Appendix for Lorrca® MaxSis
Lorrca Maxsis User Manual Page 209
Version 5.04 MRN-231-EN
The amplitude (Amp=Isc
top
– Isc
0
) is used to describe the extent of aggregation. (References 6
30
,31
31
) Aggregation kinetics are described by the time-constants T
f
and T
s
but also by t½. The latter
is the time that elapses until the peak intensity is reduced by half the amplitude (to Isc½). The
overall aggregation behaviour of the suspension in described by a single parameter: the
aggregation index. This aggregation index (AI) is a value between 0 and 100% and depends on
both the extent and kinetics of aggregation. (References (on page 215) 6
32
, 22
33
, 31
34
, 57
35
) It is
determined from the areas A and B bounded by t = t
top
and t = t
top
+ 10
as AI = 100% * A/(A+B) (see
Figure 6).
The time elapsed until the occurrence of the peak is sometimes used as an indication of the RBC-
shape recovery time. The peak occurs when the first derivative of equation 4 equals zero. The first
derivative depends on all parameters of equation 4 including the aggregation parameters. The fact
that t
top
is influenced by the aggregation process makes it an unsuitable candidate for representing
the RBC-shape recovery time.
The aggregation software allows the user to display the results of a fixed syllectogram model or to
display the best performing one (auto-mode):
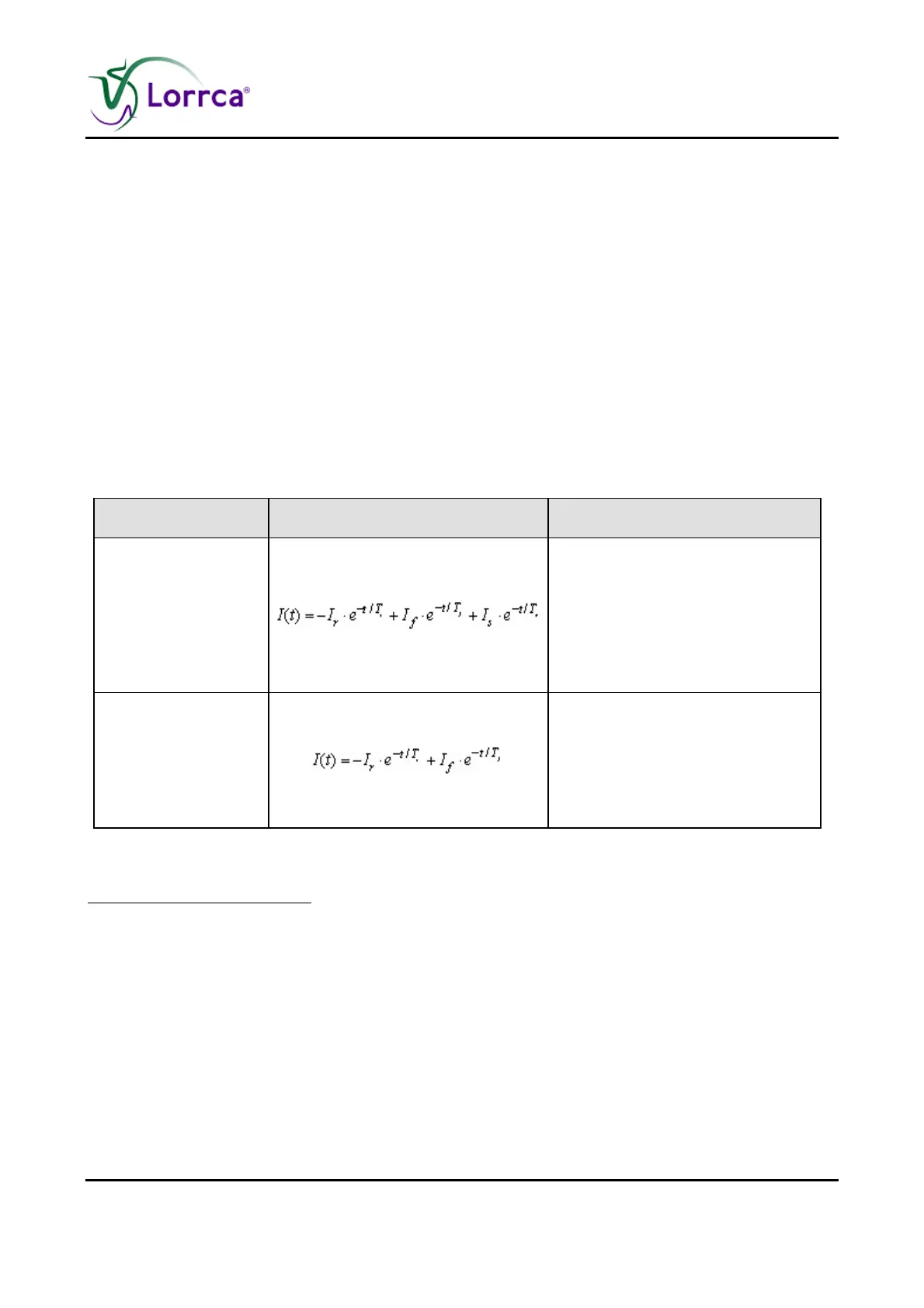
Mode
Equation Relevant program parameters
Tri-exp (rise-fall-fall)
Ir, Tr : RBC relaxation
If, Tf : RBC rouleaux formation
Is, Ts : 3D aggregate formation
Bi-exp (rise-fall)
Ir, Tr : RBC relaxation
If, Tf : Mix of RBC rouleaux and
3D aggregate formation
30
Bauersachs R.M., Wenby R.B., Meiselman H.J., Determination of specific red blood cell aggregation
indices via an automated system, Clin. Hemorheol., vol. 9, pp. 1-25, 1989.
31
Hardeman M.R., Goedhart P.T., Dobbe J.G.G., Lettinga K.P., Laser-assisted Optical Rotational Cell
Analyser (LORCA); A new instrument for measurement of various structural hemorheological parameters,
Clin. Hemorheol., vol. 14:(4), pp. 605-618, 1994.
32
Bauersachs R.M., Wenby R.B., Meiselman H.J., Determination of specific red blood cell aggregation
indices via an automated system, Clin. Hemorheol., vol. 9, pp. 1-25, 1989.
33
Donner M., Siadat M., Stoltz J.F., Erythrocyte aggregation: Approach by light scattering determination,
Biorheology, vol. 25:(1/2), pp. 367-375, 1988.
34
Hardeman M.R., Goedhart P.T., Dobbe J.G.G., Lettinga K.P., Laser-assisted Optical Rotational Cell
Analyser (LORCA); A new instrument for measurement of various structural hemorheological parameters,
Clin. Hemorheol., vol. 14:(4), pp. 605-618, 1994.
35
Stoltz J.F., Donner M., Erythrocyte aggregation: Experimental approaches and clinical implications, Int.
Angiol., vol. 6, pp. 193-201, 1987.
 Loading...
Loading...