Alteon Application Switch Operating System Application Guide
Border Gateway Protocol
126 Document ID: RDWR-ALOS-V2900_AG1302
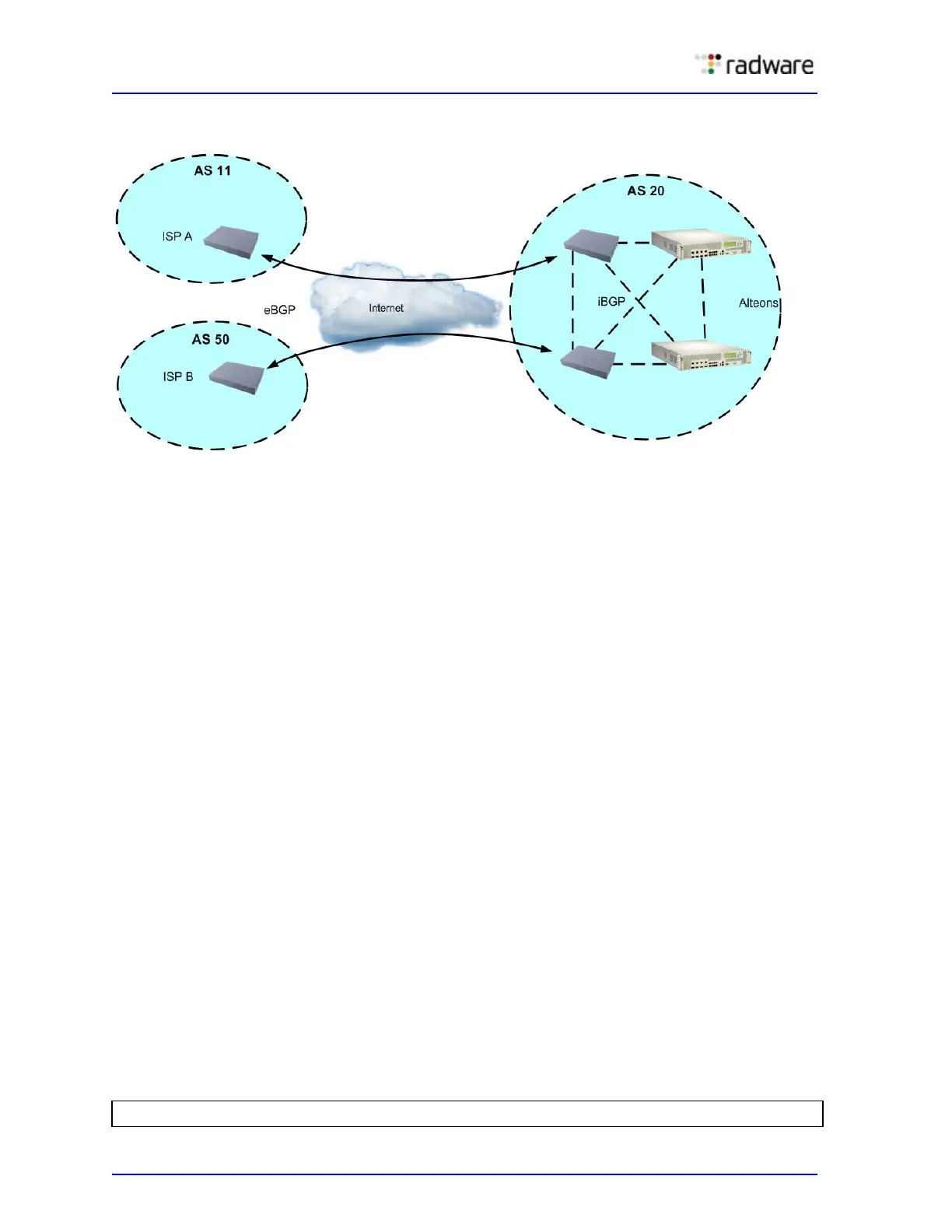
Figure 13: Example Topology using the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Typically, an AS has one or more border routers (that is, peer routers that exchange routes with
other ASs) and an internal routing scheme that enables routers in that AS to reach every other
router and destination within that AS. When Alteon advertises routes to border routers on other
autonomous systems, it is effectively committing to carry data to the IP space represented in the
route being advertised. For example, if Alteon advertises 192.204.4.0/24, it is declaring that if
another router sends it data destined for any address in 192.204.4.0/24, Alteon knows how to carry
that data to its destination.
Forming BGP Peer Routers
Two BGP routers become peers, or neighbors, once you establish a TCP connection between them.
For each new route, if a peer is configured to connect to that route (for example, if a peer is
configured to receive static routes and the new route is static), an update message is sent to that
peer containing the new route. For each route removed from the routing table, if the route has
already been sent to a peer, an update message containing the route to withdraw is sent to that
peer.
For each Internet host, your system must send a packet to that host, and that host must have a
path back to your system. Whatever system provides Internet connectivity to that host must have a
path to your system. Ultimately, the system providing the Internet connectivity must "hear a route"
which covers the section of the IP space your system is using. Otherwise, your system will not have
connectivity to the host in question.
Route Maps
A route map is used to control and modify routing information. Route maps define conditions for
redistributing routes from one routing protocol to another, or controlling routing information when
injecting it in and out of BGP. Route maps are used by OSPF only for redistributing routes. For
example, a route map is used to set a preference value for a specific route from a peer router and
another preference value for all other routes learned via the same peer router. The following
command is used to define a route map:
>> # /cfg/l3/rmap 1
(Select a route map)
 Loading...
Loading...