Appendix – Looking ‘Under the Hood’
Gettings Started with the MSP430 - Using Energia (Arduino) 8 - 33
Follow the trail. Open wiring.c to find how init() is implemented.
C:\TI\energia-0101E0010\hardware\msp430\cores\msp430\wiring.c
The init() function implements the essential code required to get the MSP430 up and running.
If you have already completed Chapter 4 – Clocking and Initialization, then you should
recognize most of these activities. At reset, you need to perform two essential activies:
Initialize the clocks (choose which clock source you want use)
Turn off the Watchdog timer (unless you want to use it, as a watchdog)
The Energia init() function takes this three steps further. They also:
Setup the Watchdog timer as a standard (i.e. interval) timer
Setup two GPIO pins
Enable interrupts globally
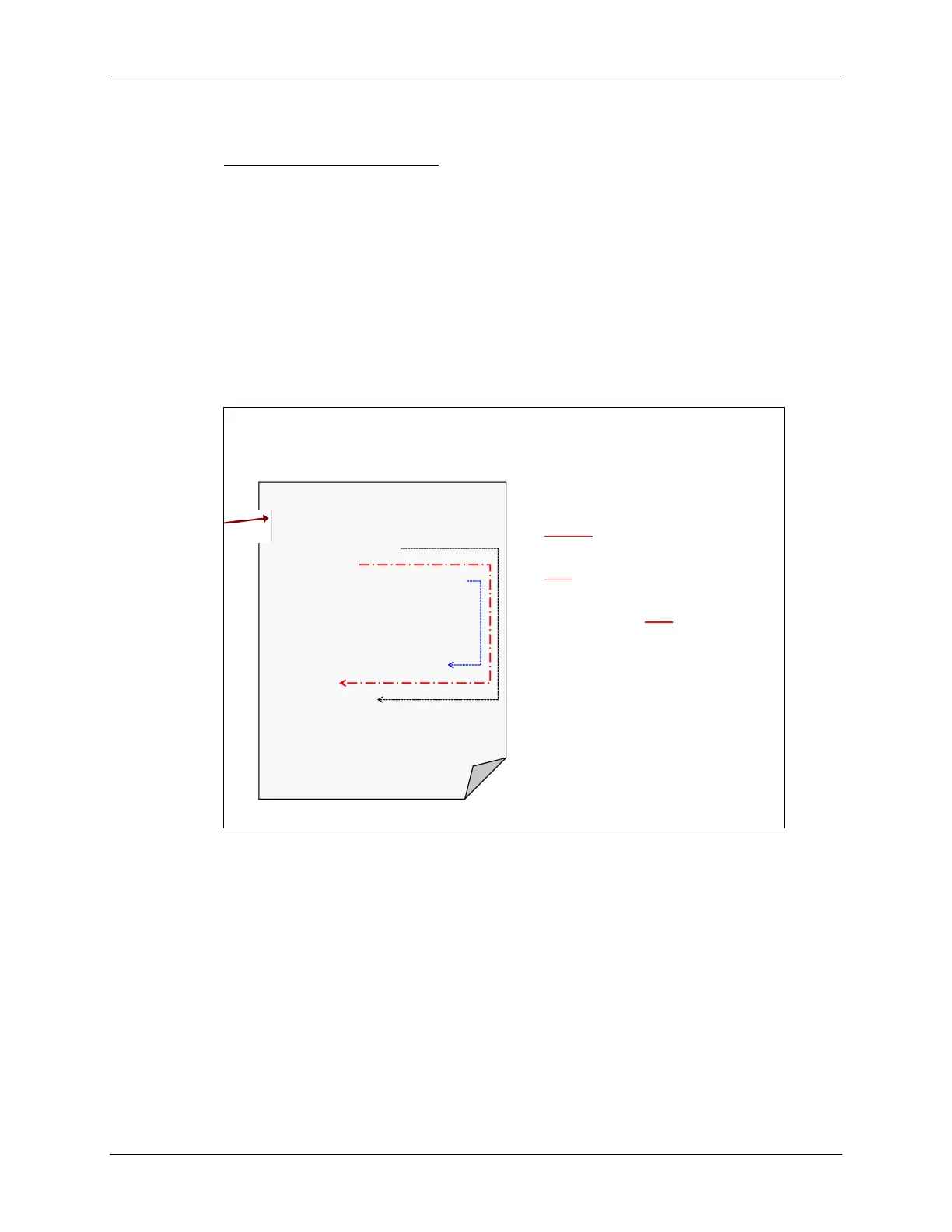
init() in wiring.c
C:\TI\energia-0101E0010\hardware\msp430\cores\msp430\
// wiring.c
void init()
{
disableWatchDog();
initClocks();
enableWatchDogIntervalMode();
// Default to GPIO (P2.6, P2.7)
P2SEL &= ~(BIT6|BIT7);
__eint();
}
enableWatchDogIntervalMode()
initClocks()
disableWatchDog()
enableWatchDog()
delayMicroseconds()
delay()
watchdog_isr ()
wiring.c provides the core files for
device specific architectures
init() is where the default
initializations are handled
As discussed in Ch 3 (Init & GPIO)
Watchdog timer (WDT+) is
disabled
Clocks are initialized (DCO 16MHz)
WDT+ set as interval timer
 Loading...
Loading...











