375
# Configure the IP address of VLAN-interface 20.
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 20
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface20] ip address 1.1.3.2 24
Verifying the configuration
# Telnet to Switch B on Switch A. The operation succeeds. (Details not shown.)
# Telnet to Switch C on Switch A. The operation fails. (Details not shown.)
# Ping Switch C from Switch A. The operation succeeds. (Details not shown.)
Telnet uses TCP, and ping uses ICMP. The results show the following:
• All TCP packets sent from Switch A are forwarded to the next hop 1.1.2.2.
• Other packets are forwarded through VLAN-interface 20.
• The local PBR configuration is effective.
Packet type-based interface PBR configuration example
Network requirements
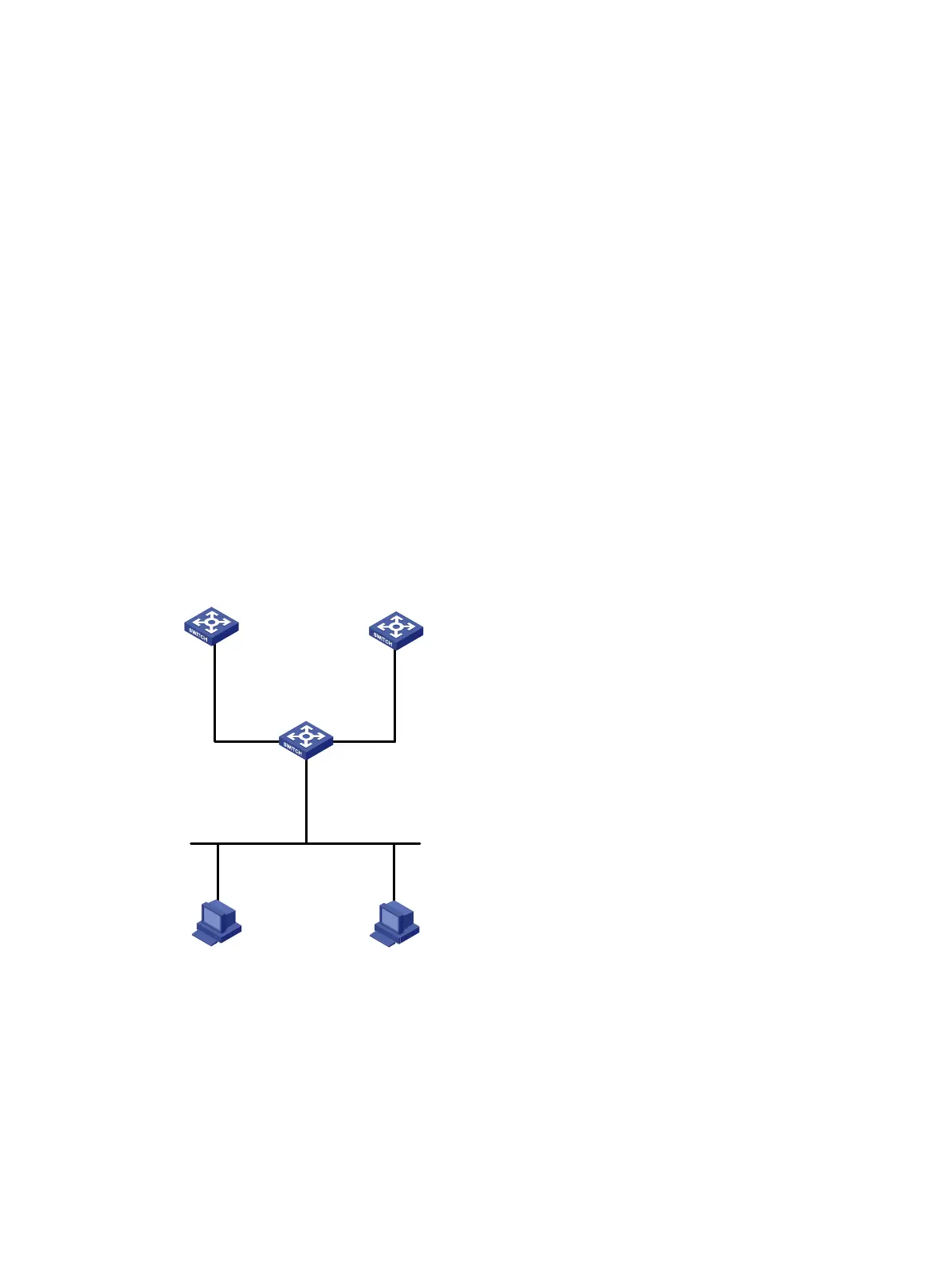
As shown in Figure 88, Switch B and Switch C cannot reach each other.
Configure PBR on Switch A to forward all TCP packets received on VLAN-interface 11 to the next
hop 1.1.2.2 (Switch B).
Figure 88 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Make sure Switch B and Switch C can reach Host A. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure Switch A:
# Create VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] vlan 10
[SwitchA-vlan10] quit
Switch A
Vlan-int11
10.110.0.10/24
Vlan-int10
1.1.2.1/24
Vlan-int20
1.1.3.1/24
Subnet
10.110.0.0/24
Vlan-int10
1.1.2.2/24
Vlan-int20
1.1.3.2/24
Switch B Switch C
Host A Host B
10.110.0.20/24
Gateway: 10.110.0.10

 Loading...
Loading...



















