Function Reference
Analog Stereo/Dual Sound
5
5-39
Analog Stereo/Dual Sound
General
The
Analog Stereo Sound or Dual Sound
is a
two-carrier system
which is used in
various countries with different sound carrier frequencies. The first sound carrier trans-
mits the mono sound, respectively channel 1 information. The second sound channel is
transmitted using an additional sound carrier.
Depending on different TV systems the two sound carriers are modulated by the follow-
ing audio signals:
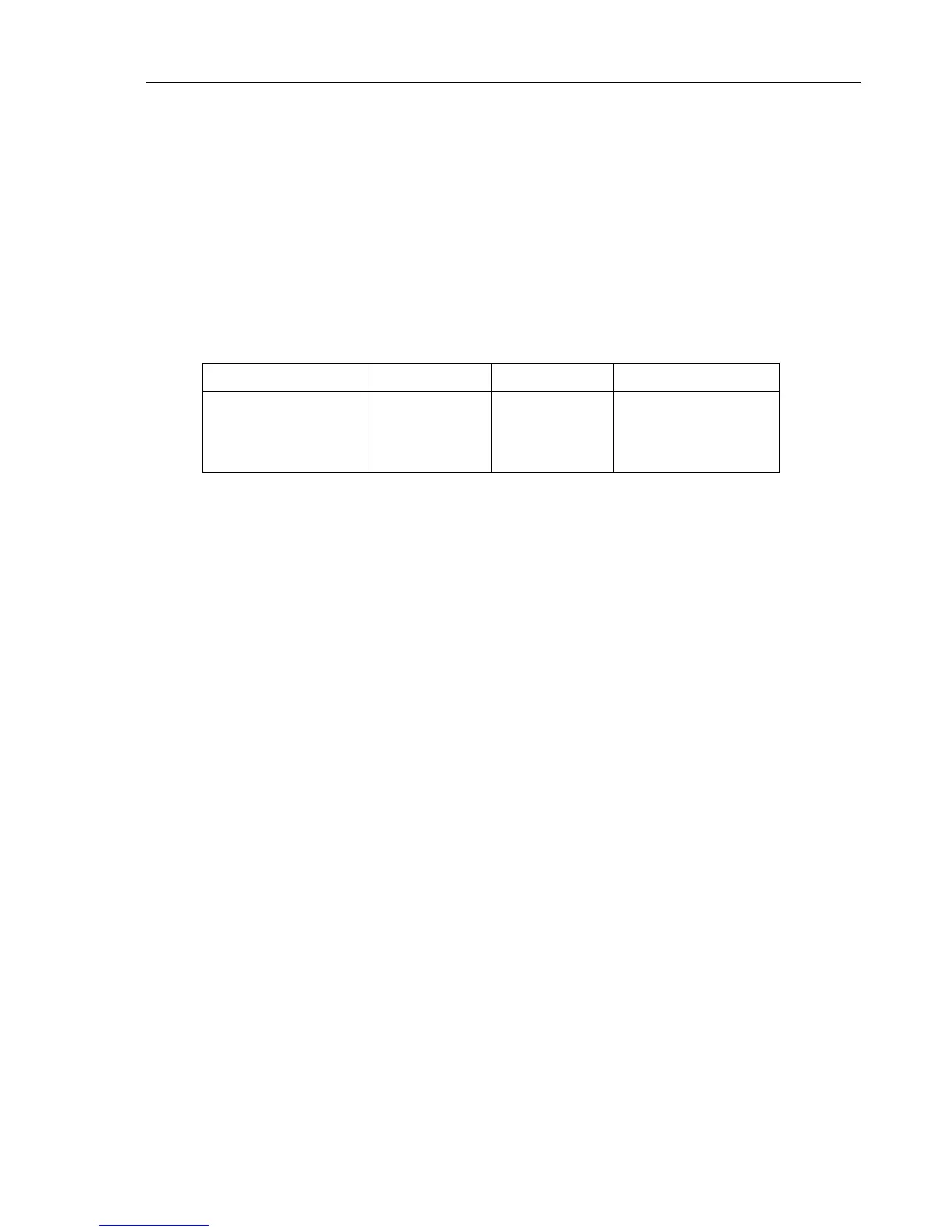
Table 5-11. Analog Stereo/Dual Audio Signals, Systems B/G and D/K
TV Systems Sound Modes Channel 1 (S1) Channel 2 (S2)
PAL B/G
and
PAL/SECAM D/K (FM A2)
Mono
Stereo
Dual
Mono
(L + R)/2 = M
Mono
Mono
R (right)
Mono (2nd language)
Germany, Switzerland, and the Netherlands have used the analog Stereo/Dual sound in
the PAL B/G system for many years. According to the transmission standard, the first
sound carrier frequency is 5.5 MHz. The second sound carrier frequency is approxi-
mately 242 kHz above the first sound carrier, 5.742 MHz. The audio signals are FM
modulated on the sound carriers.
To distinguish between Stereo- and Dual-sound transmission, an additional pilot signal
of 54.68 kHz is present on the second sound carrier. This pilot signal is AM modulated
with identification frequencies, 117.5 Hz for Stereo or 274.1 Hz for Dual Sound. The
pilot carrier and the identification frequencies are coupled with the line frequency fH.
The pre-emphasis for both sound carriers is 50 µs. The minimum LF bandwidth is 40 Hz
to 15 kHz.
For frequency spectrum of Analog Stereo Sound B/G, see Appendix D.
Eastern European Countries as Poland, Lituania, and Czech Republic are prepared to
introduce or use the analog Stereo/Dual sound for TV systems PAL/SECAM D/K
(FM A2). The first sound carrier frequency is 6.5 MHz. The second sound carrier
frequency is 6.258 MHz. The audio signals are FM modulated on the sound carriers. The
pilot carrier and identification frequencies are identical to the PAL B/G system.
 Loading...
Loading...