248
As shown in Figure 60, Router D establishes indirect EBGP peer relationships with Router A, Router
B, and Router C, and learns addresses 1.1.1.1/32, 2.2.2.2/32, and 3.3.3.3/32 through OSPF. The
following output shows the routing information on Router D.
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
1.1.1.1/32 O_INTRA 10 10 11.1.1.2 GE1/0/1
2.2.2.2/32 O_INTRA 10 20 12.1.1.2 GE1/0/2
3.3.3.3/32 O_INTRA 10 30 13.1.1.2 GE1/0/3
Router D learns network 10.0.0.0 from both Router A and Router B. Because the route learned from
Router B has a smaller IGP metric, the route is optimal. The following output shows the BGP routing
table on Router D.
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*>e 10.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 50 0 300 400e
* e 3.3.3.3 50 0 200 400e
When Router D learns network 10.0.0.0 from Router C, it compares the route with the optimal route
in its routing table. Because Router C and Router B reside in different ASs, BGP does not compare
the MEDs of the two routes. The route from Router C has a smaller IGP metric than the route from
Router B, so the route from Router C becomes optimal. The following output shows the BGP routing
table on Router D.
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*>e 10.0.0.0 1.1.1.1 60 0 200 400e
* e 10.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 50 0 300 400e
* e 3.3.3.3 50 0 200 400e
However, Router C and Router A reside in the same AS, and Router C has a greater MED, so
network 10.0.0.0 learned from Router C should not be optimal.
To avoid this problem, you can configure the bestroute compare-med command to enable MED
comparison for routes from the same AS on Router D. After that, Router D puts the routes received
from each AS into a group, selects the route with the lowest MED from each group, and compares
routes from different groups. Network 10.0.0.0 learned from Router B is the optimal route. The
following output shows the BGP routing table on Router D.
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*>e 10.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 50 0 300 400e
* e 3.3.3.3 50 0 200 400e
* e 1.1.1.1 60 0 200 400e
To enable MED comparison for routes on a per-AS basis:
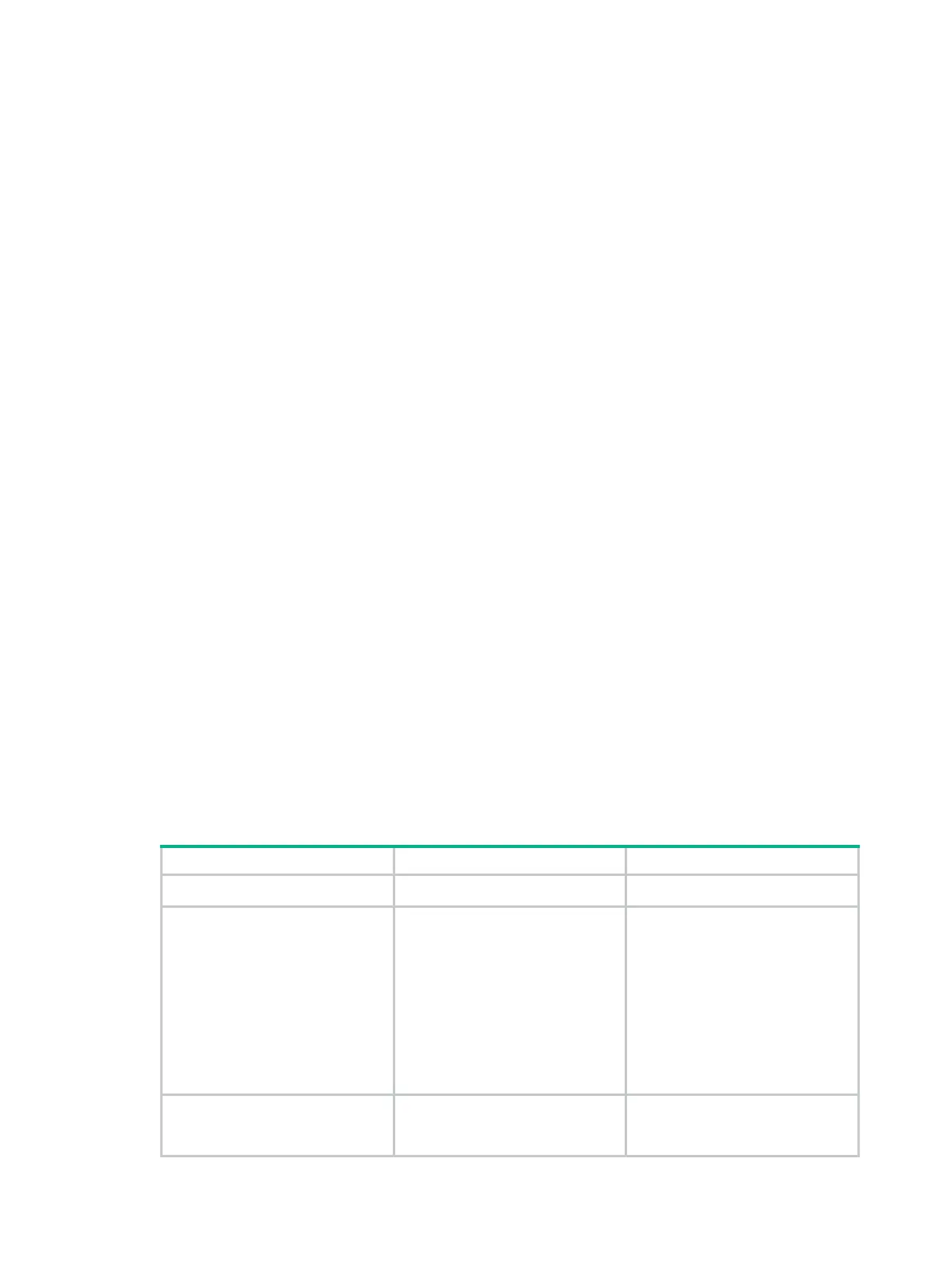
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter BGP instance view or
BGP-VPN instance view.
• Enter BGP instance view:
bgp as-number [ instance
instance-name ]
• Enter BGP-VPN instance
view:
a. bgp as-number
[ instance
instance-name ]
b. ip vpn-instance
N/A
3. Enable MED comparison for
routes on a per-AS basis.
bestroute compare-med
By default, MED comparison for
routes on a per-AS basis is
disabled.

 Loading...
Loading...



















