16 CRC
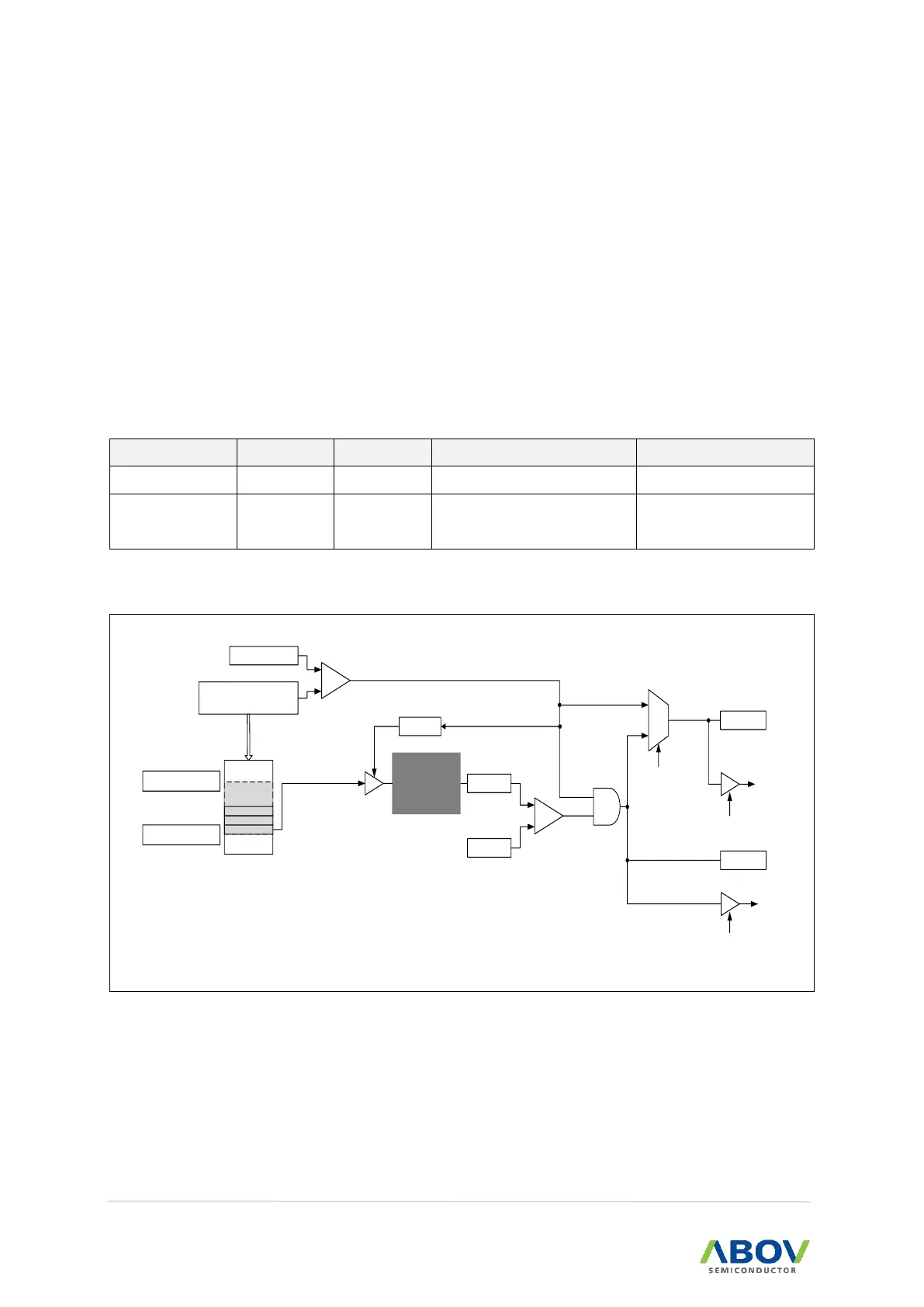
Using the CRC, it can be monitor the memory of the specified area. This is a one-time operation, and
reset is required for continuous operation. In CRC MNT mode, when the CRC read is finished,
CRC_FLAG occurs. In CRC validate mode, if the CRC validate fail after the CRC reading is finished,
CRC_FLAG occurs. CRC_FAIL indicates the status of validate results when the CRC read is finished.
If the CRC_FLAG is generated and the interrupt is enabled, interrupt service routine is served. CRC-
FLAG is not cleared by hardware. CRC-TYPE 0~3 are not supported. Validate is done by comparing
the CRC_MNT register and the CRC register value. CRC are not automatically initialized, you need to
calculate a new CRC after CRC_H, CRC_L Clear.
Table 30. CRC mode
 Loading...
Loading...