This figure illustrates the IS-IS overload bit scenario:
Figure 21: IS-IS overload bit
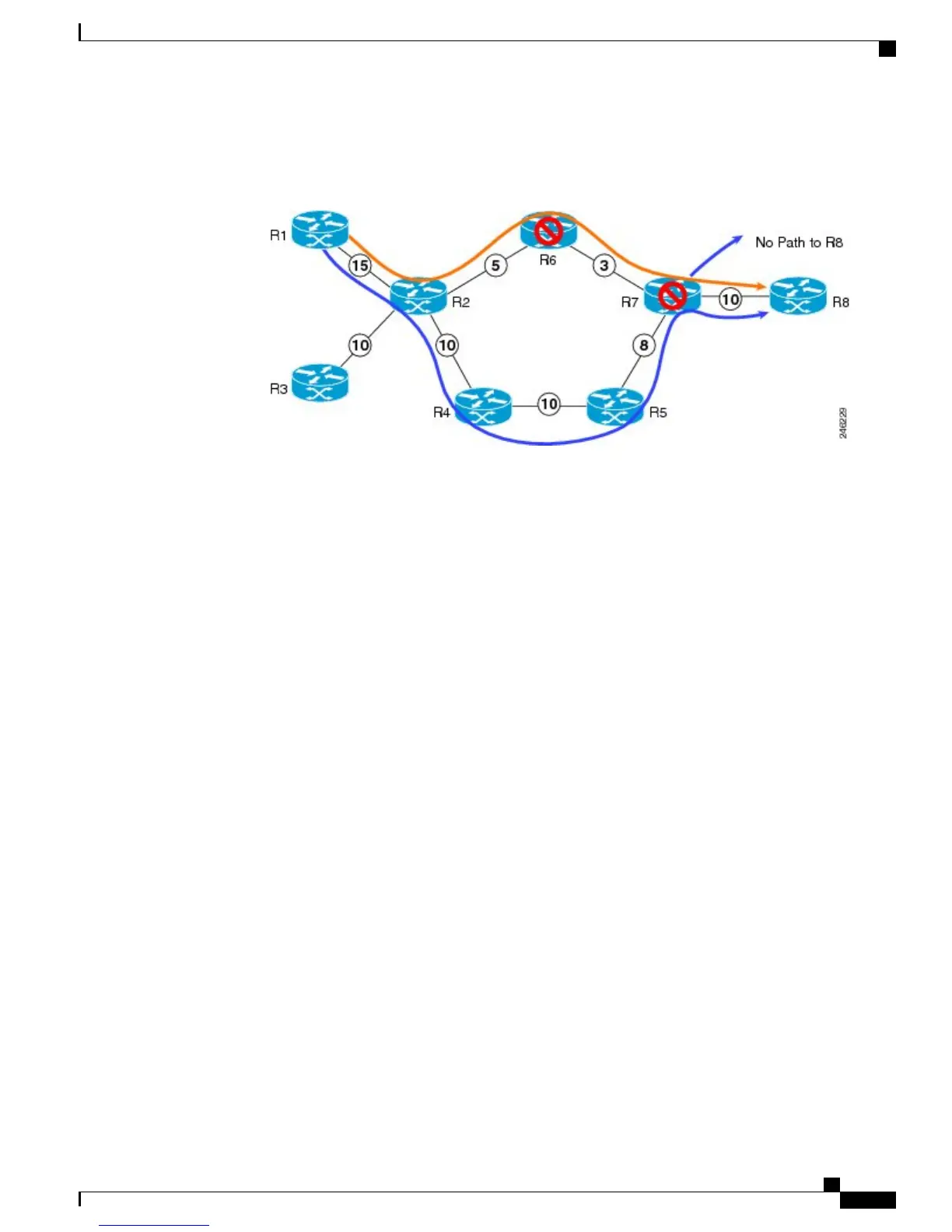
Consider a MPLS TE topology in which usage of nodes that indicated an overload situation was restricted.
In this topology, the router R7 exhibits overload situation and hence this node can not be used during TE
CSPF. To overcome this limitation, the IS-IS overload bit avoidance (OLA) feature was introduced. This
feature allows network administrators to prevent RSVP-TE label switched paths (LSPs) from being disabled
when a router in that path has its Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) overload bit set.
The IS-IS overload bit avoidance feature is activated at router R1 using this command:
mpls traffic-eng path-selection ignore overload
configure
mpls traffic-eng
path-selection ignore overload
commit
Related Topics
Configuring the Ignore Integrated IS-IS Overload Bit Setting in MPLS-TE, on page 240
Ignore Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System Overload Bit Setting in MPLS-TE, on page 177
Configure GMPLS: Example
This example shows how to set up headend and tailend routers with bidirectional optical unnumbered tunnels
using numbered TE links:
Headend Router
router ospf roswell
router-id 11.11.11.11
nsf cisco
area 23
!
area 51
interface Loopback 0
!
interface MgmtEth0/0/CPU0/1
!
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide for the Cisco CRS Router, Release 5.1.x
345
Implementing MPLS Traffic Engineering
Configure GMPLS: Example
 Loading...
Loading...