15.3 External clock (XCK)
External clocking is used by the synchronous or SPI slave modes of operation. External clock input
from the XCK pin is sampled by a synchronization logic to remove meta-stability. The output from the
synchronization logic must then pass through an edge detector before it can be used by the
Transmitter and Receiver.
This process introduces a two CPU clock period delay and the maximum frequency of the external
XCK pin is limited by the following equation:
, where fXCK is frequency of XCK, and fSCLK is frequency of main system clock (SCLK).
15.4 Synchronous mode operation
When synchronous mode or SPI mode is used, the XCKn pin will be used as either clock input (slave)
or clock output (master). The dependency between a clock edge and data sampling or data change is
the same. The basic principle is that data input on RXDn (MISOn in SPI mode) pin is sampled at the
opposite XCK clock edge at the edge in the data output on TXDn (MOSIn in SPI mode) pin is
changed.
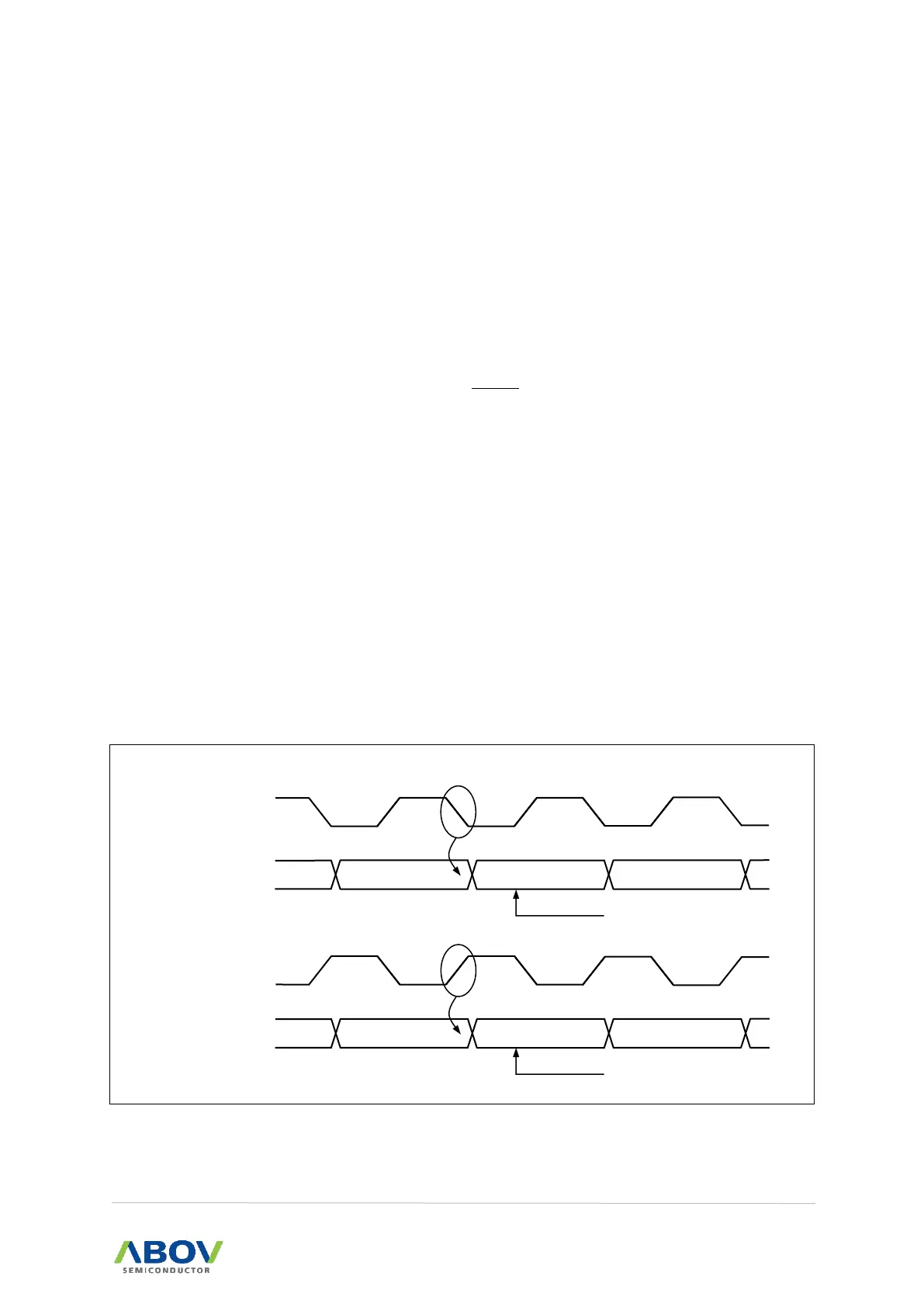
UCPOL bit in UnCTRL1 register selects which XCKn clock edge is used for data sampling and which
is used for data change. As shown in Figure 72, when UCPOL is zero, data will be changed at XCKn
rising edge and sampled at XCKn falling edge.
 Loading...
Loading...