU types
15 Level-1 LAN IS-IS hello PDU L1 LAN IIH
16 Level-2 LAN IS-IS hello PDU L2 LAN IIH
17 Point-to-Point IS-IS hello PDU P2P IIH
18 Level-1 Link State PDU L1 LSP
20 Level-2 Link State PDU L2 LSP
24 Level-1 Complete Sequence Numbers PDU L1 CSNP
25 Level-2 Complete Sequence Numbers PDU L2 CSNP
L1
L2
L1/L2 L1/L2
DIS DIS
L1 adjacencies
L2 adjacencies
PDU common header PDU specific header Variable length fields (CLV)

 Loading...
Loading...



















