GEN7iB
279
GEN series SYNCHRONIZATION METHODS
GEN series SYNCHRONIZATION METHODS
14
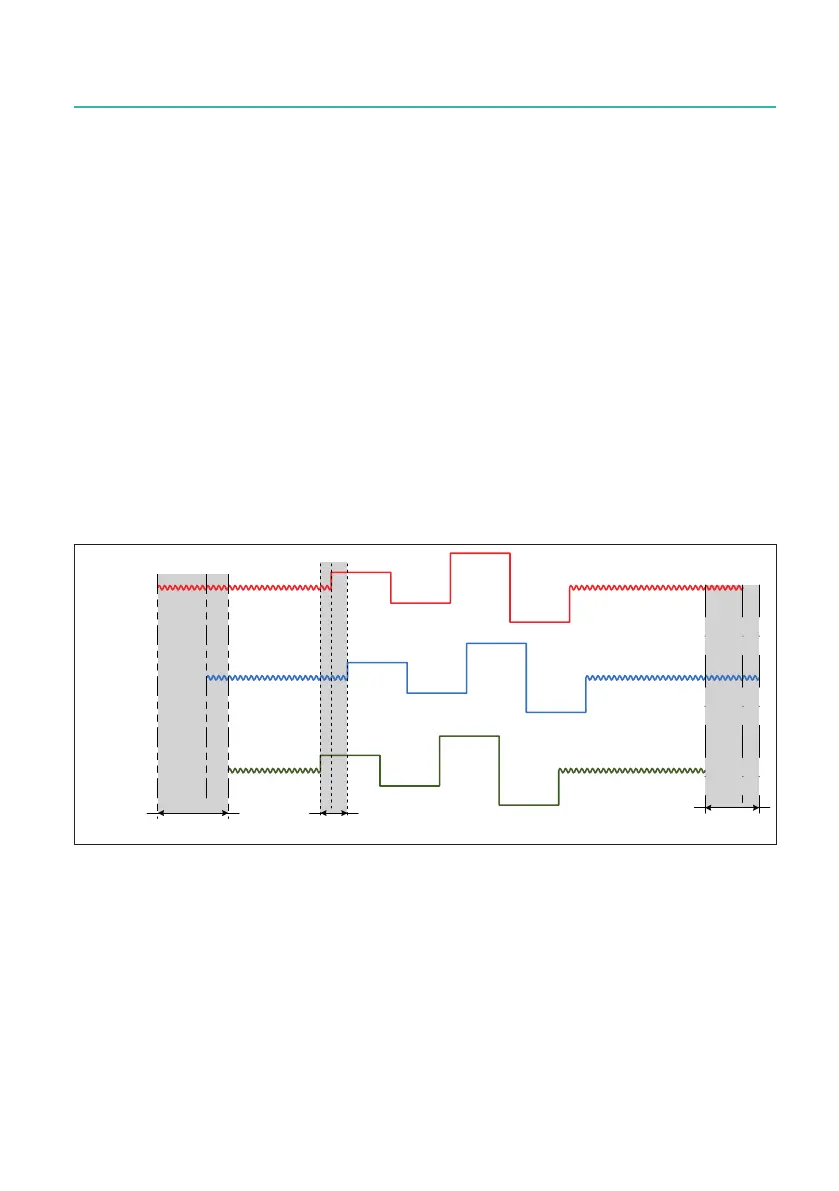
14.1.4 Start/Stop synchronization
When using multiple mainframes in continuous mode, expectations are typically that
therstsampleofeachchannelaligns.However,dependingonhowthestartandstop
actions are synchronized, this might not be the reality. The response time within GEN
seriessystemsisnotspecied,e.g.thetimefromwhentheStartbuttonhasbeen
pressedtowhenthemainframeactuallycapturestherstsample.Theresponsetime
varies and is dependent on a number of parameters, e.g. the number of acquisition
cards within the mainframe and the speed of the Windows
®
PC. Given this variation in
response, a system start should be executed in time to guarantee the recording of all
important data.
When in Single sweep, Multiple sweep or Slow-Fast Sweep mode, the start and stop
synchronization of the recording is irrelevant. The entire recorded sweep data is
determinedbythetriggeroriginwithaxedpre-andpost-triggertimeframe.Insweep-
basedrecordings,theacquisitionsystemistypicallystartedrst.Checksonallsystem
partsarethenperformedandthersttriggerisinsertedonlywhenallsystemsare
ready.
0DLQIUDPH
0DLQIUDPH
0DLQIUDPH1
W
VWDUW
W
SKDVH
W
VWRS
Fig. 14.5 Measuring start/stop synchronization accuracy

 Loading...
Loading...