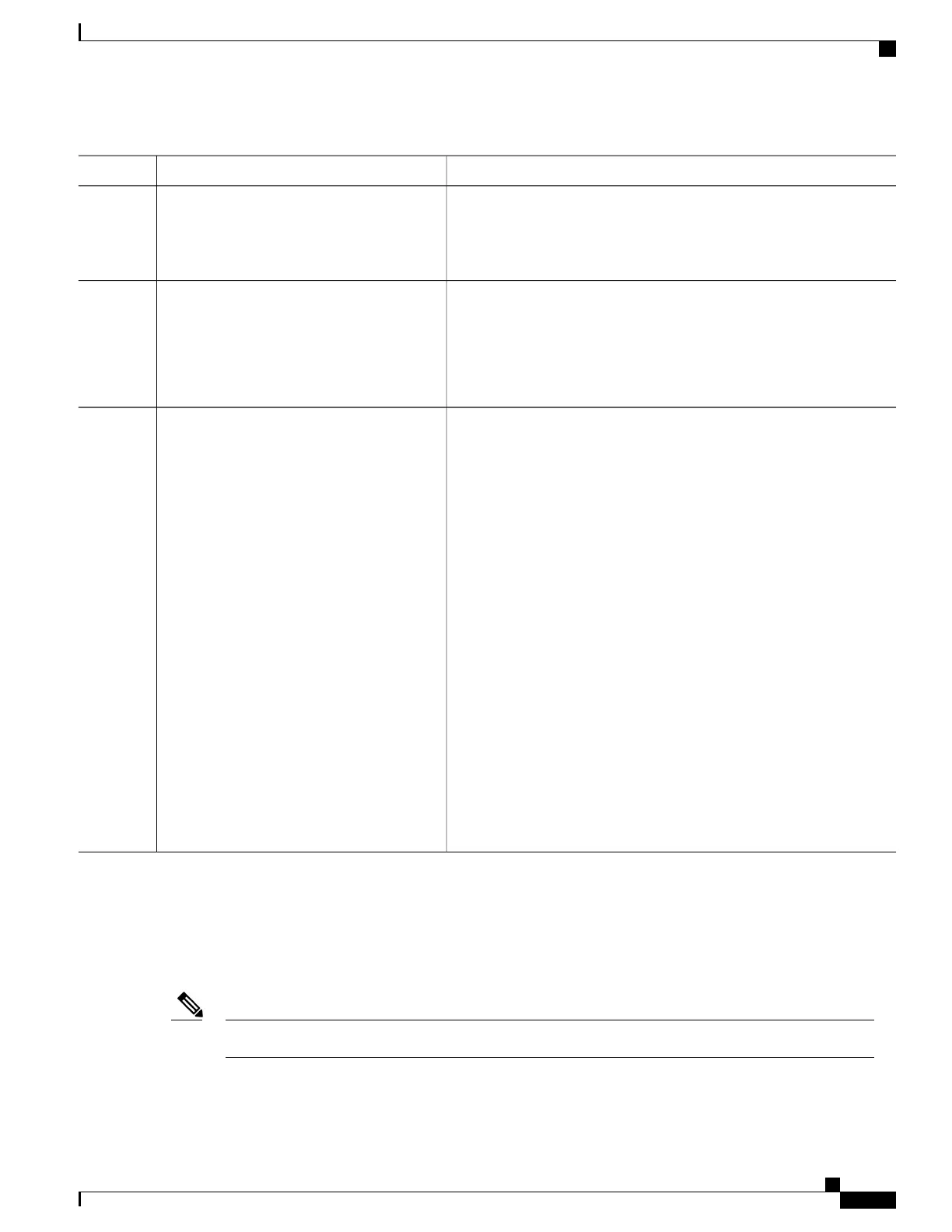
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters NTP configuration mode.ntp
Example:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config)# ntp
Step 2
Creates an access group and applies a basic IPv4 or IPv6 access list to
it.
access-group{peer | query-only | serve |
serve-only} access-list-name
Example:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-ntp)#
access-group peer access1
Step 3
Saves configuration changes.Use one of the following commands:
Step 4
•
end
•
When you issue the end command, the system prompts you to
commit changes:
Uncommitted changes found, commit them before
•
commit
Example:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-ntp)# end
exiting(yes/no/cancel)?
[cancel]:
◦
Entering yes saves configuration changes to the running
configuration file, exits the configuration session, and returns
the router to EXEC mode.
or
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-ntp)#
commit
◦
Entering no exits the configuration session and returns the
router to EXEC mode without committing the configuration
changes.
◦
Entering cancel leaves the router in the current configuration
session without exiting or committing the configuration
changes.
•
Use the commit command to save the configuration changes to
the running configuration file and remain within the configuration
session.
Configuring NTP Authentication
This task explains how to configure NTP authentication.
No specific command enables NTP; the first NTP configuration command that you issue enables NTP.Note
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router System Management Configuration Guide, Release 5.1.x
215
Implementing NTP
Configuring NTP Authentication
 Loading...
Loading...











