325
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 9.1.1.0/24:
From : 10.1.3.1 (1.1.1.1)
Rely nexthop : 10.1.3.1
Original nexthop: 10.1.3.1
OutLabel : NULL
AS-path : 100
Origin : igp
Attribute value : MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, pre 255
State : valid, internal-confed, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
The output shows the following:
• Switch F can send route information to Switch B and Switch C through the confederation by
establishing only an EBGP connection with Switch A.
• Switch B and Switch D are in the same confederation, but belong to different sub-ASs. They
obtain external route information from Switch A, and generate identical BGP route entries
although they have no direct connection in between.
BGP path selection configuration example
Network requirements
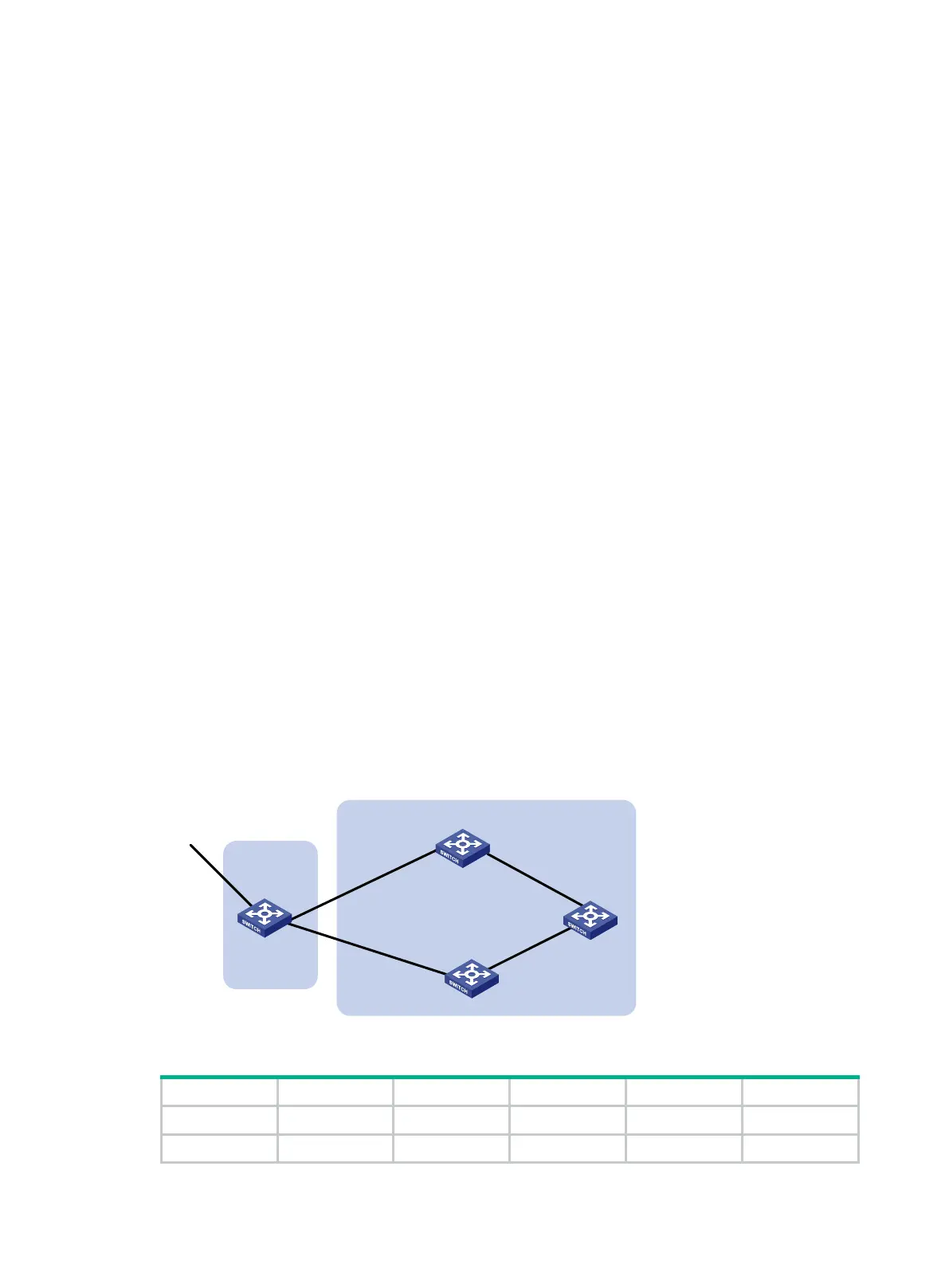
As shown in Figure 73, all switches run BGP.
• EBGP runs between Switch A and Switch B, and between Switch A and Switch C.
• IBGP runs between Switch B and Switch D, and between Switch D and Switch C. OSPF is the
IGP protocol in AS 200.
Configure routing policies, making Switch D use the route 1.0.0.0/8 from Switch C as the optimal.
Figure 73 Network diagram
Table 18 Interface and IP address assignment
Switch A Vlan-int101 1.0.0.1/8 Switch D Vlan-int400 195.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int100 192.1.1.1/24 Vlan-int300 194.1.1.1/24
Switch A
AS 100
Vlan-int101
Switch C
AS 200
Vlan-int200
Switch B
Switch D
Vlan-int100
Vlan-int200
Vlan-int400
Vlan-int400
Vlan-int300
Vlan-int300
Vlan-int100

 Loading...
Loading...



















