Alteon Application Switch Operating System Application Guide
Firewall Load Balancing
686 Document ID: RDWR-ALOS-V2900_AG1302
To view the original redirection filters that were configured for the four-subnet example, see step
3. Do this on both clean-side Alteons:
3. On the dirty-side Alteons, set the FWLB metric, on both dirty-side Alteons:
Any of the following load-balancing metrics can be used: hash, leastconns, roundrobin, minmiss,
response, or bandwidth. See Metrics for Real Server Groups, page 180
for details on using each
metric.
Note: Some metrics allow other options (such as weights) to be configured.
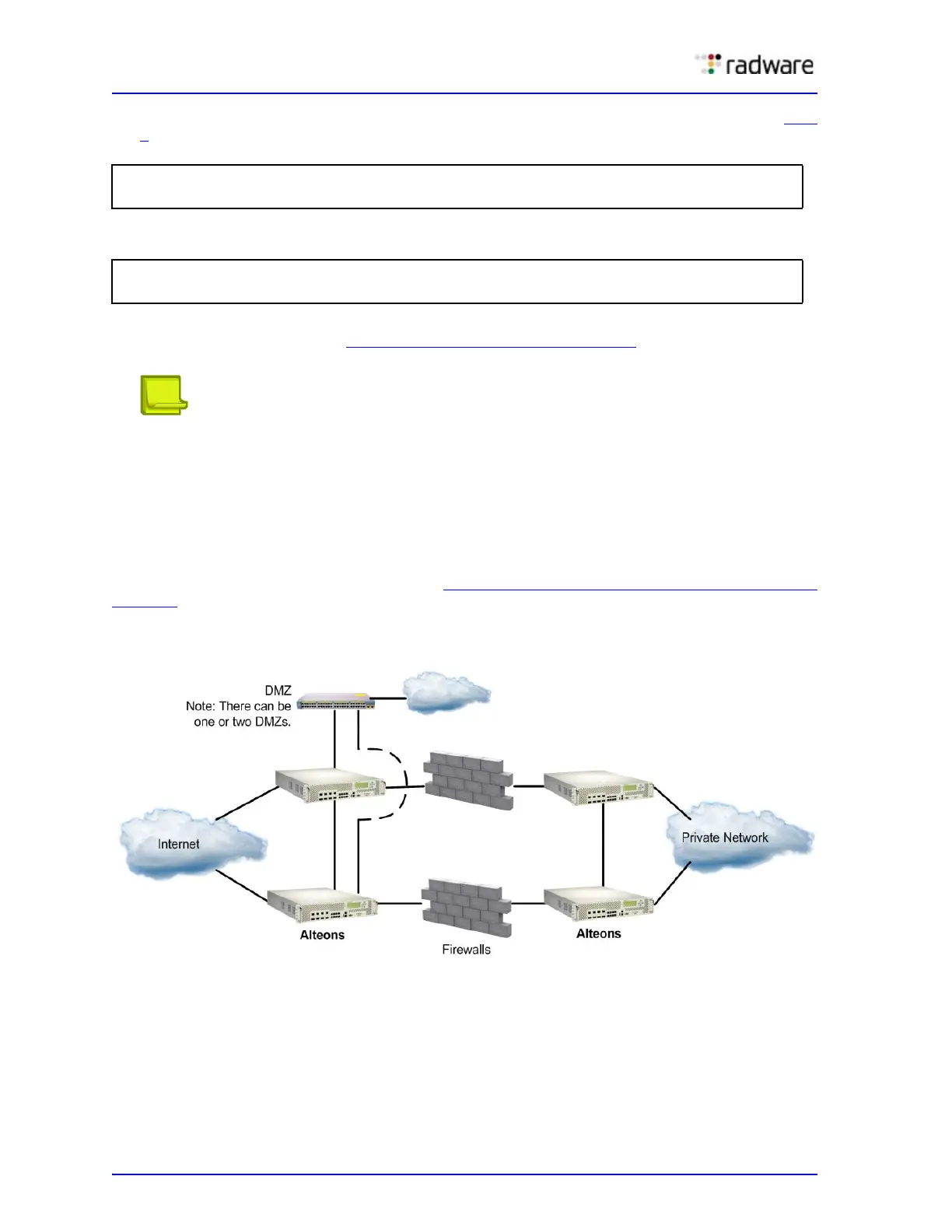
Adding a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
Implementing a DMZ in conjunction with FWLB enables Alteon to perform traffic filtering, off-loading
this task from the firewall. A DMZ is created by configuring FWLB with another real server group and
a redirection filter towards the DMZ subnets.
The DMZ servers can be connected to Alteon on the dirty side of the firewall. A typical firewall load-
balancing configuration with a DMZ is shown in Figure 115 - FWLB with a Demilitarized Done (DMZ),
page 686:
Figure 115: FWLB with a Demilitarized Done (DMZ)
The DMZ servers can be attached to Alteon directly or through an intermediate hub or Alteon. Alteon
is then configured with filters to permit or deny access to the DMZ servers. In this way, two levels of
security are implemented: one that restricts access to the DMZ through the Alteon filters and
another that restricts access to the clean network through the stateful inspection performed by the
firewalls.
>> # /cfg/slb/port 26/rts enable
>> # filt ena
>> # /cfg/slb/group 1
>> # metric <metric type>
 Loading...
Loading...