250 Understanding Your Agilent ChemStation
11 Evaluating System Suitability
Definitions for Reproducibility
Definitions for Reproducibility
For the statistical review of analytical data in terms of reproducibility the
sequence is considered as a small random sample taken out of an infinite
number of possible experimental results. To accomplish a complete set of
results, an unlimited amount of sample material as well as time would be
required. Strictly statistical data does only apply to a complete self-contained
set or population of data. Therefore a prerequisite for such a treatment is that
the selected sample can be assumed as representative for all data.
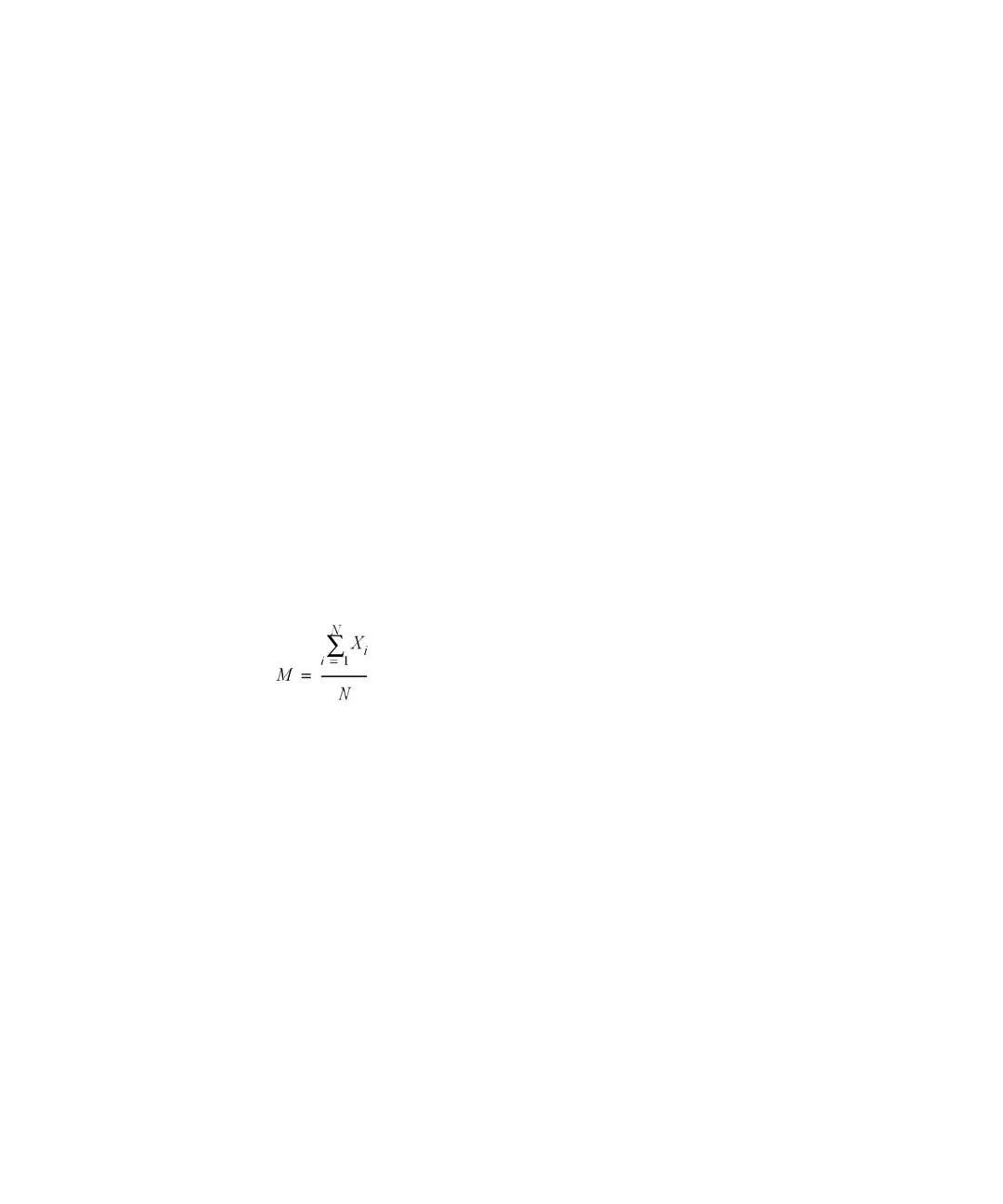
Sample Mean M
The mean value M of a random sample consisting of N measurements is
calculated from this limited set of N single observed values X
i
indexed with a
consecutive counter i according to the formula:
where:
N = number of discrete observations
X
i
= value of discrete observations indexed by i
Sample Standard Deviation S
Consider a random sample of size N. The sample standard deviation S for the
selected finite sample taken out of the large population of data is determined
by

 Loading...
Loading...










