User Guide 754
SNMP
1
SNMP
1.1 Overview
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a standard network management
protocol, widely used on TCP/IP networks. It facilitates device management using NMS
(Network Management System) applications. With SNMP, network managers can view
or modify the information of network devices, and timely troubleshoot according to
notifications sent by those devices.
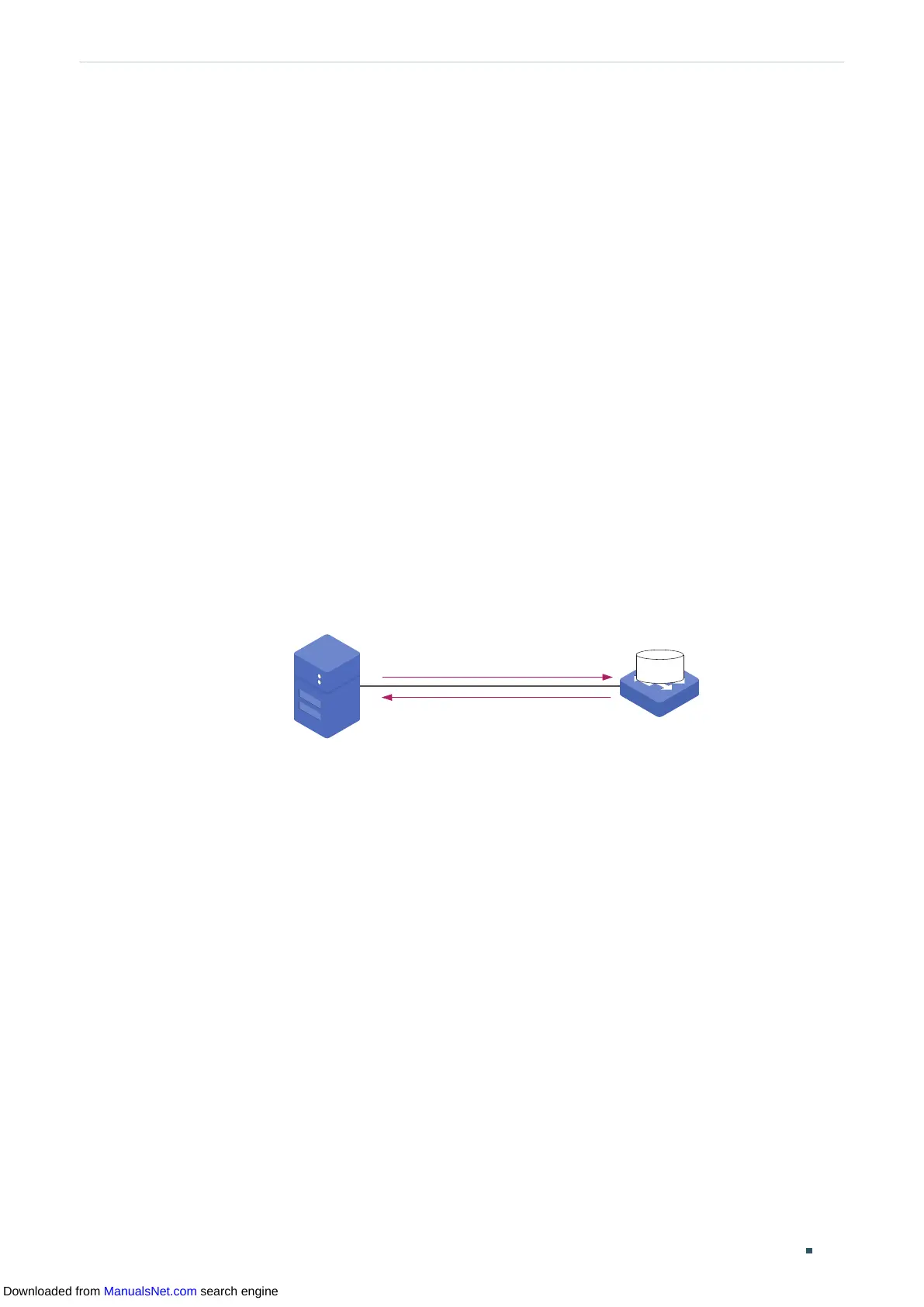
As the following figure shows, the SNMP system consists of an SNMP manager, an SNMP
agent, and a MIB (Management Information Base).
The SNMP manager is a host that runs NMS applications. The agent and MIB reside on the
managed device, such as the switch, router, host or printer. By configuring SNMP on the
switch, you define the relationship between the manager and the agent.
Figure 1-1 SNMP System
SNMP Agent
Get or set MIB objects values
Respond or send notifications
SNMP Manager
Host Running NMS
Application
Managed Device
MIB
1.2 Basic Concepts
The following basic concepts of SNMP will be introduced: SNMP manager, SNMP agent,
MIB (Management Information Base), SNMP entity, SNMP engine, Notification types and
SNMP version.
SNMP Manager
The SNMP manager uses SNMP to monitor and control SNMP agents, providing a friendly
management interface for the administrator to manage network devices conveniently.
It can get values of MIB objects from an agent or set values for them. Also, it receives
notifications from the agents so as to learn the condition of the network.
SNMP Agent
An SNMP agent is a process running on the managed device. It contains MIB objects whose
values can be requested or set by the SNMP manager. An agent can send unsolicited trap
messages to notify the SNMP manager that a significant event has occurred on the agent.
Downloaded from ManualsNet.com search engine

 Loading...
Loading...











