Section 2 NS Series Functions 2-8 Common Functional Object Functions
2-73
NS Series Programming Manual
Storage Type Details
REAL (real number) Stores as 4-byte real number at the write destination address.
(Can be set in decimal between approximately ±1.175494351 × 10
-38
and approxi-
mately ±3.402823466 × 10
+38
(7 digits enabled)).
Four-byte real numbers that conform to IEEE754.
Displayed as real number = (−1)
signed
× 1.[mantissa] × 2
index-127
.
The data format is described below.
Bits 0 to 22 (23 bits) are the mantissa, bits 23 to 30 (8 bits) are the exponent, and bit
31 indicates the sign (0: positive; 1:negative).
↑
Sign
Ex
b23 b22
The set address and the address + 1 are used (2 words) and displayed as one nu-
meral.
Real numbers are divided into 5 types: Normalized numbers, non-normalized num-
bers, zero, infinity, and non-numbers.
Normalized Numbers
If the exponent is 00000001 to 11111111,
and the mantissa is 00000000000000000000000 to 11111111111111111111111,
this is called a normalized number.
Example 1: 0100 0001 0100 1000 0000 0000 0000 0000
If the sign, exponent, and mantissa are separated, the number will appear as shown
below.
b31 b30 b23 b22 b0
01000001010010000000000000000000
2
7
2
6
2
5
2
4
2
3
2
2
2
1
2
0
2
-1
2
-2
2
-3
2
-4
2
-5
2
-6
2
-7
2
-8
2
-9
2
-10
2
-11
2
-12
2
-13
2
-14
2
-15
2
-16
2
-17
2
-18
2
-19
2
-20
2
-21
2
-22
2
-23
Sign: +
Exponent: 2
7
+ 2
1
=128 + 2 = 130
Mantissa: 2
-1
+2
-4
=0.5+0.0625=0.5625
Real number = (1+0.5625) ×2
(130-127)
=1.5625×8=12.5
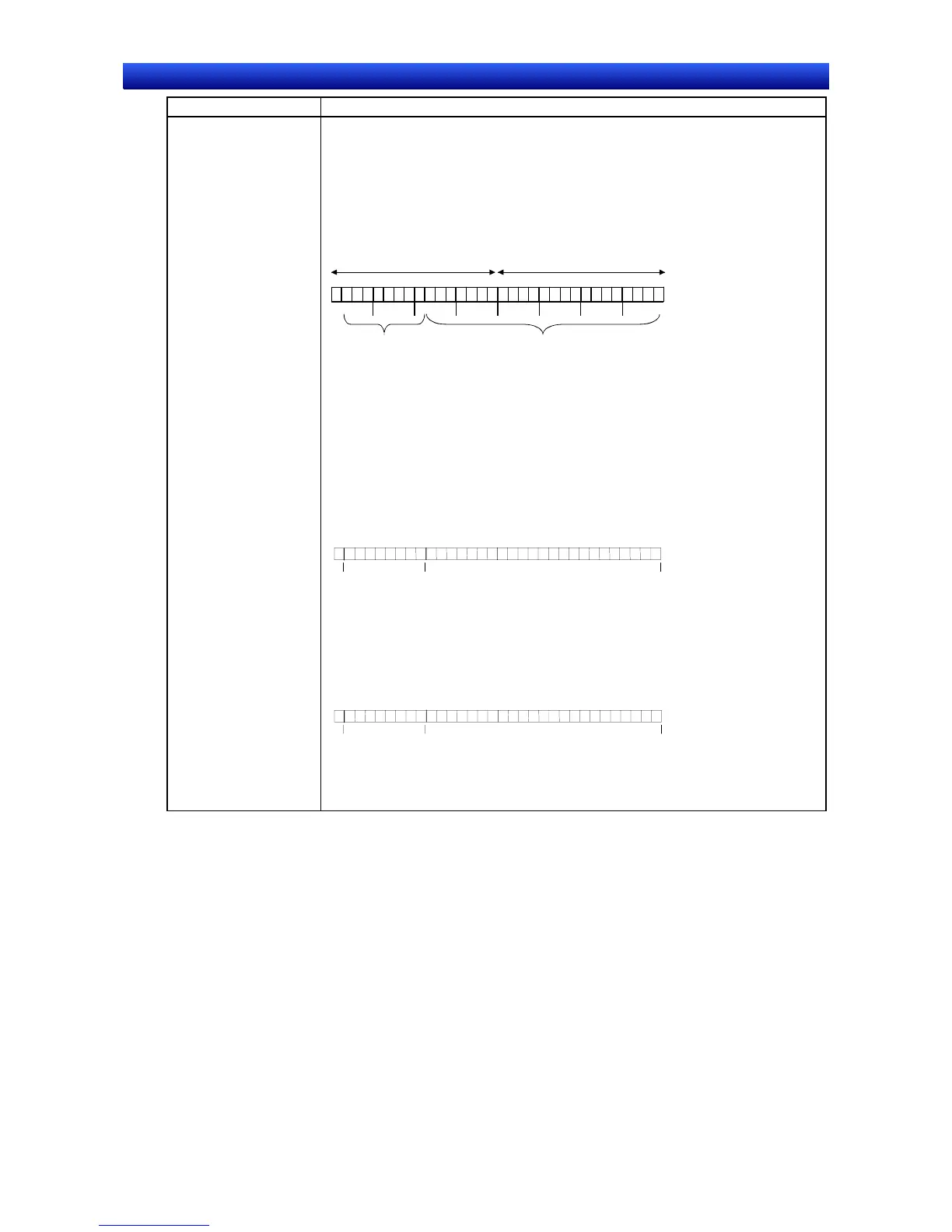
Example 2: 1100 0000 1110 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
If the sign, exponent, and mantissa are separated, the number will appear as shown
below.
b31 b30 b23 b22 b

 Loading...
Loading...