Operation Manual - Network Protocol
Quidway S3000-EI Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3
DHCP Client Configuration
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
3-1
Chapter 3 DHCP Client Configuration
3.1 Overview of DHCP Client
With expansion of network size and complication of network structure, network
configuration becomes more and more complex. It is often the case that computers
change physical positions frequently (portable computers and wireless networks for
example) and that computers exceed the IP addresses available. Dynamic host
configuration protocol (DHCP) has been developed right for this situation. DHCP is in
client/server structure, with DHCP client dynamic requesting configuration information,
while DHCP server returning configuration information base on the specific policies.
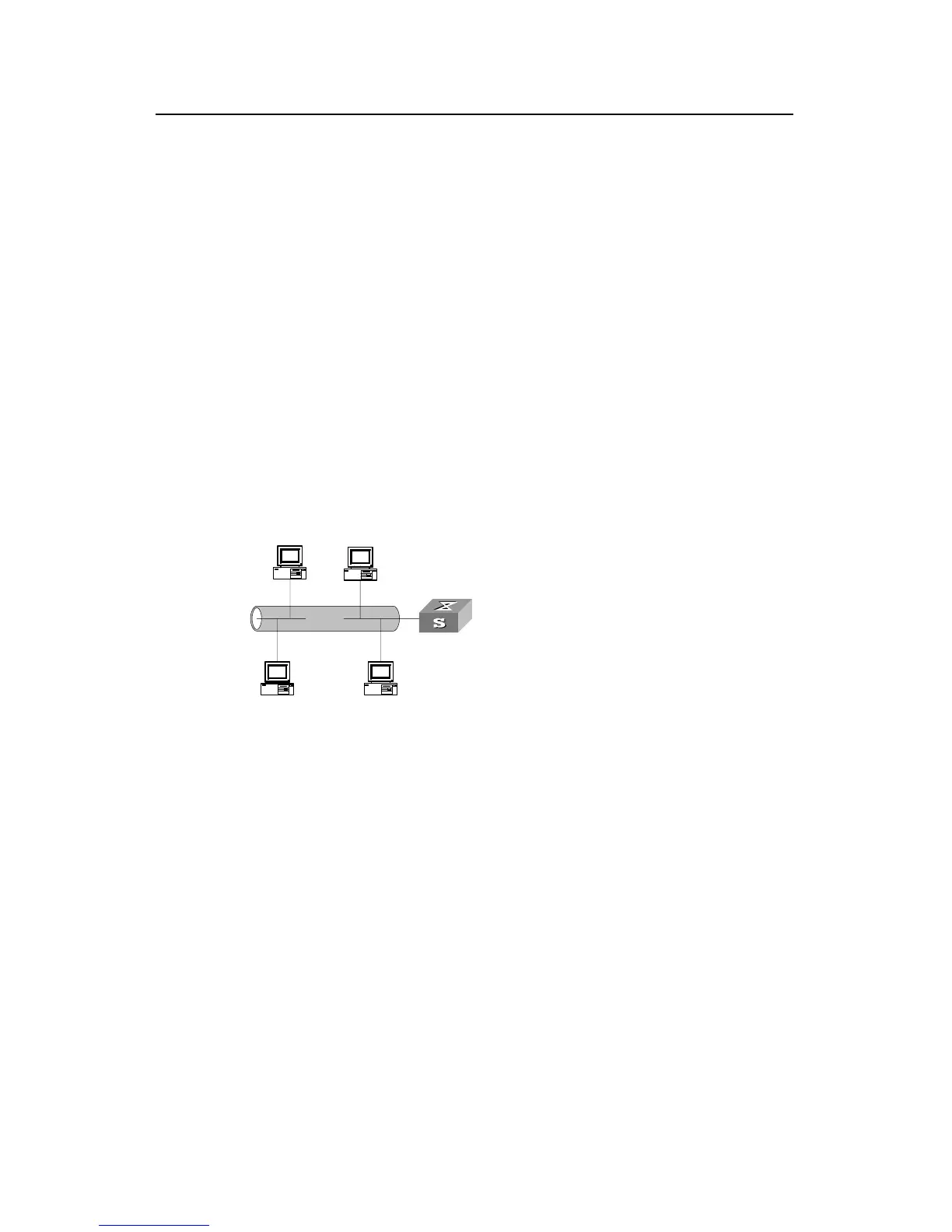
A typical DHCP application often contains a DHCP server and several clients (desktop
and laptop PCs). See the following figure.
LAN
DHCP Server
DHCP Client DHCP Client
DHCP Client DHCP Client
Figure 3-1 Typical DHCP application
To obtain valid dynamic IP addresses, DHCP client exchanges different types of
CP client logs into the network for the first time
e e, its communication with the
HCP client looks for the DHCP server. The
z e, the stage when the DHCP server allocates the IP address. After
the DHCP_Offer message containing the leased IP address and other settings.
information with the server at different stages. One of the following three situations may
occur:
1) DH
Wh n DHCP client logs into the network for the first tim
DHCP server includes these four stages:
z Discover stage, the stage when the D
client broadcasts the DHCP_Discover message and only the DHCP server can
respond.
Offer stag
receiving the DHCP_Discover message from the client, the DHCP server chooses
an IP address still available in IP address pool for the client, and sends to the client

 Loading...
Loading...








