• With a reading count (0010) equal to the scan list length (10), a step operation
consecutively closes ten channels and sends an output trigger after each channel. A scan
operation also consecutively closes ten channels but sends an output trigger only at the
end of the scan.
• With a reading count (0020) greater than the scan list length (10), stepping yields 20
channel closures and 20 output triggers. Scanning also goes through the scan list twice
but sends an output trigger only at the end of each scan.
• With a reading count (0002) less than the scan list length (10), stepping yields two
channel closures and output triggers. Scanning goes through the entire scan list and
sends an output trigger but only two readings are stored.
NOTE If the reading count divided by the scan list length is not an integer, it is rounded up.
For example, if the reading count is 15 and the scan list length is 10, there will be two
output triggers for scanning.
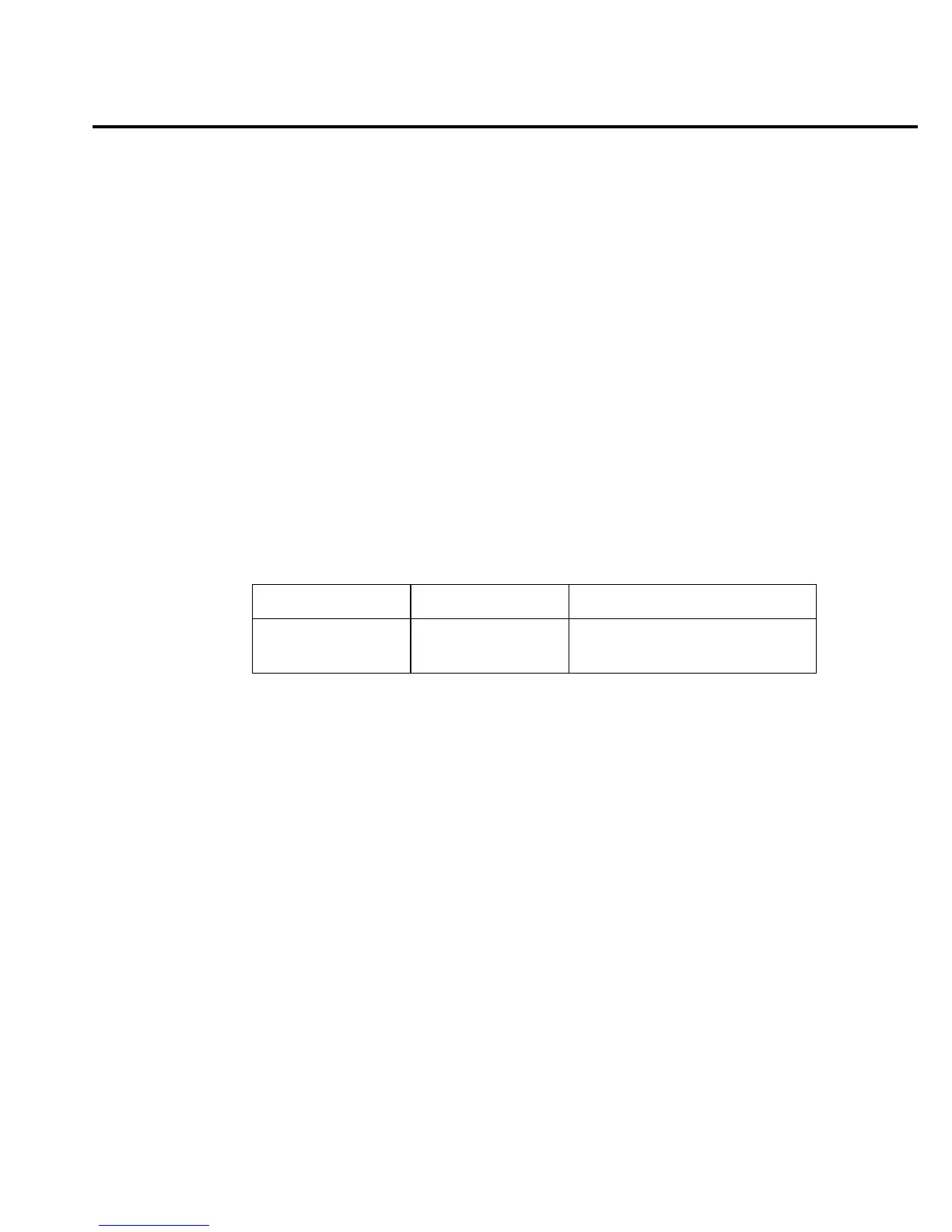
The differences between stepping and scanning counters for bus commands are summarized
in Table 3-3.
Table 3-3
Bus commands parameters for stepping and scanning counters
Operation :SAMPle:COUNt :TRIGger:COUNt
STEP 1 reading count
SCAN scan list length (reading count) / (scan list length)
Measurement Options 3-25

 Loading...
Loading...