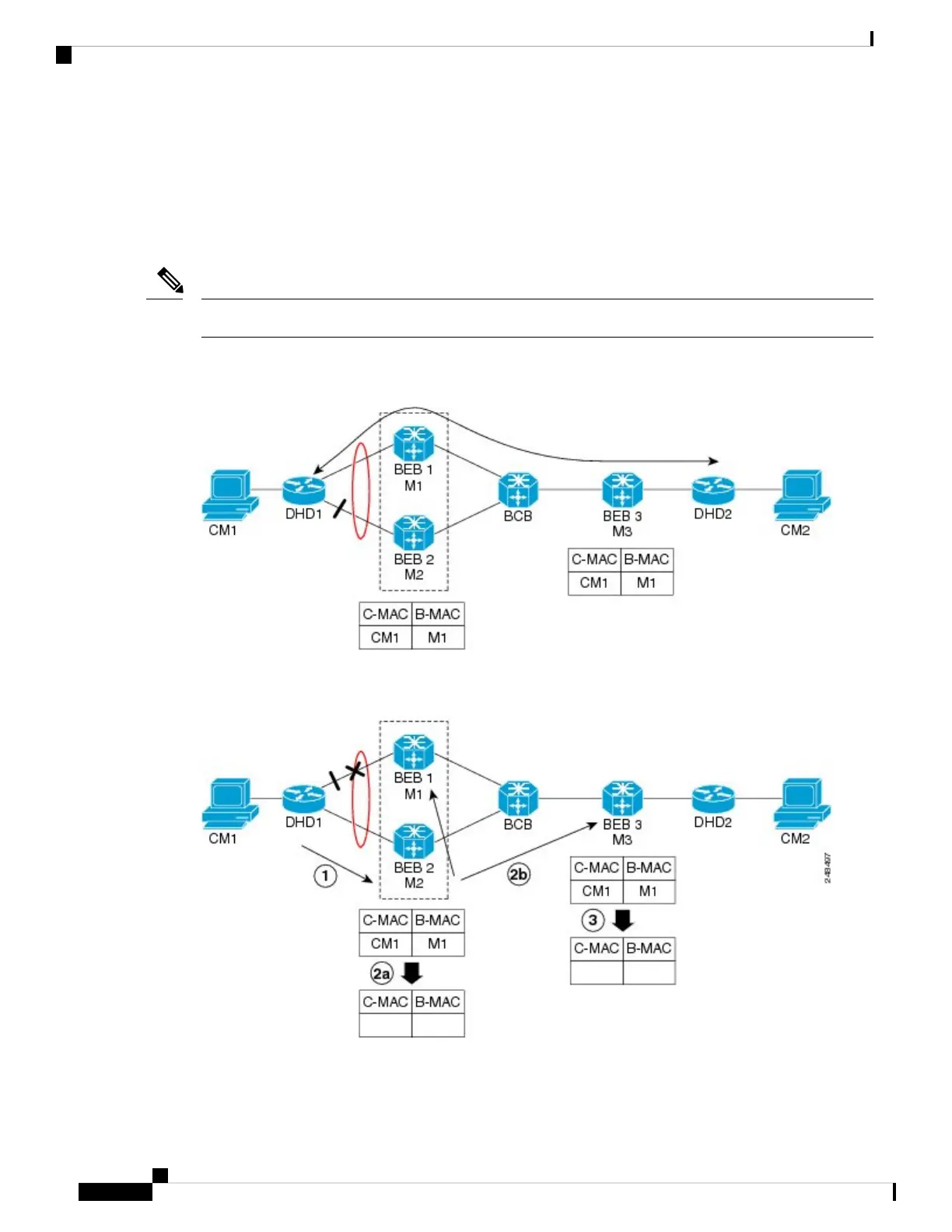
To circumvent the dropping of traffic when the link between DHD1 and BEB1 fails, BEB2 performs two
tasks:
• Flushes it’s own MAC address table for the service or services.
• Requests the remote PE that receives the MIRP packet to clear it’s own MAC table. The MIRP message
is transparent to the backbone core bridges (BCBs). The MIRP message is processed on a BEB because
only BCBs learn and forward, based on B-MAC addresses and they are transparent to C-MAC addresses.
MIRP triggers C-MAC address flushing for both native 802.1ah and PBB over VPLS.
Note
The following figure shows the operation of the MIRP.
Figure 44: MIRP Operation
L2VPN and Ethernet Services Configuration Guide for Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers, IOS XR Release 6.3.x
362
Implementing IEEE 802.1ah Provider Backbone Bridge
Multiple I-SID Registration Protocol Lite

 Loading...
Loading...











