5 Applied Instructions and Basic Usage
DVP-20PM Application Manual
5-120
API
Applicable model
20PM
137
D
D
COSH
P
P
Hyperbolic cosine of a binary
floating-point value
Bit device Word device
X Y M S F H KnX KnY KnM KnS T C D V Z
S
*
*
D
*
Note: Please refer to specifications for more information about device
ranges.
Onlyt the 32-bit instructions DCOSH and DCOSHP are valid.
F represents a floating-point value. There is a decimal point in a
floating-point value.
16-bit instruction
- - - -
32-bit instruction (6 steps)
DCOSH
Continuity
instruction
DCOSHP
Pulse
instruction
Flags
Ox O100
M1808 M1968 Zero flag
M1809 M1969 Borrow flag
M1810 M1970 Carry flag
Please refer to the additional remark below.
Explanation
Hyperbolic cosine value=(e
s
+e
-s
)/2
S: Source value (binary floating-point value); D: Hyperbolic cosine value
Example
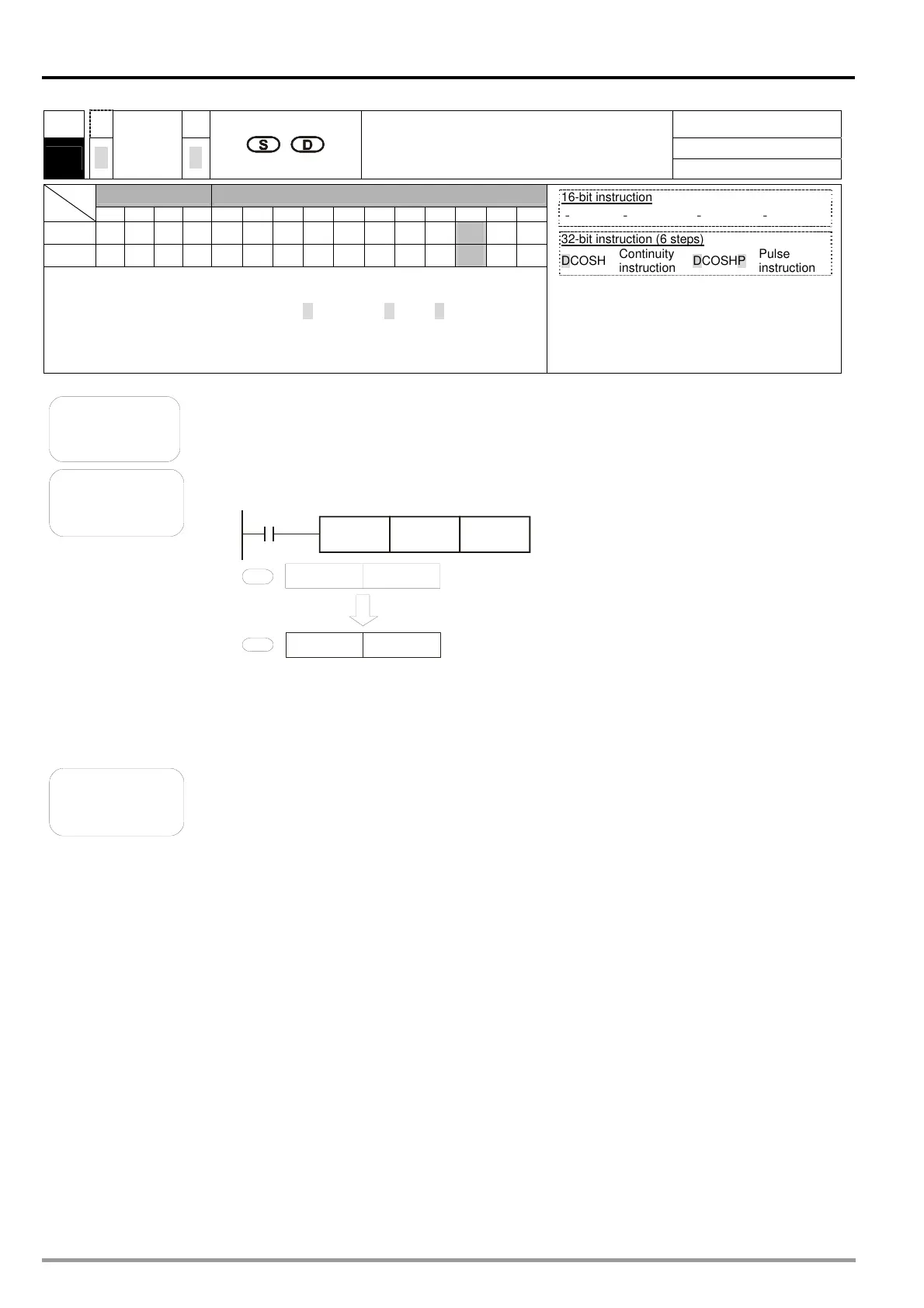
When X0 is ON, the hyperbolic cosine of the binary floating-point number in
(D1, D0) is stored in (D11, D10).
X0
DCOSH D0 D10
Binary floating-point value
Binary floating-point value
D 1 D 0
S
D
D 11 D 10
Hyperbolic cosine value
If the absolute value of a conversion result is greater than the maximum
floating-point value available, a carry flag will be ON.
If the absolute value of a conversion result is less than the minimum
floating-point value available, a borrow flag will be ON.
If a conversion result is 0, a zero flag will be ON.
Additional
rema
rk
Please refer to section 5.3 for more information about performing operations on
floating-point values.

 Loading...
Loading...