GEN7iB
292
GEN series SYNCHRONIZATION METHODS
GEN series SYNCHRONIZATION METHODS
14
After this message exchange, the slave has four timestamps from which both the slave
offset (time offset by which the slave clock leads or lags the master) and the network
delay (the time taken for packets to traverse the network link between the two nodes)
can be determined.
The link delay can be calculated as follows:
0DVWHU6ODYH
GHOD\
W
PV
W
±W
6ODYH0DVWHU
GHOD\
W
VP
W
±W
In each case, the time differences refer to times taken from different clocks which may
be offset from each other. However, if the assumption is made that the delay in one
direction is the same as the delay in the opposite direction, then the two equations can
be combined as follows:
'HOD\
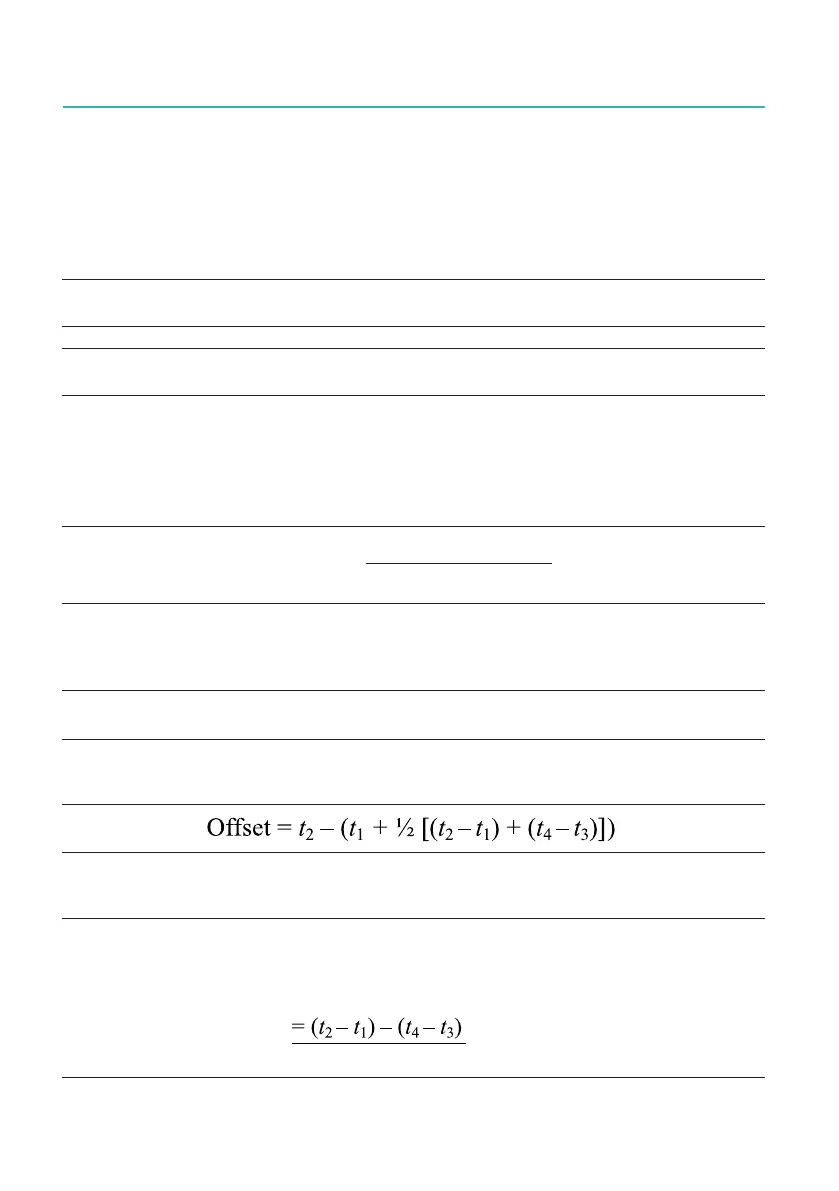
From Fig. 14.9, it can be seen that the slave clock offset (the time interval by which the
slave leads the master) is given by:
Offset = t
2
– (t
1
+ Delay)
Substituting from Fig. 14.9 above:
rearranging results in:
ò
W
±
W
±W
W
±W
W

 Loading...
Loading...