Falcon M-Class | User Guide
306
4.22.2 Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management
Ethernet Fault Management is an end-to-end per-service Ethernet layer OAM protocol that
includes proactive connectivity monitoring, fault verification, and fault isolation.
Monitoring and troubleshooting carrier networks offering Ethernet Layer 2 services is challenging.
Customers contract with service providers for end-to-end Ethernet service, and service providers
may subcontract with operators to provide equipment and networks. Compared to enterprise
networks, where Ethernet traditionally has been implemented, these constituent networks belong
to distinct organizations or departments, are substantially larger and more complex, and have a
wider user base.
Ethernet Fault Management provides a competitive advantage to service providers, for whom the
operational management of service uptime and timeliness of isolating and responding to failures is
crucial to daily operations.
The following sections explain and illustrate the basic terms of Fault Management functions.
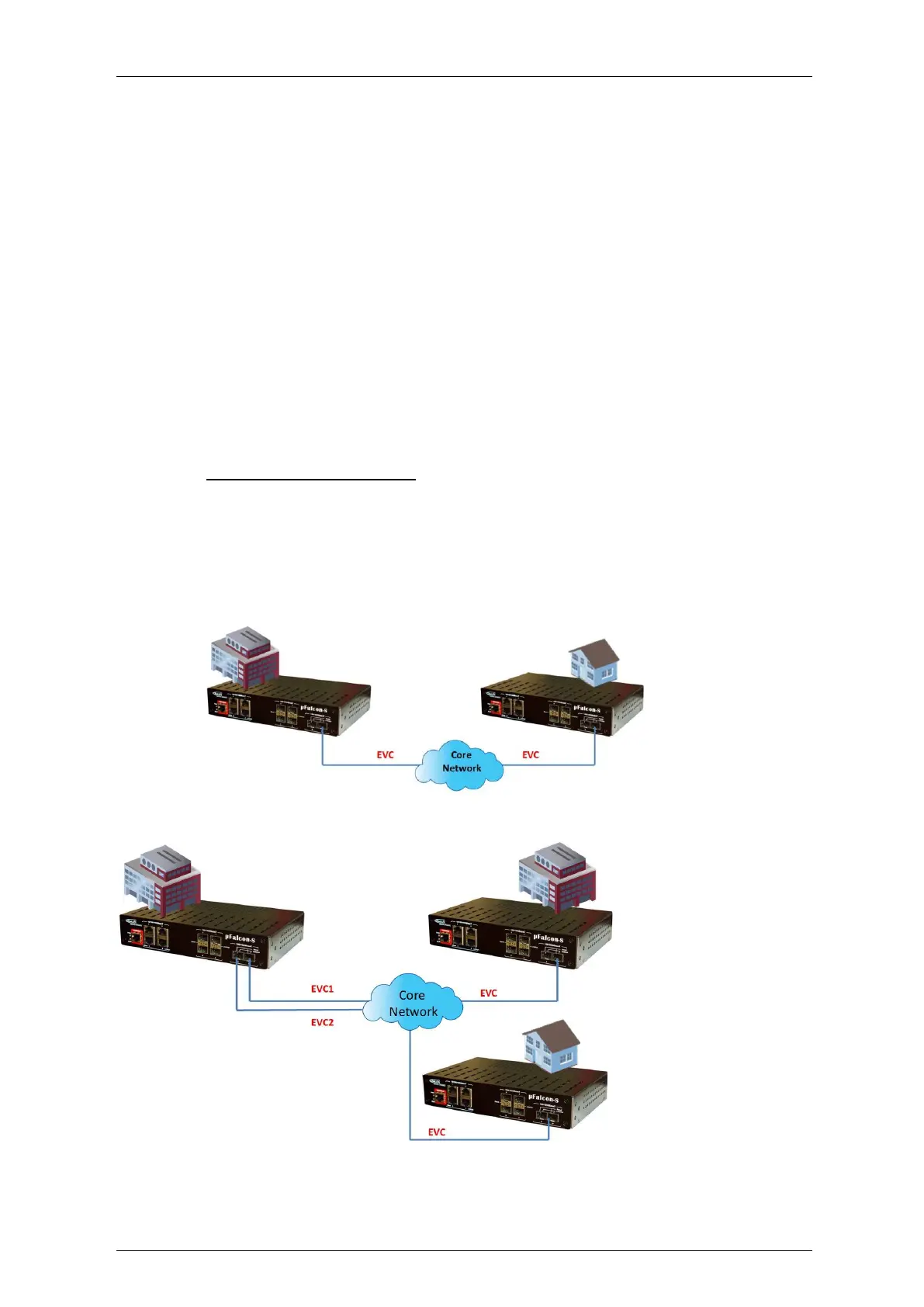
Customer Service Instance
A customer service instance is an Ethernet Virtual Connection (EVC), which is identified by an
S-VLAN within an Ethernet provider network, and is recognized by a globally unique service ID
(which is the S-VLAN tag). A customer service can be either Point-to-Point (PTP) or Multipoint-to-
Multipoint (MPTMP). See the following figures
Figure 4-169: Customer PTP Service Instance
Figure 4-170: Customer MP2MP Service Instance
 Loading...
Loading...