Alteon Application Switch Operating System Application Guide
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
138 Document ID: RDWR-ALOS-V2900_AG1302
• The Shortest Path First Tree, page 140
• Internal versus External Routing, page 140
Equal Cost Multipath Routing Support
Alteon supports equal-cost multipath (ECMP), which is a routing technique for routing packets along
multiple paths of equal cost. The routing table contains multiple next hops for any given destination.
The router load balances packets along the multiple next hops.
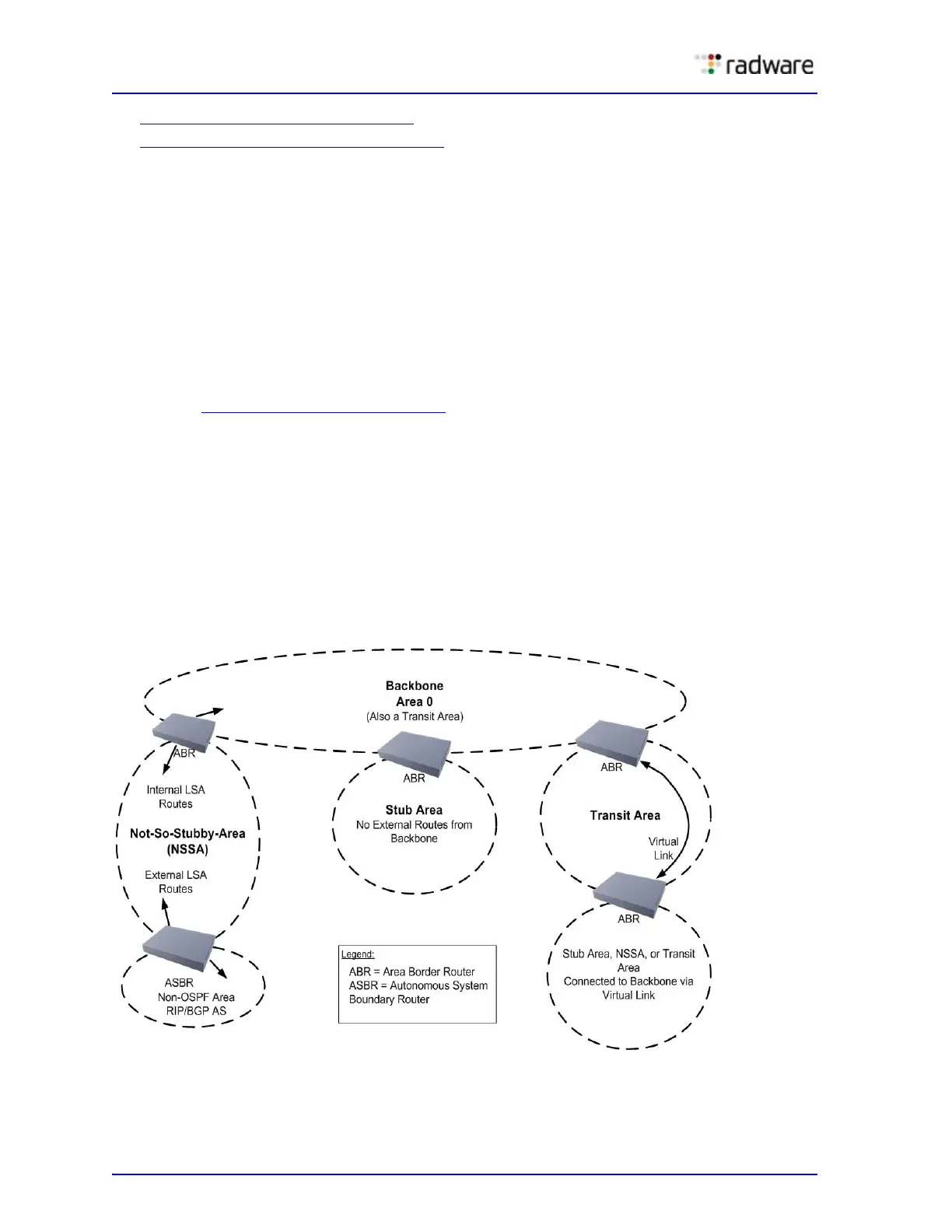
Types of OSPF Areas
An AS can be broken into logical units known as areas. In any AS with multiple areas, one area must
be designated as area 0, known as the backbone. The backbone acts as the central OSPF area. All
other areas in the AS must be connected to the backbone. Areas inject summary routing information
into the backbone, which then distributes it to other areas as needed.
As shown in Figure 17 - OSPF Areas, page 138
, OSPF defines the following types of areas:
• Stub Area—An area that is connected to only one other area. External route information is not
distributed into stub areas.
• Not-So-Stubby-Area (NSSA)—An area similar to a stub area with additional capabilities.
Routes originating from within the NSSA can be propagated to adjacent transit and backbone
areas. External routes from outside the AS can be advertised within the NSSA but are not
distributed into other areas.
• Transit Area—An area that allows area summary information to be exchanged between routing
devices. The backbone (area 0), any area that contains a virtual link to connect two areas, and
any area that is not a stub area or an NSSA, are considered transit areas.
Figure 17: OSPF Areas
 Loading...
Loading...