Typical Pipeline Systems and
Considerations
23
74-0085-05
TYPICAL PIPELINE SYSTEMS AND CONSIDERATIONS
Video and Audio Preview Implications During Capture
The most CPU intensive operation during a Pipeline capture session is projecting video and audio preview
streams. In most cases, previewing multiple streams when capturing standard definition media will not
affect the overall performance of your Pipeline capture system. However, two or more high definition
preview streams may cause excessive CPU load and prevent critical real-time media processes from
being serviced in a timely manner, leading to data loss and integrity of the resulting media file. Telestream
recommends that you view only one HD preview stream at a time on a multi-stream HD capture system.
Best Practices for Networking Pipelines
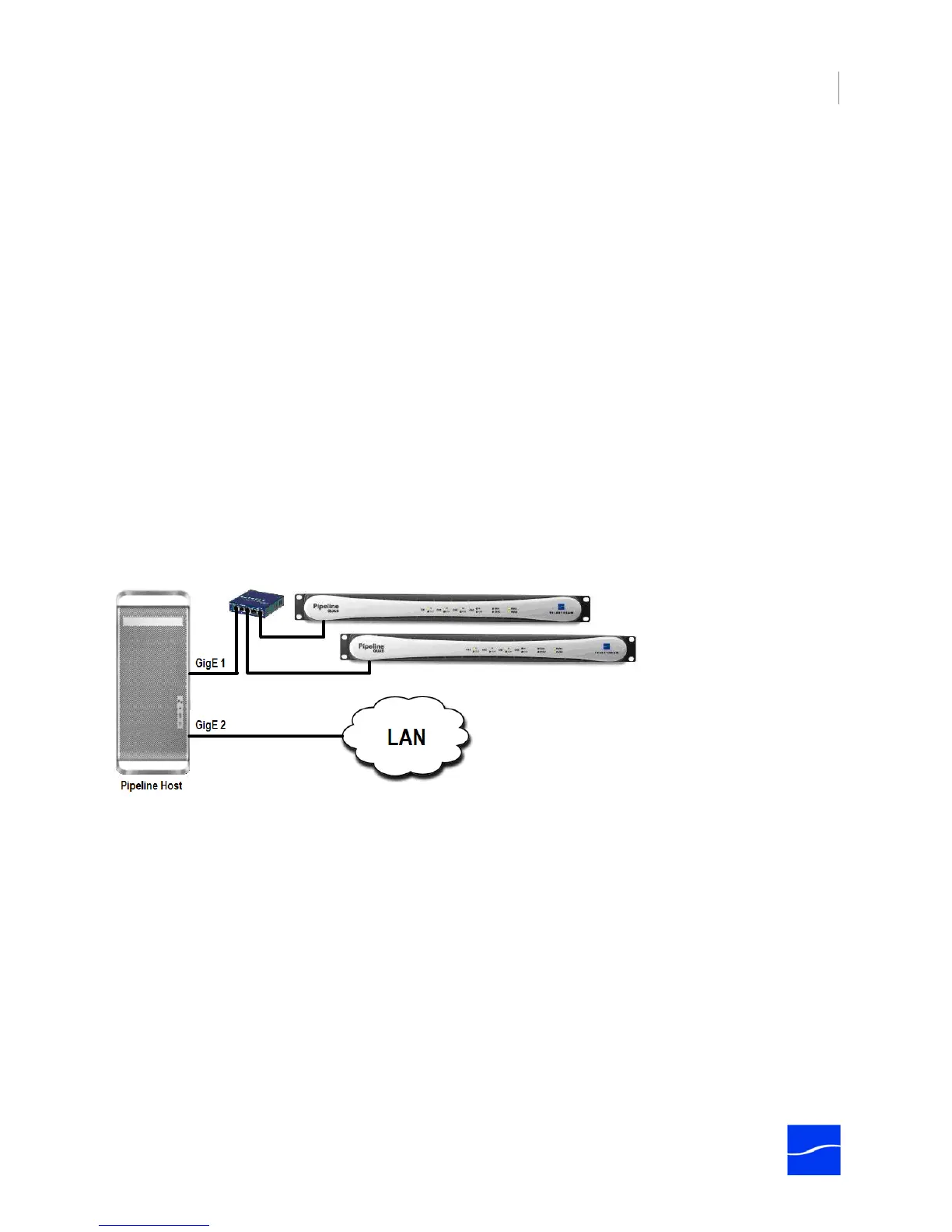
For best results, Pipeline devices should be connected directly to the Pipeline’s host system or through a
single Ethernet switch, as shown in the graphic following, depicting two Pipeline Quads on a dedicated
GigE LAN, for an 8-channel SD workflow, connected via a single switch. Multiple hops via routers and
switches increases the risk that video frames will not be processed in a timely manner, resulting in lost
frames. Special care must be taken to insure that real-time processes are executed in a timely manner.
Best practices suggest that you separate Pipeline network traffic from other traffic by using a second,
dedicated network adapter. Design your system with one (or more) Ethernet ports dedicated to the
incoming Pipeline streams and with separate Ethernet port(s) for general data and media storage traffic.
Figure 3–1. Best practices – isolated GigE LAN, dedicated Ethernet port, and a single switch.
Other network processes, such as file copying, can consume significant bandwidth and excessive network
stack cycles, causing Pipeline streams to be interrupted. When implementing a Pipeline system on an
existing general-purpose network, be aware of processes using the network that may affect Pipeline traffic.
As a rule of thumb, you should not exceed 50% usage of any single Ethernet port. For example, when
capturing Pro Res 422 HQ at 220Mbps, use one GigE Ethernet port on your host computer for every two
media streams, as depicting in the following graphic, where two Pipeline HD devices are connected to the
 Loading...
Loading...