3-19 Coverage Mapping (Option 431) Spectrum Analyzer Measurements
3-92 PN: 10580-00447 Rev. H Spectrum Analyzer MG
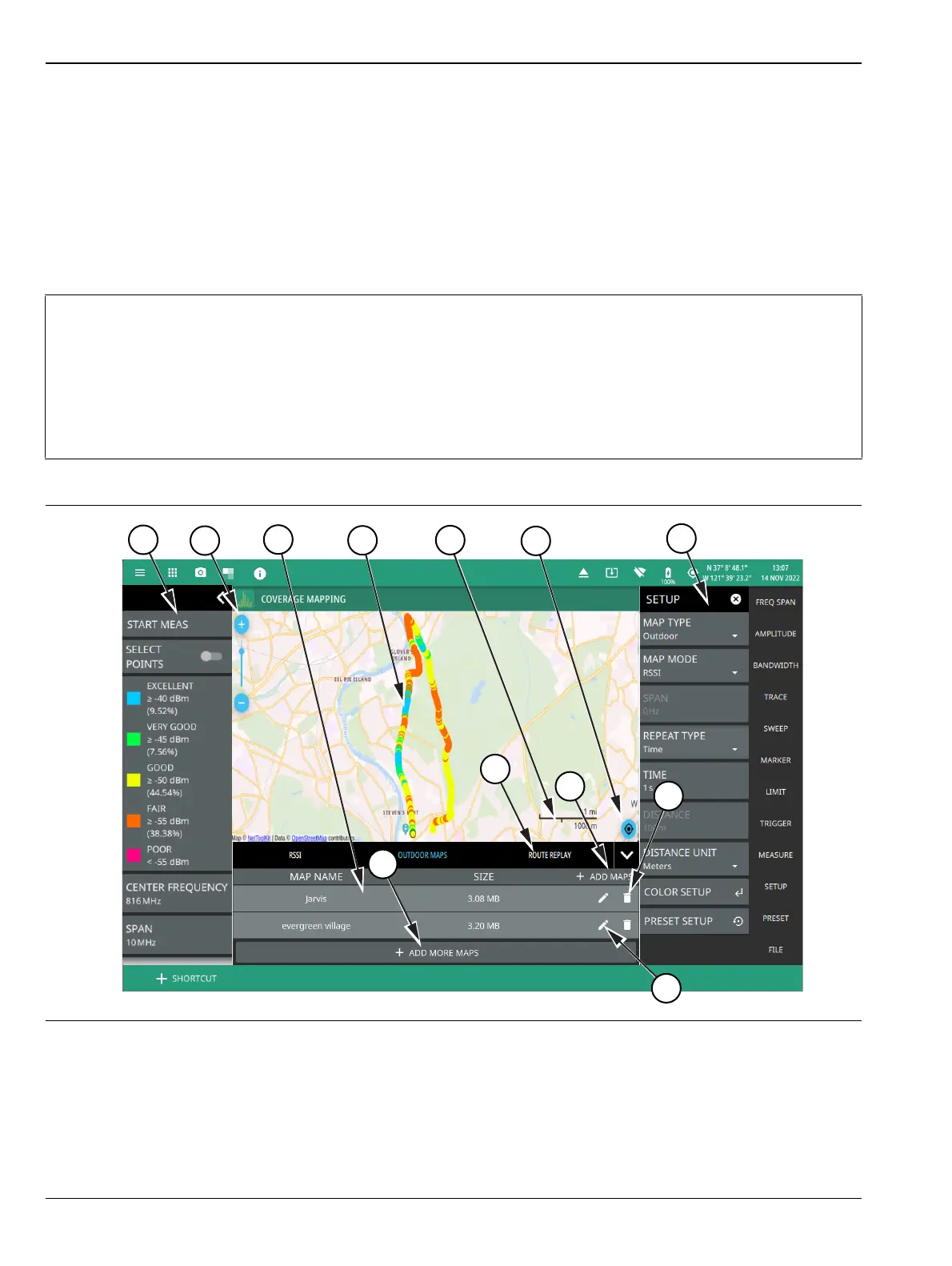
Outdoor Coverage Mapping
With a valid GNSS (GPS) signal, the instrument identifies the current location on the displayed map with a
location pin. As the location changes during a measurement, colored-coded dots corresponding to the received
signal strength/power are placed at distance or time intervals. Using GNSS (GPS) for latitude, longitude, and
altitude, data is automatically saved for each location. The instrument logs data automatically based on either
a set time or distance interval. If there is no map available when making the measurements, it is still possible
to save all of the data to a KML file and then combine the data with a map using other third party tools that
can work with KML data. You may also recall a map after taking the data without having to save and recall
the measurement data. See Figure 3-75, “Coverage Mapping (Outdoor)” on page 3-92 for an overview of the
outdoor coverage mapping interface.
Note
When selecting outdoor coverage mapping and the GNSS (GPS) is off or is turned off, GNSS (GPS)
will be enabled with a notification dialog. Aborting the GNSS (GPS) fix from the dialog does not allow
the instrument to start a coverage mapping measurement.
When saving CSV and KML files map point measurement data, the saved data is cumulative of all
data points on the map or measurements since the map points were last cleared.
Ensure to save and clear current measurement points once the maximum number of measurement
points are reached.
Figure 3-75. Coverage Mapping (Outdoor) (1 of 2)
 Loading...
Loading...