MB95630H Series
MN702-00009-2v0-E FUJITSU SEMICONDUCTOR LIMITED 611
APPENDIX A Instruction Overview
■ Meanings of Signs in Instruction Codes
Table A-1 shows the meanings of signs used in explaining instruction codes in APPENDIX A.
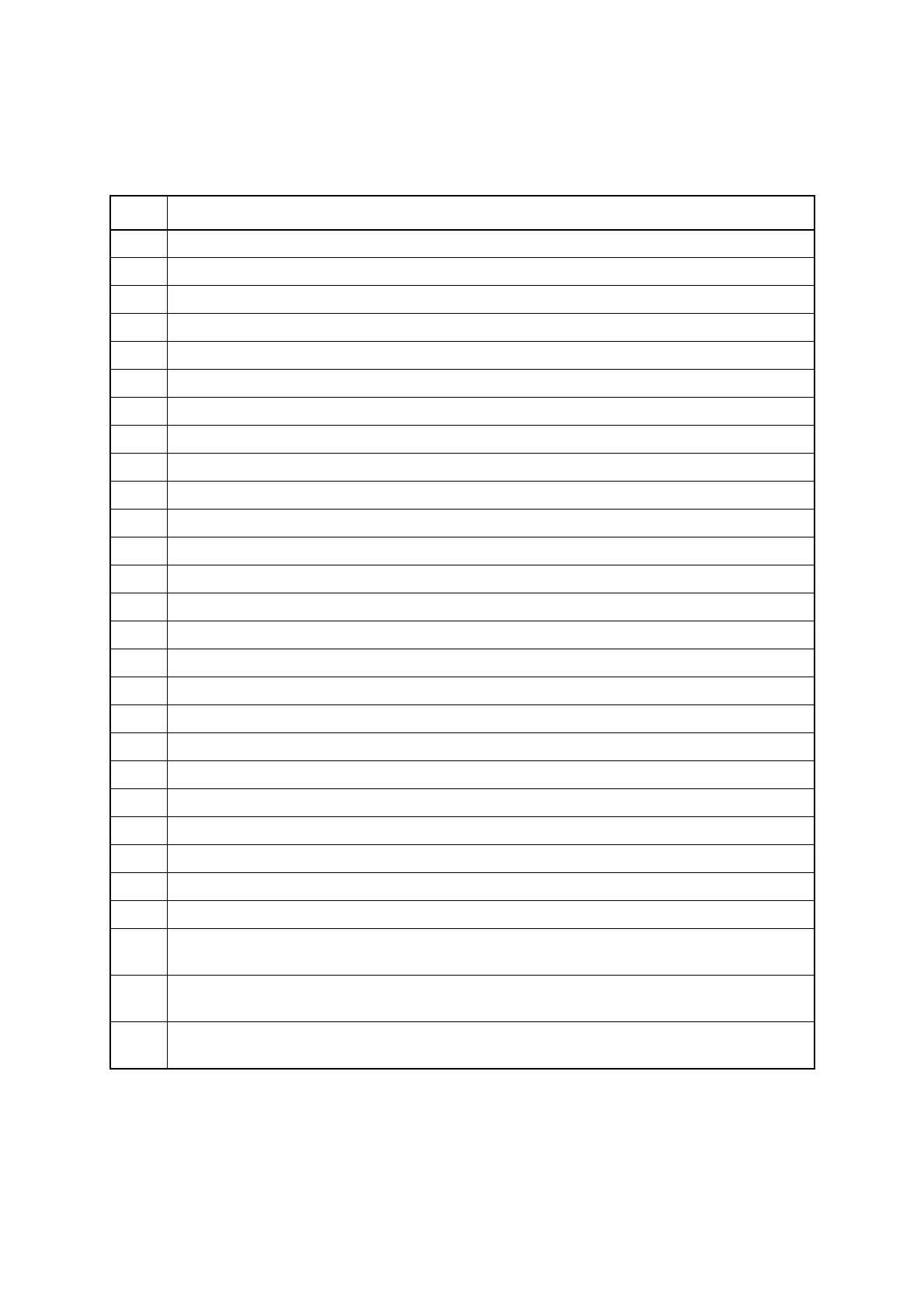
Table A-1 Meanings of Signs in Instruction Codes
Sign Meanings
dir Direct address (8-bit length)
off Offset (8-bit length)
ext Extended address (16-bit length)
#vct Vector table number (3-bit length)
#d8 Immediate data (8-bit length)
#d16 Immediate data (16-bit length)
dir:b Bit direct address (8-bit length: 3-bit length)
rel Branch relative address (8-bit length)
@ Register indirect (Example: @A, @IX, @EP)
A Accumulator (Whether 8- bit length or 16- bit length is decided by the instruction used.)
AH Upper 8-bit of accumulator (8-bit length)
AL Lower 8-bit of accumulator (8-bit length)
T Temporary accumulator (Whether 8- bit length or 16- bit length is decided by the instruction used.)
TH Upper 8-bit of temporary accumulator (8-bit length)
TL Lower 8-bit of temporary accumulator (8-bit length)
IX Index register (16-bit length)
EP Extra pointer (16-bit length)
PC Program counter (16-bit length)
SP Stack pointer (16-bit length)
PS Program status (16-bit length)
dr Either of accumulator or index register (16-bit length)
CCR Condition code register (8-bit length)
RP Register bank pointer (5-bit length)
DP Direct bank pointer (3-bit length)
Ri General-purpose register (8-bit length, i = 0 to 7)
x
This shows that x is immediate data.
(Whether 8- bit length or 16- bit length is decided by the instruction used.)
(x)
This shows that contents of x are objects of the access.
(Whether 8- bit length or 16- bit length is decided by the instruction used.)
((x))
This shows that the address that contents of x show is an object of the access.
(Whether 8- bit length or 16- bit length is decided by the instruction used.)
 Loading...
Loading...