Spectrum Analyzer Measurements 3-3 Setting Frequency Parameters
Spectrum Analyzer MG PN: 10580-00447 Rev. H 3-5
The spectrum analyzer has several mixer bands. Depending on the operating frequency, the local oscillator
may be above or below the input frequency. When the local oscillator frequency is below the input frequency,
an increase in the input frequency results in an increase in the IF output frequency. When the local oscillator
is above the input frequency, an increase in the input frequency moves it closer to the local oscillator frequency
and the IF output frequency consequently decreases. The following table shows the bands and indicates where
the LO frequency is, in relation to the RF frequency.
You need to take frequency inversion into account when processing the IF signal. Assuming that the IF has
been processed to yield I and Q data, inversion is easily done by swapping I and Q.
A residual frequency offset of the IF may exist compared to the RF due to the resolution of the first and second
local oscillators. This offset is usually on the order of several kHz, but may be up to 10 kHz or so. To determine
the residual offset, you need a second spectrum analyzer or a frequency counter.
1. Attach a signal source (or antenna) to the spectrum analyzer and set the center frequency to the center of
the signal being received.
2. Set Zero Span from the FREQ/SPAN menu, and then press IF OUTPUT and enable the IF output.
3. Attach a second spectrum analyzer to the IF Out port and set the center frequency to 300 (or 325) MHz.
4. Set the span of the second spectrum analyzer to 100 kHz with the resolution needed to be able to
measure an offset that may be 25 kHz or less.
5. Measure the frequency of the IF signal to see how far the signal is offset from 300 (or 325) MHz.
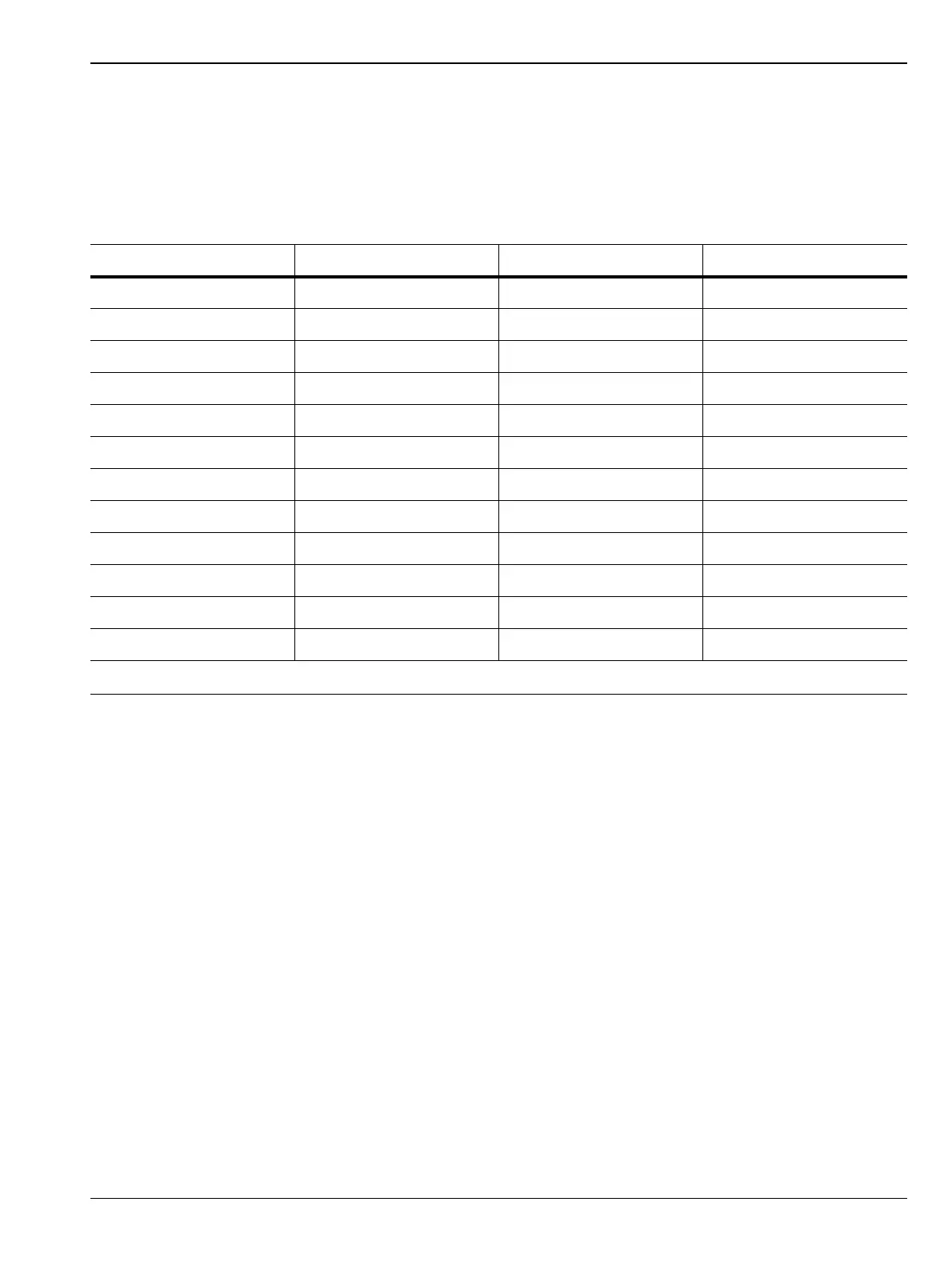
Table 3-2. IF Inversion Bands
RF Band Start Frequency (MHz) Stop Frequency (MHz) Spectrum Inversion
1 0 5350 Y
2 5350 7200 Y
3 7200 9200 Y
4 9200 11100 N
5 11100 13000 N
6 13000 16500 N
7 16500 20400 Y
8 20400 26950 Y
9 26950 33810 Y
10 33810 39900 Y
11 39900 47000 N
12 47000 54000 N
“Inverted” means that the IF is spectrally inverted from the input (as the input frequency goes higher, the IF goes lower).
“Not Inverted” means that the IF is not spectrally inverted (as the input frequency goes higher, the IF goes higher).
 Loading...
Loading...