• VPLS pseudowire reduction and mesh scalability—The number of pseudowires in an IP/MPLS core can
be significantly reduced. This is because a single VPLS service can now transport several customer
service instances thereby allowing a fewer number of pseudowires in the IP/MPLS core to transport a
large number of customer services.
• Layer 2 backbone traffic engineering—Enables explicit controls for Layer 2 traffic engineering by
separating service discrimination function and moving it to the I-tags thereby leaving the backbone
VLAN to be available for Layer 2 traffic engineering functions.
• Point-to-point service scalability and optimization-enables point-to-point service implementation that
includes multiple options for service multiplexing as well as end point discovery.
• Backbone flood traffic reduction—Since there are fewer MAC addresses in the core of the network, the
amount of flood traffic in the core network is reduced as there are fewer MAC addresses to be relearnt
when MAC tables get flushed due to topology changes.
IEEE 802.1ah Standard for Provider Backbone Bridging Overview
The IEEE 802.1ah Provider Backbone Bridge feature encapsulates or decapsulates end-user traffic on a
Backbone Edge Bridge (BEB) at the edge of the Provider Backbone Bridged Network (PBBN). A Backbone
Core Bridge (BCB) based network provides internal transport of the IEEE 802.1ah encapsulated frames within
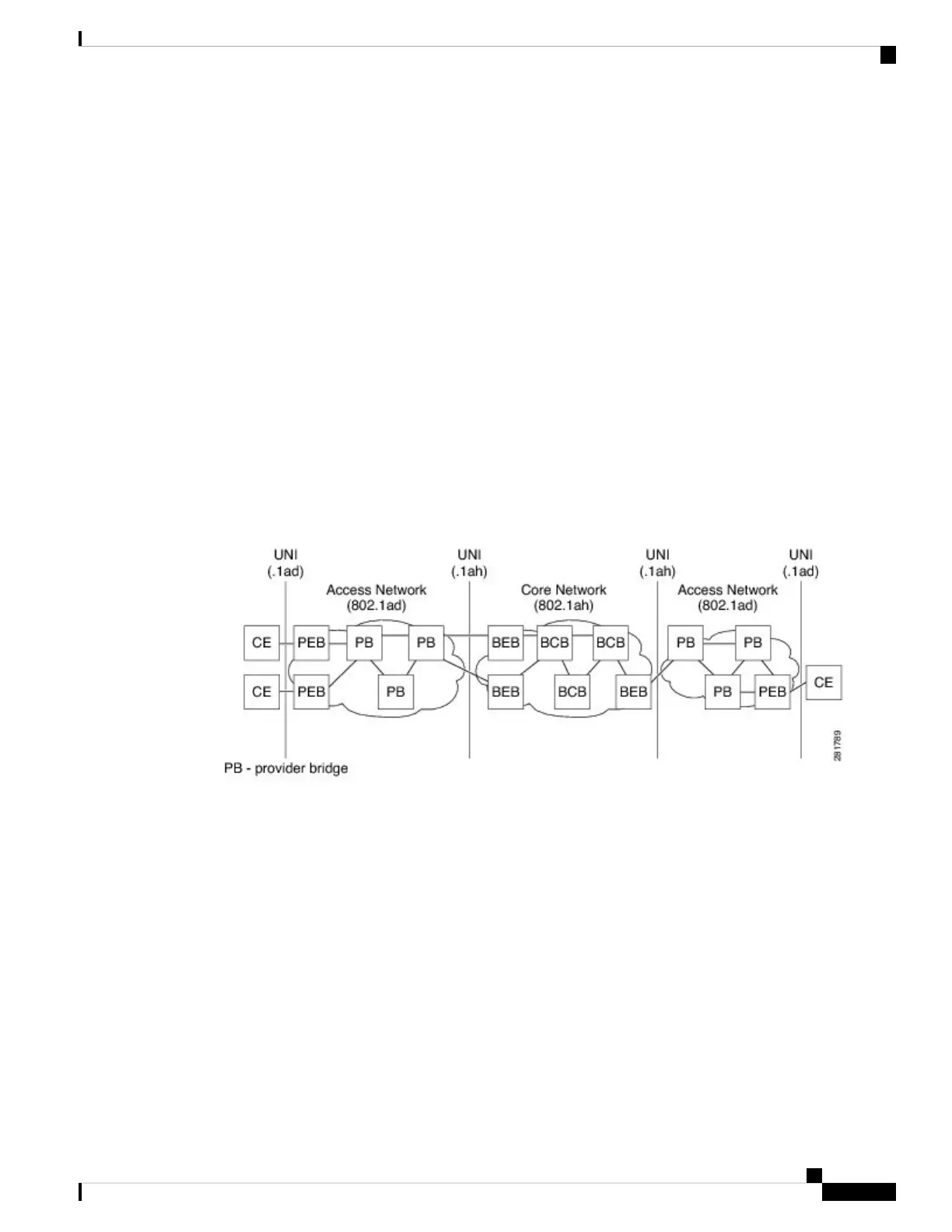
the PBBN. The following figure shows a typical 802.1ah PBB network.
Figure 40: IEEE 802.1ah Provider Backbone Bridge
The following figure shows a typical provider backbone network topology.
L2VPN and Ethernet Services Configuration Guide for Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.3.x
357
Implementing IEEE 802.1ah Provider Backbone Bridge
IEEE 802.1ah Standard for Provider Backbone Bridging Overview

 Loading...
Loading...











