396
3. Enable the GR capability for
RIPng.
graceful-restart
By default, RIPng GR is disabled.
4. (Optional.) Set the GR
interval.
graceful-restart interval
interval
By default, the GR interval is 60
seconds.
Configuring RIPng NSR
Nonstop routing (NSR) backs up RIPng routing information from the active process to the standby
process. After an active/standby switchover, NSR can complete route regeneration without tearing
down adjacencies or impacting forwarding services.
NSR does not require the cooperation of neighboring devices to recover routing information, and it is
typically used more often than GR.
A device that has RIPng NSR enabled cannot act as GR restarter.
To enable RIPng NSR:
1. Enter system view.
N/A
2. Enter RIPng view.
ripng
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ]
N/A
3. Enable RIPng NSR.
non-stop-routing
By default, RIPng NSR is disabled.
RIPng NSR enabled for a RIPng
process takes effect only on that
process. If multiple RIPng processes
exist, enable RIPng NSR for each
process as a best practice.
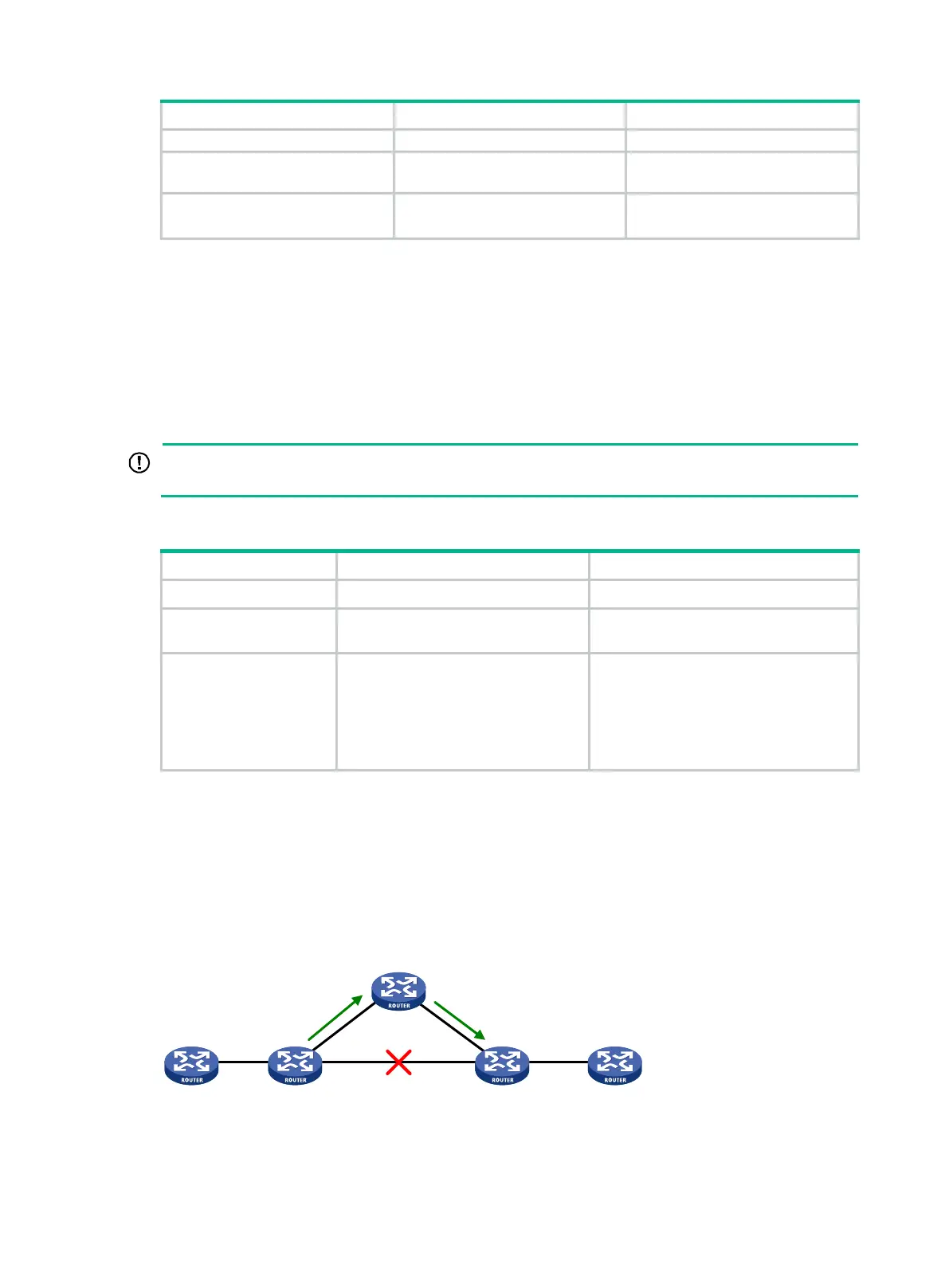
Configuring RIPng FRR
A link or router failure on a path can cause packet loss and even routing loop until RIPng completes
routing convergence based on the new network topology. FRR enables fast rerouting to minimize the
impact of link or node failures.
Figure 92 Network diagram for RIPng FRR
As shown in Figure 92, configure FRR on Router B by using a routing policy to specify a backup next
hop. When the primary link fails, RIPng directs packets to the backup next hop. At the same time,
Backup next hop: Router C
Router ENext hop: Router D
Router A Router B

 Loading...
Loading...



















