PROGRAM EDIT
Page 106 S2000 Operator’s Manual - Version 1.30
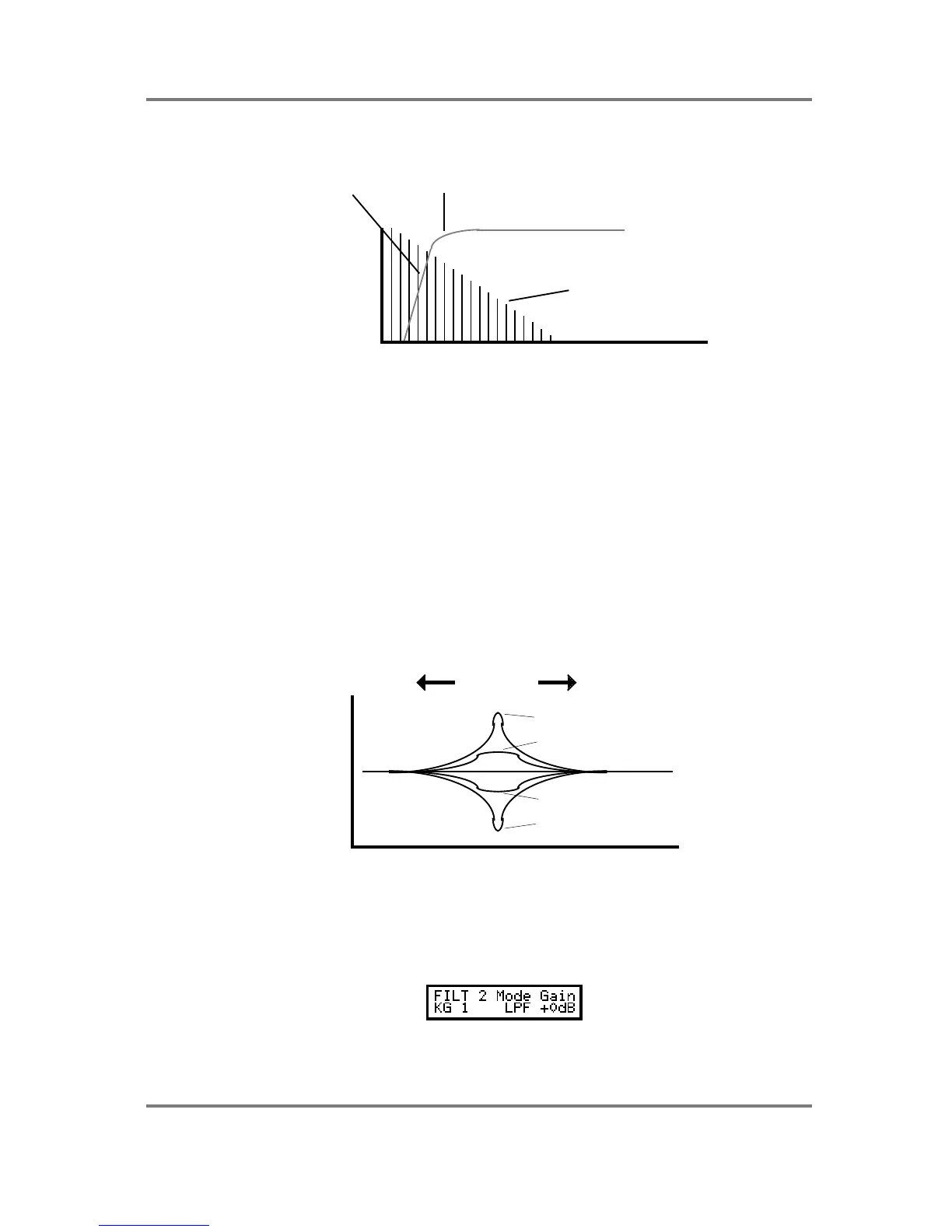
The high pass filter offers this response slope:
HARMONICS
CUTOFF FREQUENCYROLL-OFF SLOPE
L
E
V
E
L
FREQUENCY
In this example, you can see that low frequency components are removed whilst high
frequencies pass through. This filter can be used to make sounds very thin and brittle. For
example, this type of filter may be used effectively on an oboe sound or harpsichord sound.
When the resonance is increased, the area around the cutoff frequency is boosted and so
harmonics around that frequency will be emphasised.
The final mode selection is quite unlike those shown above. Selecting EQ turns the second
filter bank into a simple one band equaliser with variable frequency and resonant cut/boost that
can be used for a variety of different effects. With the EQ filter selection, the ‘straight’ sound
from Filter 1 is also passed through unaffected and you can use this EQ section to highlight
specific frequencies in the sound. This filter is also able to be controlled by any of the
modulation sources we have seen so far and using it with a high resonance setting in
conjunction with any of these modulation sources, you may create interesting sounds not
unlike phase shifting.
The response slope for the EQ selection is shown below:
CUTOFF
FREQUENCY
L
E
V
E
L
FREQUENCY
With resonance at 16, the frequency response is flat but as the resonance is increased, the
gain of the filter is boosted around that frequency. If the resonance is decreased, the gain is
cut as the resonance gets sharper.
The first of the FILT 2 pages is as follows:
The MODE parameter sets the filter mode and the GAIN parameter allows you to cut the overall
level by -6dB. The GAIN parameter is useful in overcoming excessive level increases (and
 Loading...
Loading...