2.14 Sensors and switches
2.14.1 Revolution sensor on target wheel
Speed sensor A is situated on the timing system carter.
The sensor detects the signal from the target wheel
B
(60 - 2teeth)
situated on the crankshaft pulley. It sends it to the ECU as an
analogical signal.
The sensor sends and analogue signal to the ECU.
The sensor produces a 5V square wave signal having a Hall effect
while the crankshaft in rotation detects its position and speed.
The data sent by this sensor enables the ECU to pilot fuel
anticipation injection for each piston.
For gap adjusting see
Par. 9.15.1.5
.
2.14.2 Camshaft sensor
Camshaft sensor C is situated on the timing system carter.
The purpose of the camshaft sensor C is to identify the position of
the camshaft control gear E with respect to the engine shaft and
consequently the position of the pistons with respect to the T.D.C..
The sensor produces a 5V square wave signal having a Hall effect
while the camshaft in rotation detects the phases of the 4 strokes
of the 1st cylinder. As a consequence, ECU by means of internal
calculations, also recognises the phases of the other cylinders.
The data sent by this sensor enables the ECU to pilot fuel
anticipation injection for each piston.
For gap adjusting see
Par. 9.15.1.4
.
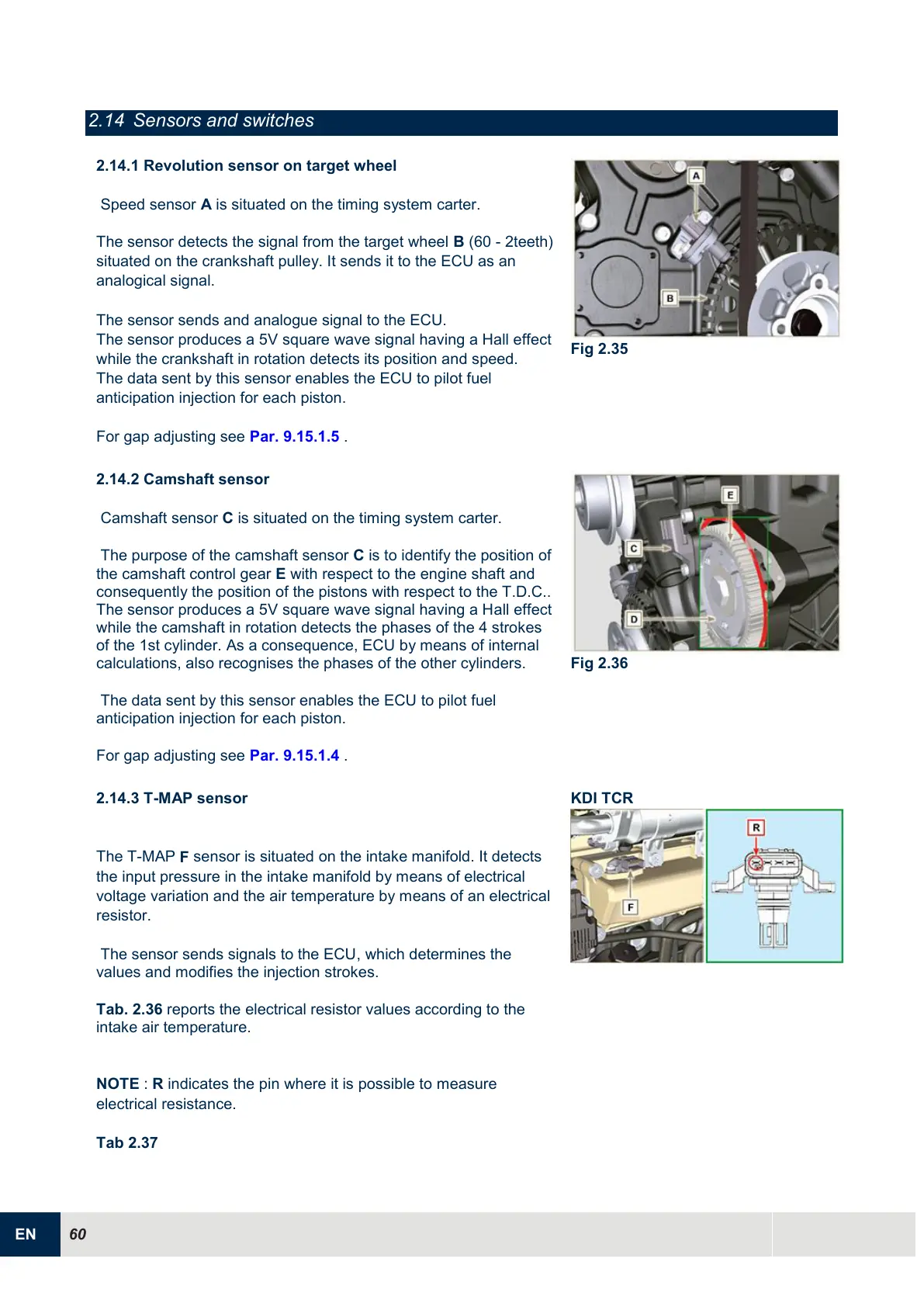
2.14.3 T-MAP sensor
The T-MAP
F
sensor is situated on the intake manifold. It detects
the input pressure in the intake manifold by means of electrical
voltage variation and the air temperature by means of an electrical
resistor.
The sensor sends signals to the ECU, which determines the
values and modifies the injection strokes.
Tab. 2.36 reports the electrical resistor values according to the
intake air temperature.
NOTE
:
R
indicates the pin where it is possible to measure
electrical resistance.
Tab 2.37

 Loading...
Loading...