Function Manual
192 01/2017
Another recent development with respect to EN 61508 is its system approach, which extends the technical requirements to
include the entire safety installation from the sensor to the actuator, the quantification of the probability of hazardous failure
due to random hardware failures, and the creation of documentation covering all phases of the safety-related lifecycle of the
E/E/PES.
Risks are intrinsic in machines due to their design and functionality. For this reason, the Machinery Directive requires that a
risk assessment be performed for each machine and, if necessary, the level of risk reduced until the residual risk is less than
the tolerable risk. To assess these risks, the following standards must be applied:
EN ISO 12100-1 "Safety of Machinery - basic terminology, general principles for design"
EN ISO 13849-1 (successor to EN 954-1) "Safety-related parts of control systems"
EN ISO 12100-1 focuses on the risks to be analyzed and the design principles for minimizing risk.
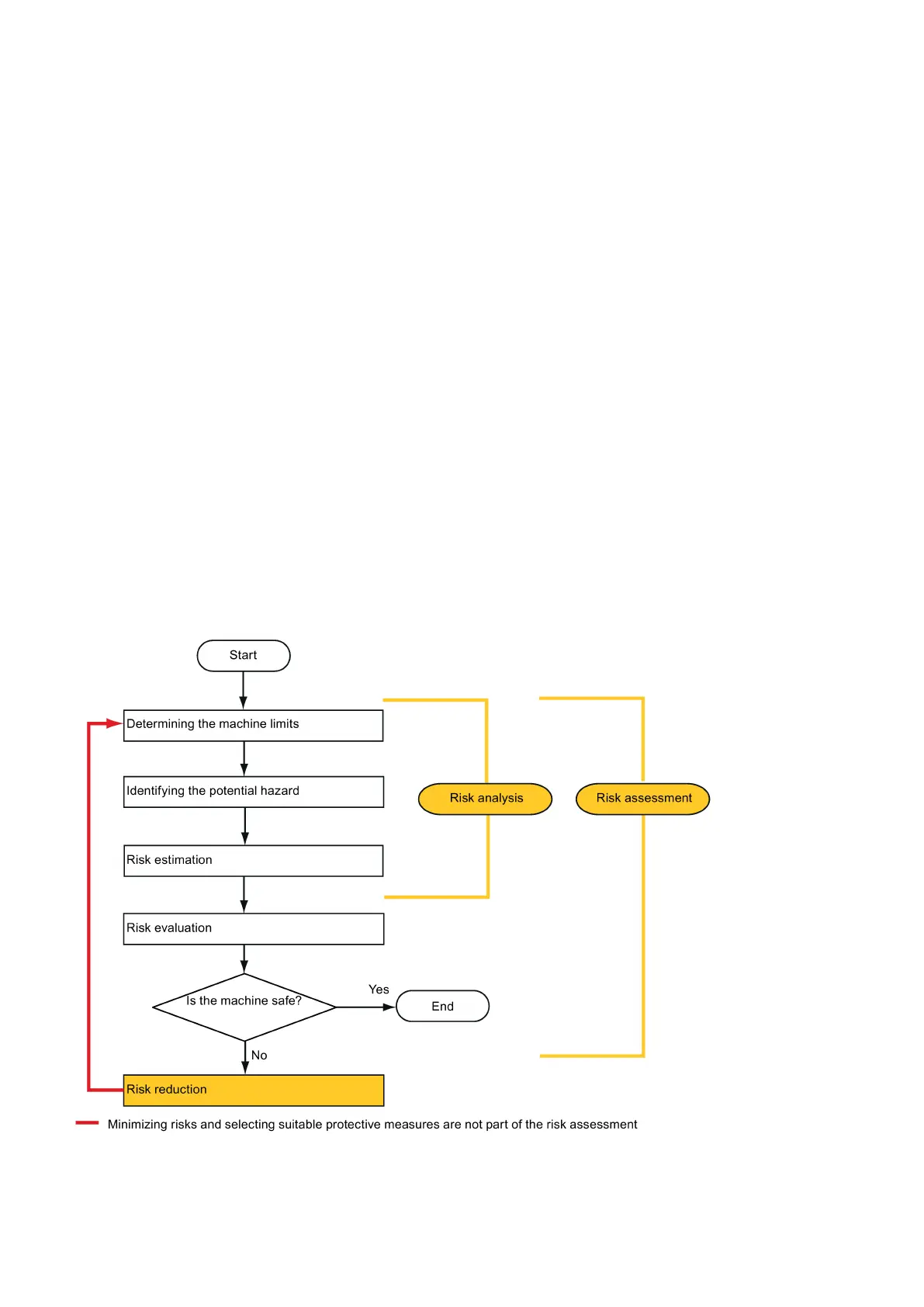
The risk assessment is a procedure that allows hazards resulting from machines to be systematically investigated. Where
necessary, the risk assessment is followed by a risk reduction procedure. When the procedure is repeated, this is known as
an iterative process. This can help eliminate hazards (as far as this is possible) and can act as a basis for implementing
suitable protective measures.
The risk assessment involves the following:
● Risk analysis
– Determines the limits of the machine (EN ISO 12100-1)
– Identification of the hazards (EN ISO 12100-114)
– Estimating the level of risk (EN 1050 Paragraph 7)
● Risk evaluation
As part of the iterative process to achieve the required level of safety, a risk assessment is carried out after the risk
estimation. A decision must be made here as to whether the residual risk needs to be reduced. If the risk is to be further
reduced, suitable protective measures must be selected and applied. The risk assessment must then be repeated.
Iterative process for achieving safety:

 Loading...
Loading...




















