Flow-Aware Transport Pseudowires (FAT PW) provide the capability to identify individual flows within a
pseudowire and provide routers the ability to use these flows to loadbalance traffic. FAT PWs are used to
loadbalance traffic in the core when equal cost multipaths (ECMP) are used. A flow label is created based on
indivisible packet flows entering a pseudowire; and is inserted as the lower most label in the packet. Routers
can use the flow label for loadbalancing which provides a better traffic distribution across ECMP paths or
link-bundled paths in the core.
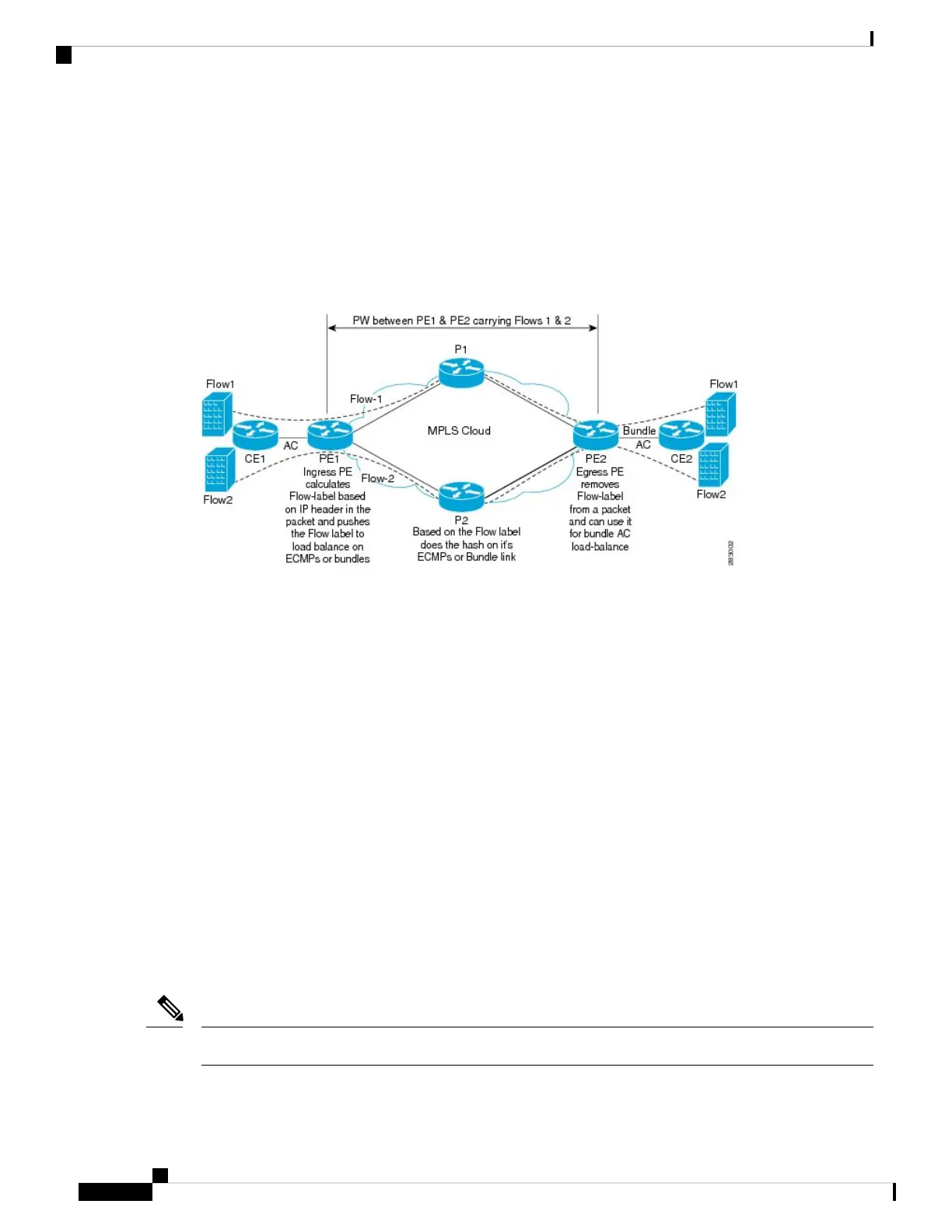
The following figure shows a FAT PW with two flows distributing over ECMPs and bundle links.
Figure 28: FAT PW with two flows distributing over ECMPs and Bundle-Links
An additional label is added to the stack, called the flow label, which contains the flow information of a virtual
circuit (VC). A flow label is a unique identifier that distinguishes a flow within the PW, and is derived from
source and destination MAC addresses, and source and destination IP addresses. The flow label contains the
end of label stack (EOS) bit set and inserted after the VC label and before the control word (if any). The
ingress PE calculates and forwards the flow label. The FAT PW configuration enables the flow label. The
egress PE discards the flow label such that no decisions are made.
All core routers perform load balancing based on the flow-label in the FAT PW. Therefore, it is possible to
distribute flows over ECMPs and link bundles.
Pseudowire Headend
Pseudowires (PWs) enable payloads to be transparently carried across IP/MPLS packet-switched networks
(PSNs). PWs are regarded as simple and manageable lightweight tunnels for returning customer traffic into
core networks. Service providers are now extending PW connectivity into the access and aggregation regions
of their networks.
Pseudowire Headend (PWHE) is a technology that allows termination of access pseudowires (PWs) into a
Layer 3 (VRF or global) domain or into a Layer 2 domain. PWs provide an easy and scalable mechanism for
tunneling customer traffic into a common IP/MPLS network infrastructure. PWHE allows customers to
provision features such as QOS access lists (ACL), L3VPN on a per PWHE interface basis, on a service
Provider Edge (PE) router.
Encapsulation default is not supported by PWHE.
Note
L2VPN and Ethernet Services Configuration Guide for Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.3.x
222
Implementing Multipoint Layer 2 Services
Pseudowire Headend

 Loading...
Loading...











