Manitowoc Published 11-06-15, Control # 040-13 5-31
2250 SERVICE/MAINTENANCE MANUAL HOISTS
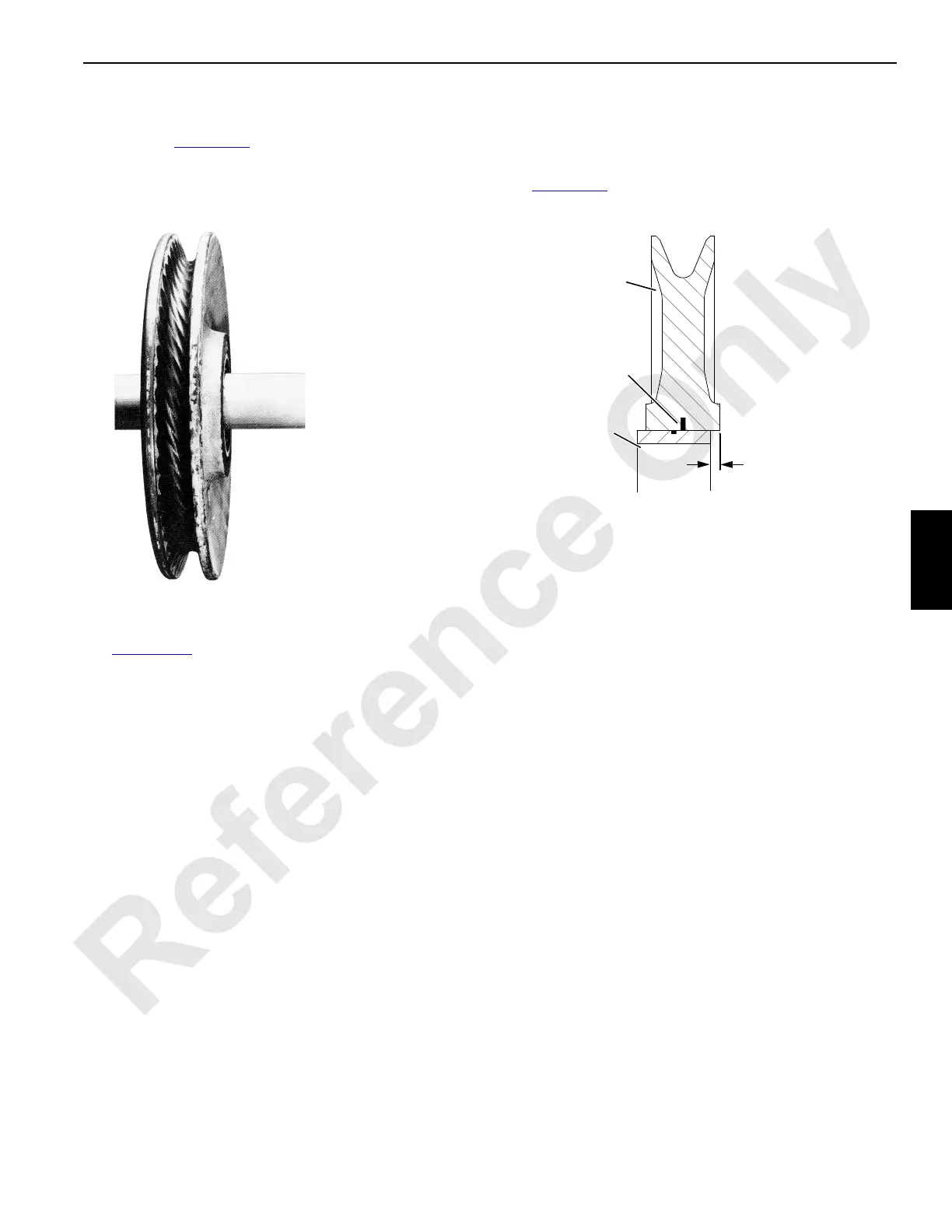
6. Re-machine or replace steel sheaves, drums, or rollers
that have been corrugated by the wire rope’s print as
shown in Figure 5-27
.
NOTE: Depending on the type of wire rope used, It is
normal for nylon sheaves to show the wire rope
print. Do not re-machine nylon sheaves.
7. Inspect nylon sheaves for excessive measured for
excessive tread diameter wear at locations E in
Figure 5-29
. Measure at three positions to check for
uneven wear.
Wear must not exceed limits given in table. Replace
worn or damaged sheave.
NOTE: Nylon sheaves cannot be accurately inspected
using conventional methods such as sheave
gauges.
Due to the characteristics of nylon sheaves, the
nylon material will actually move to better support
the wire rope as the sheave wears normally.
Nylon sheave properties will be degraded in
temperatures above 140°F. (60ºC).
8. Inspect nylon sheaves to verify they have not separated
and “walked off” steel inserts or bearings as shown in
Figure 5-28
. Maximum sideways displacement is 1/8 in.
(3 mm). Replace worn or damaged sheaves.
9. Make sure sheaves, drums, and rollers are properly
lubricated according to lubrication instructions in
Section 9.
Many current production sheaves are not equipped with
grease fittings, but are packed with grease at assembly.
Repack the bearings of these sheaves with CraneLUBE
EP #2 grease when the sheaves are overhauled.
Due to application and design variations, it is not
possible to give specific grease repacking intervals or
life expectancy of components.
NOTE: For some sheaves, the seals are an integral part of
the bearing. Therefore, if a seal is damaged during
repacking, the complete bearing may have to be
replaced.
FIGURE 5-27
S150
“Corrugated” steel sheave,
roller, or drum will cause wire
rope to wear rapidly.
Steel Insert
or Bearing
Nylon
Sheave
Improper
Snap Ring
Engagement
FIGURE 5-28
1/8 in (3 mm)
Maximum Sideways
Displacement
 Loading...
Loading...











