896 Appendix A: Functions and Instructions
ans(1)[2] ¸
r
2
ë 3ør
2
You can also (or instead) include unknowns that
do not appear in the expressions. For example,
you can include z as an unknown to extend the
previous example to two parallel intersecting
cylinders of radius r. The cylinder zeros illustrate
how families of zeros might contain arbitrary
constants in the form
ck
, where
k
is an integer
suffix from 1 through 255. The suffix resets to 1
when you use
ClrHome or ƒ 8:Clear Home.
zeros({x^2+y^2ì r^2,
(x
ì r)^2+y^2ì r^2},{x,y,z}) ¸
r
2
3ør
2
@1
r
2
ë 3ør
2
@1
For polynomial systems, computation time or
memory exhaustion may depend strongly on the
order in which you list unknowns. If your initial
choice exhausts memory or your patience, try
rearranging the variables in the expressions
and/or
varOrGuess
list.
If you do not include any guesses and if any
expression is non-polynomial in any variable but
all expressions are linear in the unknowns,
zeros() uses Gaussian elimination to attempt to
determine all real zeros.
zeros({x+
e
^(z)ù yì 1,xì yì sin(z)},{x,y
})
¸
e
z
øsin(z)+1
e
z
+1
ë (sin(z)ì 1)
e
z
+1
If a system is neither polynomial in all of its
variables nor linear in its unknowns,
zeros()
determines at most one zero using an
approximate iterative method. To do so, the
number of unknowns must equal the number of
expressions, and all other variables in the
expressions must simplify to numbers.
Each unknown starts at its guessed value if there
is one; otherwise, it starts at 0.0.
zeros({
e
^(z)ùyì1,ëyìsin(z)},
{y,z})
¸
[]
.041… 3.183…
Use guesses to seek additional zeros one by one.
For convergence, a guess may have to be rather
close to a zero.
zeros({
e
^(z)ù yì 1,ë yì sin(z)},
{y,z=2
p}) ¸
[]
.001… 6.281…
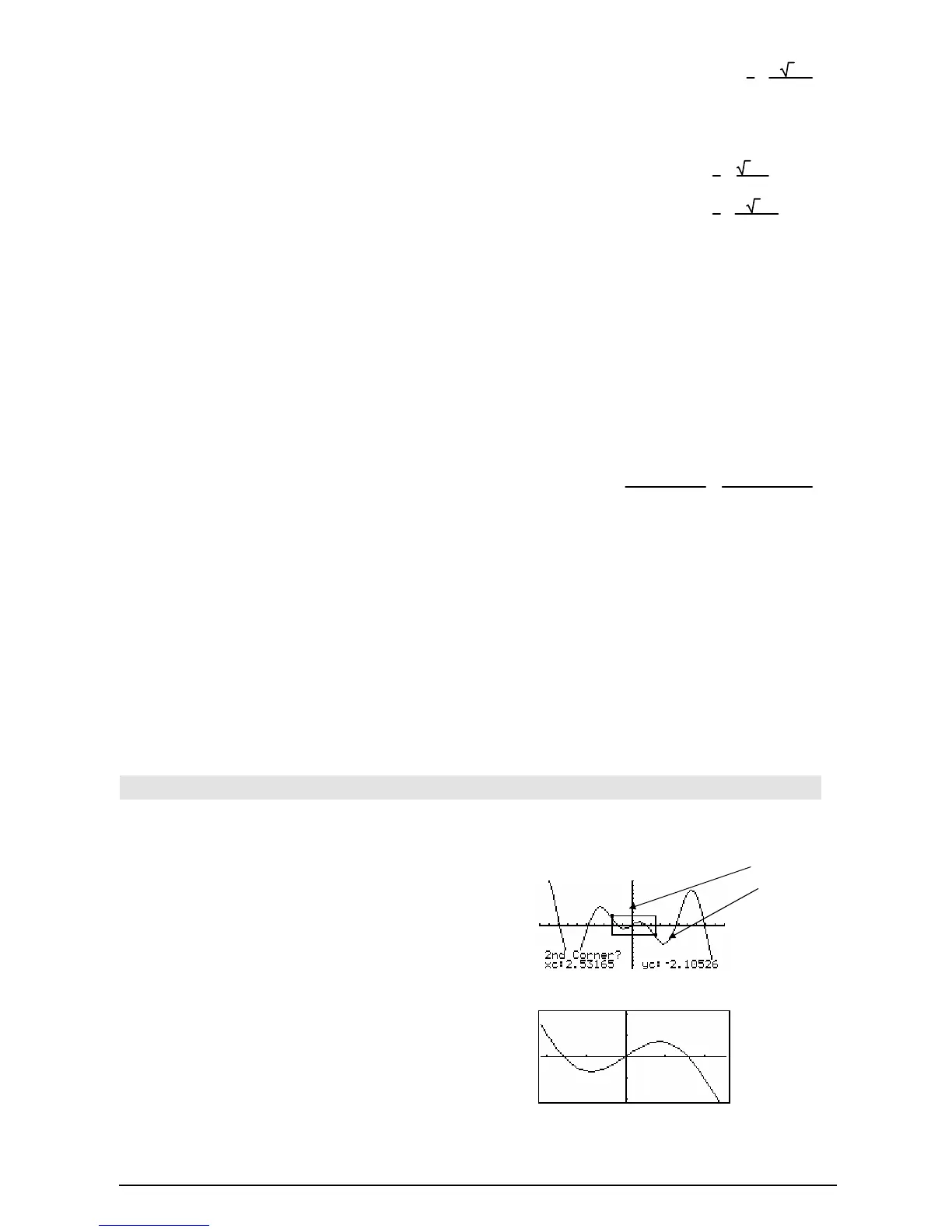
ZoomBox CATALOG
ZoomBox
Displays the Graph screen, lets you draw a box
that defines a new viewing window, and updates
the window.
In function graphing mode:
1.25xù cos(x)! y1(x) ¸ Done
ZoomStd:ZoomBox
¸
The display after defining ZoomBox by pressing
¸ the second time.
1st corner
2nd corner
 Loading...
Loading...











