Section 2 CPU
Rev. 7.00 Mar 10, 2005 page 27 of 652
REJ09B0042-0700
2.2 Register Descriptions
2.2.1 General Registers
All the general registers can be used as both data registers and address registers.
When used as data registers, they can be accessed as 16-bit registers (R0 to R7), or the high bytes
(R0H to R7H) and low bytes (R0L to R7L) can be accessed separately as 8-bit registers.
When used as address registers, the general registers are accessed as 16-bit registers (R0 to R7).
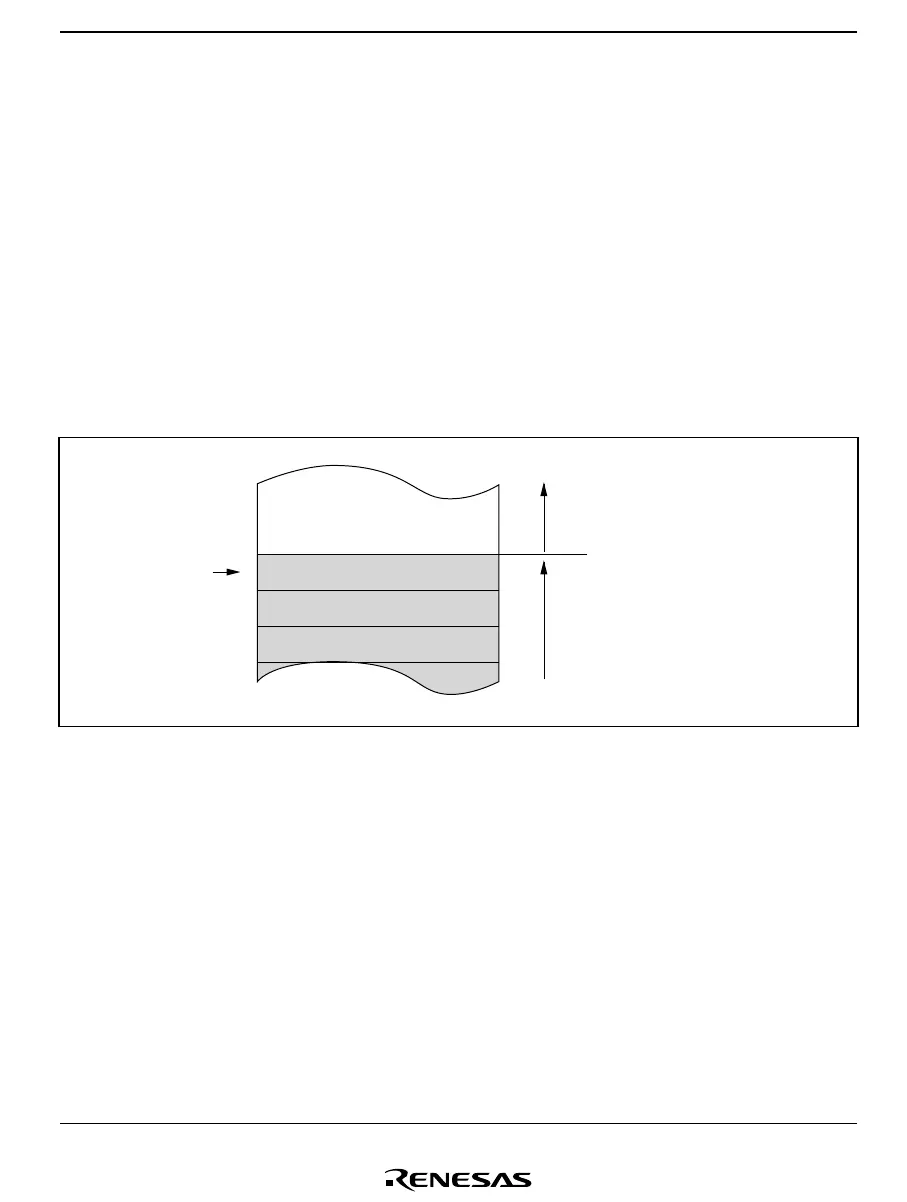
R7 also functions as the stack pointer (SP), used implicitly by hardware in exception processing
and subroutine calls. When it functions as the stack pointer, as indicated in figure 2.2, SP (R7)
points to the top of the stack.
Lower address side [H'0000]
Upper address side [H'FFFF]
Unused area
Stack area
SP (R7)
Figure 2.2 Stack Pointer
2.2.2 Control Registers
The CPU control registers include a 16-bit program counter (PC) and an 8-bit condition code
register (CCR).
Program Counter (PC)
This 16-bit register indicates the address of the next instruction the CPU will execute. All
instructions are fetched 16 bits (1 word) at a time, so the least significant bit of the PC is ignored
(always regarded as 0).

 Loading...
Loading...











